ρ (Ω.m) L (m) AV(V) R (N) I(A) 0.540 5.22 0.500 1.028 5.82 0.276 1.543 5.94 0.187 Table 17.1 Resistivities and Temperature Coefficients of Resistivity for Various Materials (at 20°C) Temperature Coefficient of Resistivity [('C)-'] Resistivity (N• m) Material Silver 1.59 x 10-8 1.7 x 10-8 3.8 x 10-3 3.9 x 10-3 Copper Gold 2.44 X 10-8 3.4 X 10-3 3.9 x 10-3 4.5 x 10-3 5.0 x 10-3 3.92 x 10 3.9 x 10 Aluminum 2.82 x 10-8 Tungsten 5.6 x 10-8 Iron 10.0 x 10-8 Platinum 11 x 10-8 22 x 10-8 150 x 10-8 3.5 x 10-5 -3 Lead -3 Nichrome" 0.4 x 10-3 -0.5 x 10-3 -48 x 10-3 - 75 x 10-3 Carbon Germanium 0.46 Silicon 640 Glass 1010-1014 Hard rubber =1013 1015 75 x 1016 Sulfur Quartz (fused) *A nickel-chromium alloy commonly used in heating elements.
Ohm's law
Ohm’s law is a prominent concept in physics and electronics. It gives the relation between the current and the voltage. It is used to analyze and construct electrical circuits. Ohm's law states that the voltage across a conductor is directly proportional to the current flowing through it.
Path of Least Resistance
In a series of alternate pathways, the direction of least resistance is the actual or metaphorical route that offers the least resistance to forwarding motion by a given individual or body.
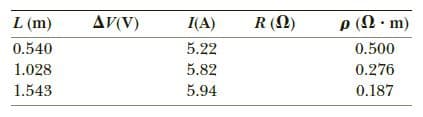
An experiment is
of Nichrome in the form of wires with different lengths
and cross - sectional areas. For one set of measurements, a
student uses 30.0 - gauge wire, which has a cross - sectional
area of 7.30 x 10-8 m2. The student measures the potential
difference across the wire and the current in the wire with a
voltmeter and an ammeter, respectively. For each of the measurements
given in the following table taken on wires of three
different lengths, calculate the resistance of the wires and the
corresponding value of the resistivity.
What is the average value of the resistivity, and how does this
value compare with the value given in Table 17.1?
![Table 17.1 Resistivities and Temperature Coefficients of Resistivity
for Various Materials (at 20°C)
Temperature Coefficient
of Resistivity
[('C)-']
Resistivity
(N• m)
Material
Silver
1.59 x 10-8
1.7 x 10-8
3.8 x 10-3
3.9 x 10-3
Copper
Gold
2.44 X 10-8
3.4 X 10-3
3.9 x 10-3
4.5 x 10-3
5.0 x 10-3
3.92 x 10
3.9 x 10
Aluminum
2.82 x 10-8
Tungsten
5.6 x 10-8
Iron
10.0 x 10-8
Platinum
11 x 10-8
22 x 10-8
150 x 10-8
3.5 x 10-5
-3
Lead
-3
Nichrome"
0.4 x 10-3
-0.5 x 10-3
-48 x 10-3
- 75 x 10-3
Carbon
Germanium
0.46
Silicon
640
Glass
1010-1014
Hard rubber
=1013
1015
75 x 1016
Sulfur
Quartz (fused)
*A nickel-chromium alloy commonly used in heating elements.](/v2/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fcontent.bartleby.com%2Fqna-images%2Fquestion%2F8710dbee-149c-4b1a-ad34-ec526b6df74a%2F3195a216-d438-4e56-a447-a8271c65be64%2Fy27yqx.jpeg&w=3840&q=75)
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 1 images


