Q#1 Although people would surely avoid getting into the elevator with you, suppose that you weigh yourself while on an elevator that is moving. Would you weigh more than, less khan, or the same as when the scale is on a stationary floor? In Fig.a, a passenger of mass m 72.2 kg stands on a platform scale in an elevator cab. We are concerned with the scale readings when the cab is stationary and when it is moving up or down. (a) Find a general solution for the scale reading, whatever the vertical motion of the cab. Passenger These forces compete. Their net force causes a vertical (b) acceleration. (a) tationary or movine
Q#1 Although people would surely avoid getting into the elevator with you, suppose that you weigh yourself while on an elevator that is moving. Would you weigh more than, less khan, or the same as when the scale is on a stationary floor? In Fig.a, a passenger of mass m 72.2 kg stands on a platform scale in an elevator cab. We are concerned with the scale readings when the cab is stationary and when it is moving up or down. (a) Find a general solution for the scale reading, whatever the vertical motion of the cab. Passenger These forces compete. Their net force causes a vertical (b) acceleration. (a) tationary or movine
University Physics Volume 1
18th Edition
ISBN:9781938168277
Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Chapter6: Applications Of Newton's Laws
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1CQ: Solving Problems with Newton’s Laws To sirmulate the apparent weightlessness of space orbit,...
Related questions
Question
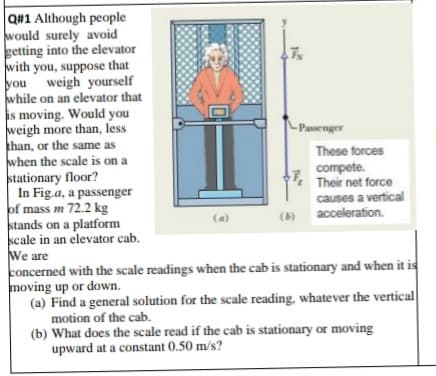
Transcribed Image Text:Q#1 Although people
would surely avoid
getting into the elevator
with you, suppose that
you weigh yourself
while on an elevator that
is moving. Would you
weigh more than, less
khan, or the same as
when the scale is on a
stationary floor?
In Fig.a, a passenger
of mass m 72.2 kg
stands on a platform
scale in an elevator cab.
We are
concerned with the scale readings when the cab is stationary and when it is
moving up or down.
(a) Find a general solution for the scale reading, whatever the vertical
motion of the cab.
(b) What does the scale read if the cab is stationary or moving
upward at a constant 0.50 m/s?
- Passenger
These forces
compete.
Their net force
causes a vertical
acceleration.
(a)
(b)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

University Physics Volume 1
Physics
ISBN:
9781938168277
Author:
William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:
OpenStax - Rice University

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:
9781133104261
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

University Physics Volume 1
Physics
ISBN:
9781938168277
Author:
William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:
OpenStax - Rice University

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:
9781133104261
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning