QUESTION 1 Consider some unknown compound containing only copper and oxygen. In order to determine the empirical formula, a sample of the compound is decomposed into the elements copper and oxygen. The original sample had a mass of 0.6349 g prior to decomposition. After the reaction, 0.5073 g of pure copper solid was recovered. How many moles of copper were initially in the sample? As always, you should include a unit (mol). Use 63.55 g/mol as the molar mass of copper. .01000 mol Copper QUESTION 2 Since the original compound only contained copper and oxygen, once you extract and measure the amount of copper you can determine the amount of oxygen from the difference to the starting mass. In a 0.6349 g sample of the compound, if 0.5066 g of pure copper is extracted, how many moles of oxygen must have been in the compound? Use 16.00 g/mol as the molar mass of atomic oxygen. I .008019
QUESTION 1 Consider some unknown compound containing only copper and oxygen. In order to determine the empirical formula, a sample of the compound is decomposed into the elements copper and oxygen. The original sample had a mass of 0.6349 g prior to decomposition. After the reaction, 0.5073 g of pure copper solid was recovered. How many moles of copper were initially in the sample? As always, you should include a unit (mol). Use 63.55 g/mol as the molar mass of copper. .01000 mol Copper QUESTION 2 Since the original compound only contained copper and oxygen, once you extract and measure the amount of copper you can determine the amount of oxygen from the difference to the starting mass. In a 0.6349 g sample of the compound, if 0.5066 g of pure copper is extracted, how many moles of oxygen must have been in the compound? Use 16.00 g/mol as the molar mass of atomic oxygen. I .008019
Introductory Chemistry: A Foundation
9th Edition
ISBN:9781337399425
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Chapter9: Chemical Quantities
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 7CR
Related questions
Question
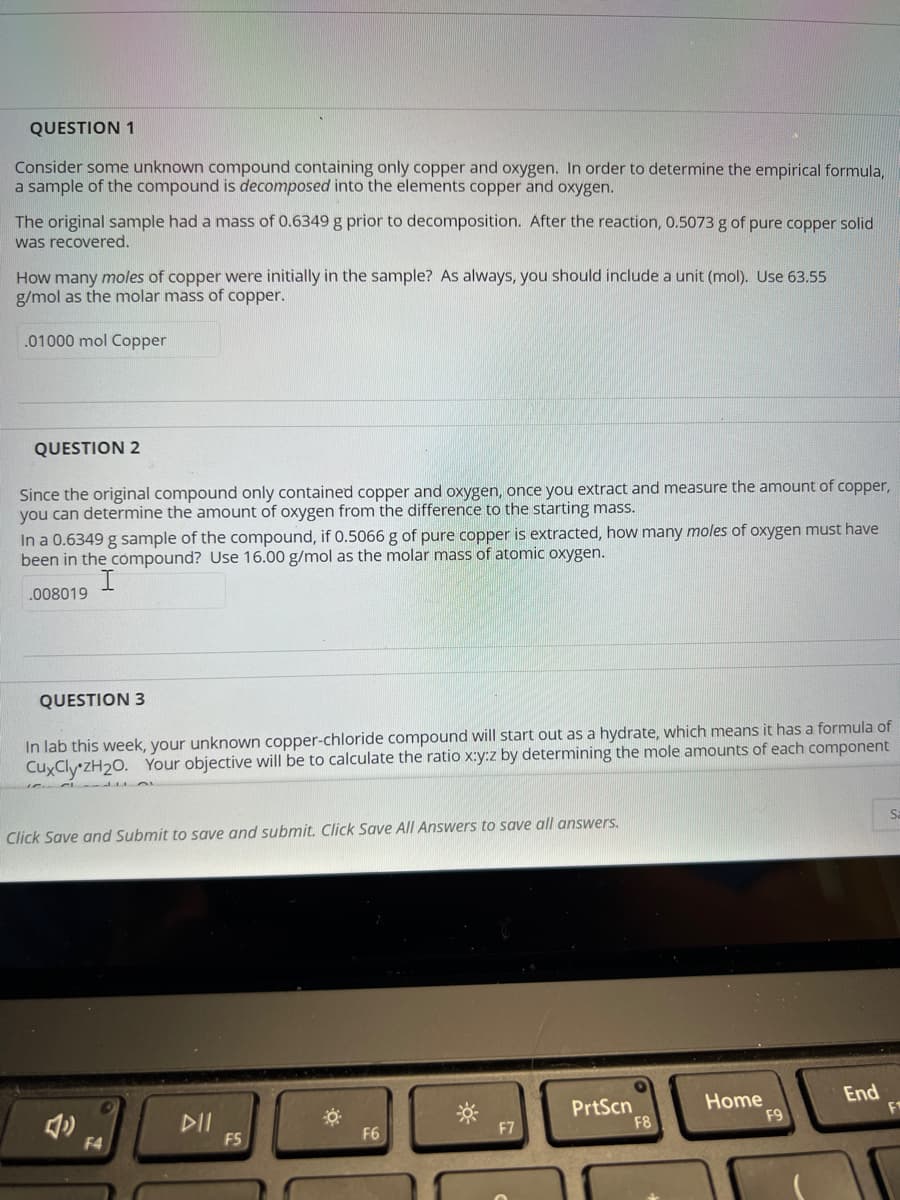
Transcribed Image Text:QUESTION 1
Consider some unknown compound containing only copper and oxygen. In order to determine the empirical formula,
a sample of the compound is decomposed into the elements copper and oxygen.
The original sample had a mass of 0.6349 g prior to decomposition. After the reaction, 0.5073 g of pure copper solid
was recovered.
How many moles of copper were initially in the sample? As always, you should include a unit (mol). Use 63.55
g/mol as the molar mass of copper.
.01000 mol Copper
QUESTION 2
Since the original compound only contained copper and oxygen, once you extract and measure the amount of copper,
you can determine the amount of oxygen from the difference to the starting mass.
In a 0.6349 g sample of the compound, if 0.5066 g of pure copper is extracted, how many moles of oxygen must have
been in the compound? Use 16.00 g/mol as the molar mass of atomic oxygen.
.008019
QUESTION 3
In lab this week, your unknown copper-chloride compound will start out as a hydrate, which means it has a formula of
CuxCly zH₂0. Your objective will be to calculate the ratio x:y:z by determining the mole amounts of each component
Click Save and Submit to save and submit. Click Save All Answers to save all answers.
F4
DII
F5
☀
F6
F7
PrtScn
F8
Home
F9
End
FT
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 5 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Introductory Chemistry: A Foundation
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337399425
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781133949640
Author:
John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: An Atoms First Approach
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079243
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Introductory Chemistry: A Foundation
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337399425
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781133949640
Author:
John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: An Atoms First Approach
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079243
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning
