Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
13th Edition
ISBN:9781133382119
Author:Swokowski
Publisher:Swokowski
Chapter10: Sequences, Series, And Probability
Section10.2: Arithmetic Sequences
Problem 38E
Related questions
Concept explainers
Riemann Sum
Riemann Sums is a special type of approximation of the area under a curve by dividing it into multiple simple shapes like rectangles or trapezoids and is used in integrals when finite sums are involved. Figuring out the area of a curve is complex hence this method makes it simple. Usually, we take the help of different integration methods for this purpose. This is one of the major parts of integral calculus.
Riemann Integral
Bernhard Riemann's integral was the first systematic description of the integral of a function on an interval in the branch of mathematics known as real analysis.
Question
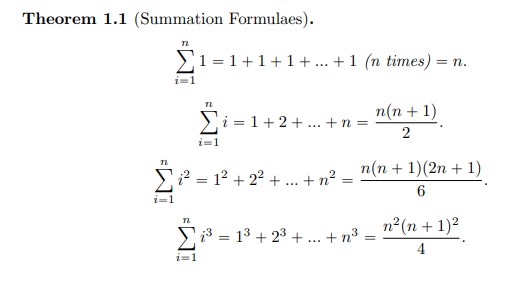
Transcribed Image Text:Theorem 1.1 (Summation Formulaes).
>1 = 1+1+1 + ... +1 (n times) = n.
i=1
n(n+ 1)
2
>i = 1+2+ ... +n =
i=1
n(n + 1)(2n + 1)
Si² = 12 + 22 + .. + n²
i=1
n2(n + 1)2
i3 = 13 + 23 + .. + n³ :
%3D
4
i=1
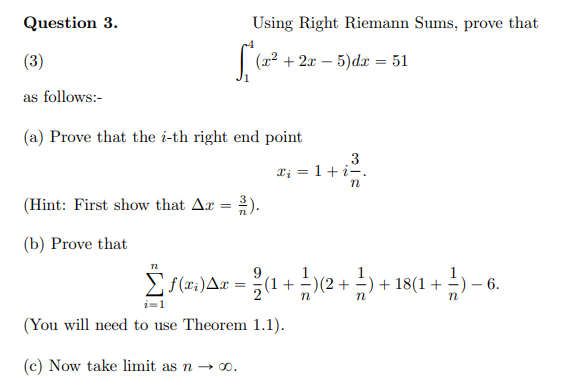
Transcribed Image Text:Question 3.
Using Right Riemann Sums, prove that
(3)
(22 + 2x – 5)dx = 51
as follows:-
(a) Prove that the i-th right end point
3
Ti = 1+i-.
(Hint: First show that Ax = 2).
(b) Prove that
9.
E f(2:)Ax = (1 +-)2 + -) + 18(1 +
6.
n
(You will need to use Theorem 1.1).
(c) Now take limit as n → o.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, calculus and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage