Question 9 Below select all statements that are true about the difference between jumps and procedure calls: ▸ IO ▸ If the condition for a jump instruction is not satisfied, the CPU returns from the current function to the previous one. If the condition for a jump instruction is not satisfied, the CPU continues execution starting with the following instruction. If the condition for a jump instruction is satisfied, the CPU overwrites the program counter 10 register with the memory address contained in the instruction. If the condition for a jump instruction is satisfied, the CPU pushes the value of the program counter r0 register onto the stack. When a procedure call is executed, the CPU pushes the value of the stack pointer r1 onto the stack. When a procedure call is executed, the CPU pushes the address of the following instruction onto the stack. When a return instruction is executed, the CPU pops the value on top of the stack into the program counter 10 register. When a return instruction is executed, the CPU pops the stack frame into the stack pointer r1 register. 'S
Question 9 Below select all statements that are true about the difference between jumps and procedure calls: ▸ IO ▸ If the condition for a jump instruction is not satisfied, the CPU returns from the current function to the previous one. If the condition for a jump instruction is not satisfied, the CPU continues execution starting with the following instruction. If the condition for a jump instruction is satisfied, the CPU overwrites the program counter 10 register with the memory address contained in the instruction. If the condition for a jump instruction is satisfied, the CPU pushes the value of the program counter r0 register onto the stack. When a procedure call is executed, the CPU pushes the value of the stack pointer r1 onto the stack. When a procedure call is executed, the CPU pushes the address of the following instruction onto the stack. When a return instruction is executed, the CPU pops the value on top of the stack into the program counter 10 register. When a return instruction is executed, the CPU pops the stack frame into the stack pointer r1 register. 'S
Chapter4: Processor Technology And Architecture
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 15VE: A(n) ________________ instruction always alters the instruction execution sequence. A(n)...
Related questions
Topic Video
Question
Question à
Full explain this question and text typing work only thanks
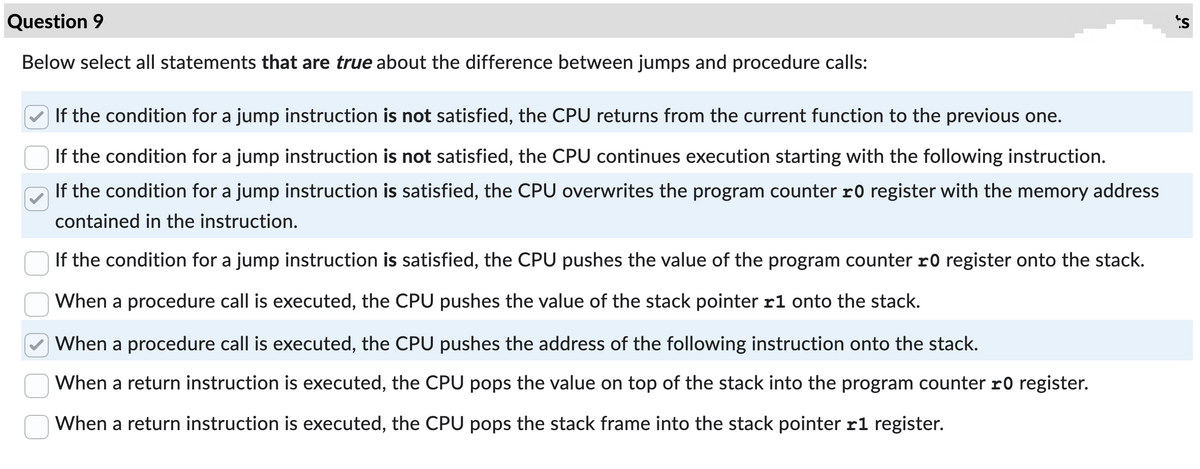
Transcribed Image Text:Question 9
Below select all statements that are true about the difference between jumps and procedure calls:
If the condition for a jump instruction is not satisfied, the CPU returns from the current function to the previous one.
If the condition for a jump instruction is not satisfied, the CPU continues execution starting with the following instruction.
If the condition for a jump instruction is satisfied, the CPU overwrites the program counter 10 register with the memory address
contained in the instruction.
If the condition for a jump instruction is satisfied, the CPU pushes the value of the program counter 10 register onto the stack.
When a procedure call is executed, the CPU pushes the value of the stack pointer r1 onto the stack.
When a procedure call is executed, the CPU pushes the address of the following instruction onto the stack.
When a return instruction is executed, the CPU pops the value on top of the stack into the program counter 10 register.
When a return instruction is executed, the CPU pops the stack frame into the stack pointer r1 register.
s
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, computer-science and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Systems Architecture
Computer Science
ISBN:
9781305080195
Author:
Stephen D. Burd
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Information Systems (MindTap Course…
Computer Science
ISBN:
9781285867168
Author:
Ralph Stair, George Reynolds
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Systems Architecture
Computer Science
ISBN:
9781305080195
Author:
Stephen D. Burd
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Information Systems (MindTap Course…
Computer Science
ISBN:
9781285867168
Author:
Ralph Stair, George Reynolds
Publisher:
Cengage Learning