Quant A company produces two products, X and Y, which use material and labor as inputs. Fixed amounts of labor and material are available for production each month. In addition, the demand for product Y each month is limited; product X has no constraint on the number of units that can be sold. Ouestions 33 and 34 are based on the following information. A graphical depiction of these production and demand constraints is presented on the next page. Material constraint Demand constraint 6. Labor constraint 7 8. Units of Product 33. The feasible solution region is bounded by the lines connecting points 3, 4, 6, and 7. b. 1, 5, 6, and 8. 2, 4, 5, 6, and 8. с. d. 3, 5, 6, and 7. a. (CIA, Adapted) 34. If a series of profit lines for X and Y are drawn on the graph, the mix of X and Y that will result in the maximum profit can be determined from the last point in the feasible solution region touched by a profit line. any point on the boundary of the feasible solution region touched by a profit line. the first point on the feasible solution region boundary that intersects a profit line. d. a, b. C. any point on the demand constraint that intersects a profit line. (CIA, Adapted) Units of Product
Quant A company produces two products, X and Y, which use material and labor as inputs. Fixed amounts of labor and material are available for production each month. In addition, the demand for product Y each month is limited; product X has no constraint on the number of units that can be sold. Ouestions 33 and 34 are based on the following information. A graphical depiction of these production and demand constraints is presented on the next page. Material constraint Demand constraint 6. Labor constraint 7 8. Units of Product 33. The feasible solution region is bounded by the lines connecting points 3, 4, 6, and 7. b. 1, 5, 6, and 8. 2, 4, 5, 6, and 8. с. d. 3, 5, 6, and 7. a. (CIA, Adapted) 34. If a series of profit lines for X and Y are drawn on the graph, the mix of X and Y that will result in the maximum profit can be determined from the last point in the feasible solution region touched by a profit line. any point on the boundary of the feasible solution region touched by a profit line. the first point on the feasible solution region boundary that intersects a profit line. d. a, b. C. any point on the demand constraint that intersects a profit line. (CIA, Adapted) Units of Product
Practical Management Science
6th Edition
ISBN:9781337406659
Author:WINSTON, Wayne L.
Publisher:WINSTON, Wayne L.
Chapter2: Introduction To Spreadsheet Modeling
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 20P: Julie James is opening a lemonade stand. She believes the fixed cost per week of running the stand...
Related questions
Question
100%
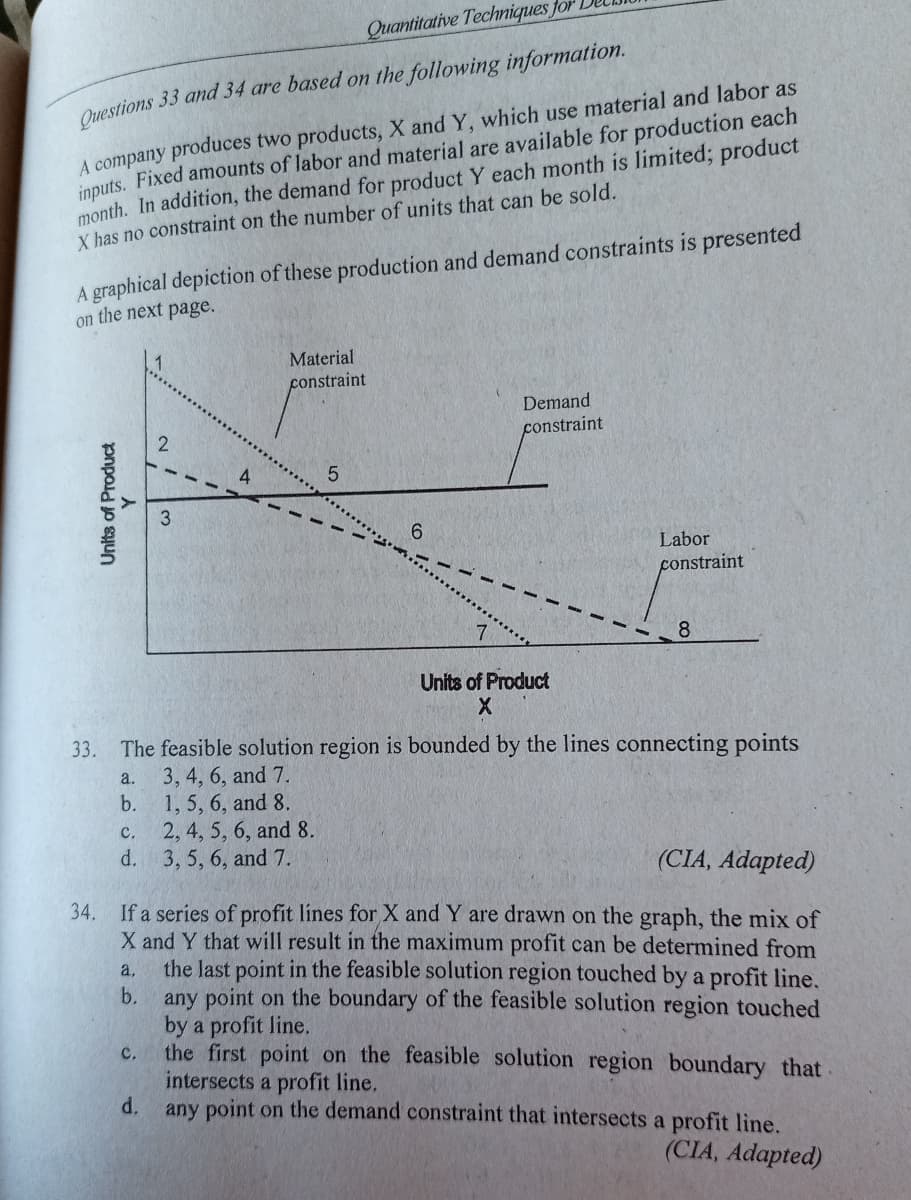
Transcribed Image Text:Quantitative Techniques for
A company produces two products, X and Y, which use material and labor as
inputs. Fixed amounts of labor and material are available for production each
month. In addition, the demand for product Y each month is limited; product
X has no constraint on the number of units that can be sold.
Questions 33 and 34 are based on the following information.
A graphical depiction of these production and demand constraints is presented
on the next page.
Material
constraint
Demand
constraint
2
6.
Labor
constraint
7.
8.
Units of Product
33. The feasible solution region is bounded by the lines connecting points
3, 4, 6, and 7.
b. 1, 5, 6, and 8.
2, 4, 5, 6, and 8.
d. 3, 5, 6, and 7.
a.
C.
(CIA, Adapted)
34. If a series of profit lines for X and Y are drawn on the graph, the mix of
X and Y that will result in the maximum profit can be determined from
the last point in the feasible solution region touched by a profit line.
b. any point on the boundary of the feasible solution region touched
by a profit line.
the first point on the feasible solution region boundary that
intersects a profit line.
d.
a,
c.
any point on the demand constraint that intersects a profit line.
(CIA, Adapted)
Units of Product
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, operations-management and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Practical Management Science
Operations Management
ISBN:
9781337406659
Author:
WINSTON, Wayne L.
Publisher:
Cengage,

Operations Management
Operations Management
ISBN:
9781259667473
Author:
William J Stevenson
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Operations and Supply Chain Management (Mcgraw-hi…
Operations Management
ISBN:
9781259666100
Author:
F. Robert Jacobs, Richard B Chase
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Practical Management Science
Operations Management
ISBN:
9781337406659
Author:
WINSTON, Wayne L.
Publisher:
Cengage,

Operations Management
Operations Management
ISBN:
9781259667473
Author:
William J Stevenson
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Operations and Supply Chain Management (Mcgraw-hi…
Operations Management
ISBN:
9781259666100
Author:
F. Robert Jacobs, Richard B Chase
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education


Purchasing and Supply Chain Management
Operations Management
ISBN:
9781285869681
Author:
Robert M. Monczka, Robert B. Handfield, Larry C. Giunipero, James L. Patterson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Production and Operations Analysis, Seventh Editi…
Operations Management
ISBN:
9781478623069
Author:
Steven Nahmias, Tava Lennon Olsen
Publisher:
Waveland Press, Inc.