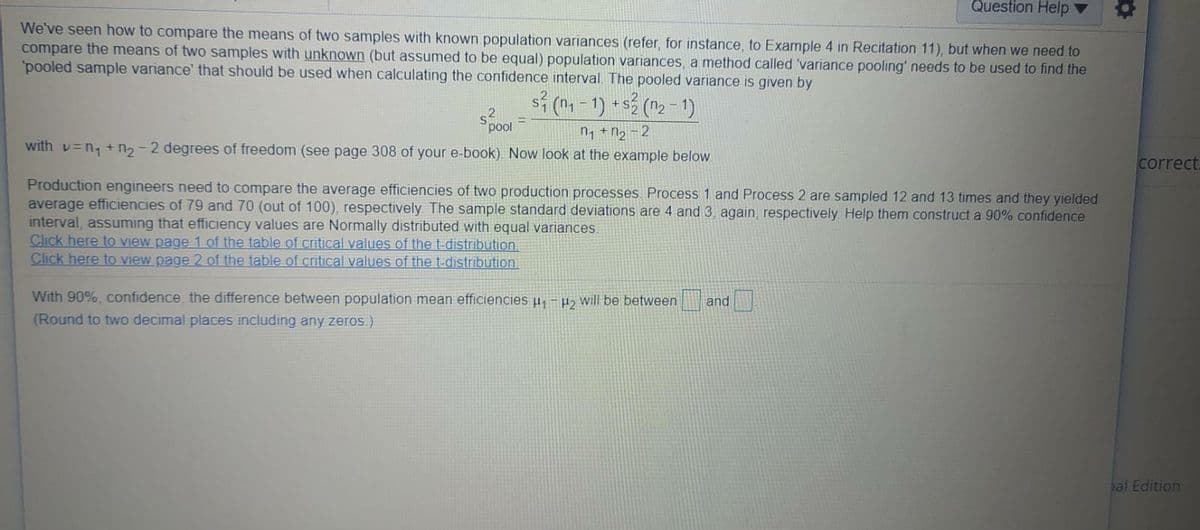
Question Help v We've seen how to compare the means of two samples with known population variances (refer, for instance, to Example 4 in Recitation 11), but when we need to compare the means of two samples with unknown (but assumed to be equal) population variances, a method called 'variance pooling' needs to be used to find the pooled sample variance' that should be used when calculating the confidence interval. The pooled variance is given by si (n - 1) + s3 (n2 pool n +n2-2 with v=n, + n2-2 degrees of freedom (see page 308 of your e-book). Now look at the example below Production engineers need to compare the average efficiencies of two production processes Process 1 and Process 2 are sampled 12 and 13 times and they yielded average efficiencies of 79 and 70 (out of 100), respectively The sample standard deviations are 4 and 3, again, respectively Help them construct a 90% confidence interval, assuming that efficiency values are Normally distributed with equal variances Click here to View page 1 of the table of critical values of the t-distribution, Click here to view page 2 of the table of critical values of the t.distribution. With 90%, confidence, the difference between population mean efficiencies µ, -p, will be betweena (Round to two decimal places including any zeros.) and
Question Help v We've seen how to compare the means of two samples with known population variances (refer, for instance, to Example 4 in Recitation 11), but when we need to compare the means of two samples with unknown (but assumed to be equal) population variances, a method called 'variance pooling' needs to be used to find the pooled sample variance' that should be used when calculating the confidence interval. The pooled variance is given by si (n - 1) + s3 (n2 pool n +n2-2 with v=n, + n2-2 degrees of freedom (see page 308 of your e-book). Now look at the example below Production engineers need to compare the average efficiencies of two production processes Process 1 and Process 2 are sampled 12 and 13 times and they yielded average efficiencies of 79 and 70 (out of 100), respectively The sample standard deviations are 4 and 3, again, respectively Help them construct a 90% confidence interval, assuming that efficiency values are Normally distributed with equal variances Click here to View page 1 of the table of critical values of the t-distribution, Click here to view page 2 of the table of critical values of the t.distribution. With 90%, confidence, the difference between population mean efficiencies µ, -p, will be betweena (Round to two decimal places including any zeros.) and
Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897, 0079039898, 2018
18th Edition
ISBN:9780079039897
Author:Carter
Publisher:Carter
Chapter10: Statistics
Section10.5: Comparing Sets Of Data
Problem 3BGP
Related questions
Question
100%
Transcribed Image Text:Question Help ▼
We've seen how to compare the means of two samples with known population variances (refer, for instance, to Example 4 in Recitation 11), but when we need to
compare the means of two samples with unknown (but assumed to be equal) population variances, a method called 'variance pooling' needs to be used to find the
'pooled sample variance' that should be used when calculating the confidence interval. The pooled variance is given by
s (n-1)
+s (n2 -1)
pool
n, +n, -2
with v=n, + n2 -2 degrees of freedom (see page 308 of your e-book). Now look at the example below
correct.
Production engineers need to compare the average efficiencies of two production processes. Process 1 and Process 2 are sampled 12 and 13 times and they yielded
average efficiencies of 79 and 70 (out of 100), respectively The sample standard deviations are 4 and 3 again, respectively Help them construct a 90% confidence
interval, assuming that efficiency values are Normally distributed with equal variances.
Click here to view page 1 of the table of critical values of the t-distribution.
Click here tO view page 2 of the table of critical values of the t-distribution.
With 90%, confidence, the difference between population mean efficiencies u,-P> will be between
(Round to two decimal places including any zeros.)
and
al Edition
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, probability and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897…
Algebra
ISBN:
9780079039897
Author:
Carter
Publisher:
McGraw Hill

College Algebra (MindTap Course List)
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305652231
Author:
R. David Gustafson, Jeff Hughes
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897…
Algebra
ISBN:
9780079039897
Author:
Carter
Publisher:
McGraw Hill

College Algebra (MindTap Course List)
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305652231
Author:
R. David Gustafson, Jeff Hughes
Publisher:
Cengage Learning