Question 3.2: Let G : z(1) =-1+÷e“, 0si< 2n and C, : z(1) =1+÷e“, 0si<2n and C: z(1) = 2e“, 0
Question 3.2: Let G : z(1) =-1+÷e“, 0si< 2n and C, : z(1) =1+÷e“, 0si<2n and C: z(1) = 2e“, 0
Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
13th Edition
ISBN:9781133382119
Author:Swokowski
Publisher:Swokowski
Chapter11: Topics From Analytic Geometry
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 47RE
Related questions
Question
Let:C1: z(t)=-1+1/2*e^it,0<=t<=2pi and C2: z(t)=1+1/2*e^it,0<=t<=2pi and C; z(t)=2e^it,0<=t<=2pi.
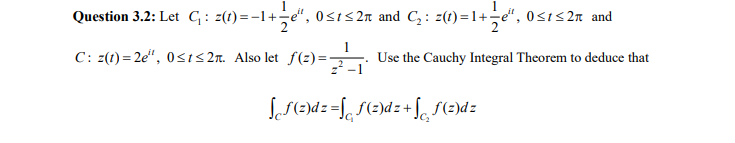
Transcribed Image Text:Question 3.2: Let G: z(1)=-1+-e“, 0<1<2n and C, : z(1)=1+-e", 0<1< 2n and
C: z(1) = 2e", 0<IS 2n. Also let f(2) =
Use the Cauchy Integral Theorem to deduce that
LS()d z =[, S(=)dz+ S S(=)dz
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, advanced-math and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage

Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)
Trigonometry
ISBN:
9781337278461
Author:
Ron Larson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage

Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)
Trigonometry
ISBN:
9781337278461
Author:
Ron Larson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning