Required information [The following information applies to the questions displayed below.] Execusmart Consultants has provided business consulting services for several years. The company has been using the percentage of credit sales method to estimate bad debts but switched at the end of the first quarter this year to the aging of accounts receivable method. The company entered into the following partial list of transactions. a. During January, the company provided services for $270,000 on credit. b. On January 31, the company estimated bad debts using 1 percent of credit sales. c. On February 4, the company collected $135,000 of accounts receivable. d. On February 15, the company wrote off a $500 account receivable. e. During February, the company provided services for $220,000 on credit. f. On February 28, the company estimated bad debts using 1 percent of credit sales. g. On March 1, the company loaned $14,000 to an employee, who signed a 9% note due in 3 months. h. On March 15, the company collected $500 on the account written off one month earlier. i. On March 31, the company accrued interest earned on the note. j. On March 31, the company adjusted for uncollectible accounts, based on the following aging analysis, which includes the preceding transactions (as well as others not listed). Prior to the adjustment, Allowance for Doubtful Accounts had an unadjusted credit balance of $7,400. Number of Days Unpaid 31-60 61–90 Total 0–30 Over 90 Customer $ 1,300 2,700 91,100 Arrow Ergonomics Asymmetry Architecture Others (not shown to save space) Weight Whittlers 2$ 600 500 200 $2,700 4,700 46,000 34,700 2,700 5,700 2,700 $97,800 Total Accounts Receivable $38,000 $46,500 $5,900 $7,400 Estimated Uncollectible (%) 3% 10% 20% 40% Required: 1. For items (a)-G), analyze the amount and direction (+ or -) of effects on specific financial statement accounts and the overall accounting equation. TIP: In item (), you must first calculate the desired ending balance before adjusting the Allowance for Doubtful Accounts. (Do not round intermediate calculations. Enter any decreases to Assets, Liabilities, or Stockholders Equity with a minus sign.) Stockholders' Equity Liabilities Assets a. b. C. d. e. f. g. h. i. j.
Required information [The following information applies to the questions displayed below.] Execusmart Consultants has provided business consulting services for several years. The company has been using the percentage of credit sales method to estimate bad debts but switched at the end of the first quarter this year to the aging of accounts receivable method. The company entered into the following partial list of transactions. a. During January, the company provided services for $270,000 on credit. b. On January 31, the company estimated bad debts using 1 percent of credit sales. c. On February 4, the company collected $135,000 of accounts receivable. d. On February 15, the company wrote off a $500 account receivable. e. During February, the company provided services for $220,000 on credit. f. On February 28, the company estimated bad debts using 1 percent of credit sales. g. On March 1, the company loaned $14,000 to an employee, who signed a 9% note due in 3 months. h. On March 15, the company collected $500 on the account written off one month earlier. i. On March 31, the company accrued interest earned on the note. j. On March 31, the company adjusted for uncollectible accounts, based on the following aging analysis, which includes the preceding transactions (as well as others not listed). Prior to the adjustment, Allowance for Doubtful Accounts had an unadjusted credit balance of $7,400. Number of Days Unpaid 31-60 61–90 Total 0–30 Over 90 Customer $ 1,300 2,700 91,100 Arrow Ergonomics Asymmetry Architecture Others (not shown to save space) Weight Whittlers 2$ 600 500 200 $2,700 4,700 46,000 34,700 2,700 5,700 2,700 $97,800 Total Accounts Receivable $38,000 $46,500 $5,900 $7,400 Estimated Uncollectible (%) 3% 10% 20% 40% Required: 1. For items (a)-G), analyze the amount and direction (+ or -) of effects on specific financial statement accounts and the overall accounting equation. TIP: In item (), you must first calculate the desired ending balance before adjusting the Allowance for Doubtful Accounts. (Do not round intermediate calculations. Enter any decreases to Assets, Liabilities, or Stockholders Equity with a minus sign.) Stockholders' Equity Liabilities Assets a. b. C. d. e. f. g. h. i. j.
Chapter6: Business Expenses
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 44P
Related questions
Question
![Required information
[The following information applies to the questions displayed below.]
Execusmart Consultants has provided business consulting services for several years. The company has been using the
percentage of credit sales method to estimate bad debts but switched at the end of the first quarter this year to the aging
of accounts receivable method. The company entered into the following partial list of transactions.
a. During January, the company provided services for $270,000 on credit.
b. On January 31, the company estimated bad debts using 1 percent of credit sales.
c. On February 4, the company collected $135,000 of accounts receivable.
d. On February 15, the company wrote off a $500 account receivable.
e. During February, the company provided services for $220,000 on credit.
f. On February 28, the company estimated bad debts using 1 percent of credit sales.
g. On March 1, the company loaned $14,000 to an employee, who signed a 9% note due in 3 months.
h. On March 15, the company collected $500 on the account written off one month earlier.
i. On March 31, the company accrued interest earned on the note.
j. On March 31, the company adjusted for uncollectible accounts, based on the following aging analysis, which includes
the preceding transactions (as well as others not listed). Prior to the adjustment, Allowance for Doubtful Accounts had
an unadjusted credit balance of $7,400.
Number of Days Unpaid
31-60
61–90
Total
0–30
Over 90
Customer
$ 1,300
2,700
91,100
Arrow Ergonomics
Asymmetry Architecture
Others (not shown to save space)
Weight Whittlers
2$
600
500
200
$2,700
4,700
46,000
34,700
2,700
5,700
2,700
$97,800
Total Accounts Receivable
$38,000
$46,500
$5,900
$7,400
Estimated Uncollectible (%)
3%
10%
20%
40%](/v2/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fcontent.bartleby.com%2Fqna-images%2Fquestion%2Fb946a811-cc83-4daf-974b-7bfdc95f8357%2Fad7e8ed7-ab5e-41e8-ae29-6f2f27233455%2Fdvddrjs.png&w=3840&q=75)
Transcribed Image Text:Required information
[The following information applies to the questions displayed below.]
Execusmart Consultants has provided business consulting services for several years. The company has been using the
percentage of credit sales method to estimate bad debts but switched at the end of the first quarter this year to the aging
of accounts receivable method. The company entered into the following partial list of transactions.
a. During January, the company provided services for $270,000 on credit.
b. On January 31, the company estimated bad debts using 1 percent of credit sales.
c. On February 4, the company collected $135,000 of accounts receivable.
d. On February 15, the company wrote off a $500 account receivable.
e. During February, the company provided services for $220,000 on credit.
f. On February 28, the company estimated bad debts using 1 percent of credit sales.
g. On March 1, the company loaned $14,000 to an employee, who signed a 9% note due in 3 months.
h. On March 15, the company collected $500 on the account written off one month earlier.
i. On March 31, the company accrued interest earned on the note.
j. On March 31, the company adjusted for uncollectible accounts, based on the following aging analysis, which includes
the preceding transactions (as well as others not listed). Prior to the adjustment, Allowance for Doubtful Accounts had
an unadjusted credit balance of $7,400.
Number of Days Unpaid
31-60
61–90
Total
0–30
Over 90
Customer
$ 1,300
2,700
91,100
Arrow Ergonomics
Asymmetry Architecture
Others (not shown to save space)
Weight Whittlers
2$
600
500
200
$2,700
4,700
46,000
34,700
2,700
5,700
2,700
$97,800
Total Accounts Receivable
$38,000
$46,500
$5,900
$7,400
Estimated Uncollectible (%)
3%
10%
20%
40%
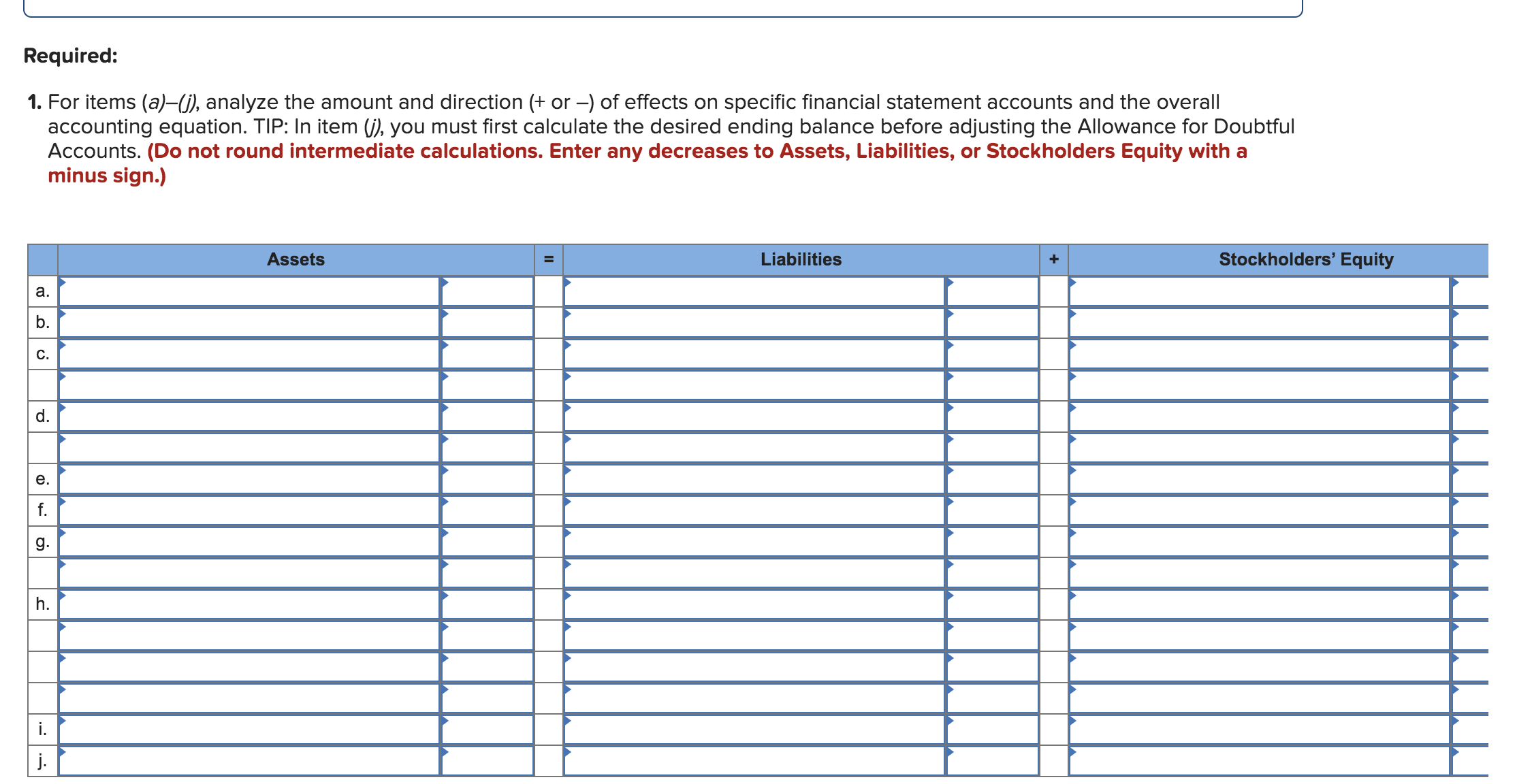
Transcribed Image Text:Required:
1. For items (a)-G), analyze the amount and direction (+ or -) of effects on specific financial statement accounts and the overall
accounting equation. TIP: In item (), you must first calculate the desired ending balance before adjusting the Allowance for Doubtful
Accounts. (Do not round intermediate calculations. Enter any decreases to Assets, Liabilities, or Stockholders Equity with a
minus sign.)
Stockholders' Equity
Liabilities
Assets
a.
b.
C.
d.
e.
f.
g.
h.
i.
j.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 3 images

Recommended textbooks for you


College Accounting, Chapters 1-27
Accounting
ISBN:
9781337794756
Author:
HEINTZ, James A.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning,

Cornerstones of Financial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:
9781337690881
Author:
Jay Rich, Jeff Jones
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


College Accounting, Chapters 1-27
Accounting
ISBN:
9781337794756
Author:
HEINTZ, James A.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning,

Cornerstones of Financial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:
9781337690881
Author:
Jay Rich, Jeff Jones
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Financial Accounting: The Impact on Decision Make…
Accounting
ISBN:
9781305654174
Author:
Gary A. Porter, Curtis L. Norton
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Accounting Volume 1
Accounting
ISBN:
9781947172685
Author:
OpenStax
Publisher:
OpenStax College

Financial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:
9781337272124
Author:
Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan Duchac
Publisher:
Cengage Learning