Retrospective reimbursement provides financial incentives for medical care. a. efficient; inefficient O b. excessive; efficient c. insufficient; efficient O d. excessive; insufficient medical care; prospective reimbursement provides financial incentives for
Retrospective reimbursement provides financial incentives for medical care. a. efficient; inefficient O b. excessive; efficient c. insufficient; efficient O d. excessive; insufficient medical care; prospective reimbursement provides financial incentives for
Chapter15: Medical Care Reform In The United States
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 2QAP
Related questions
Question
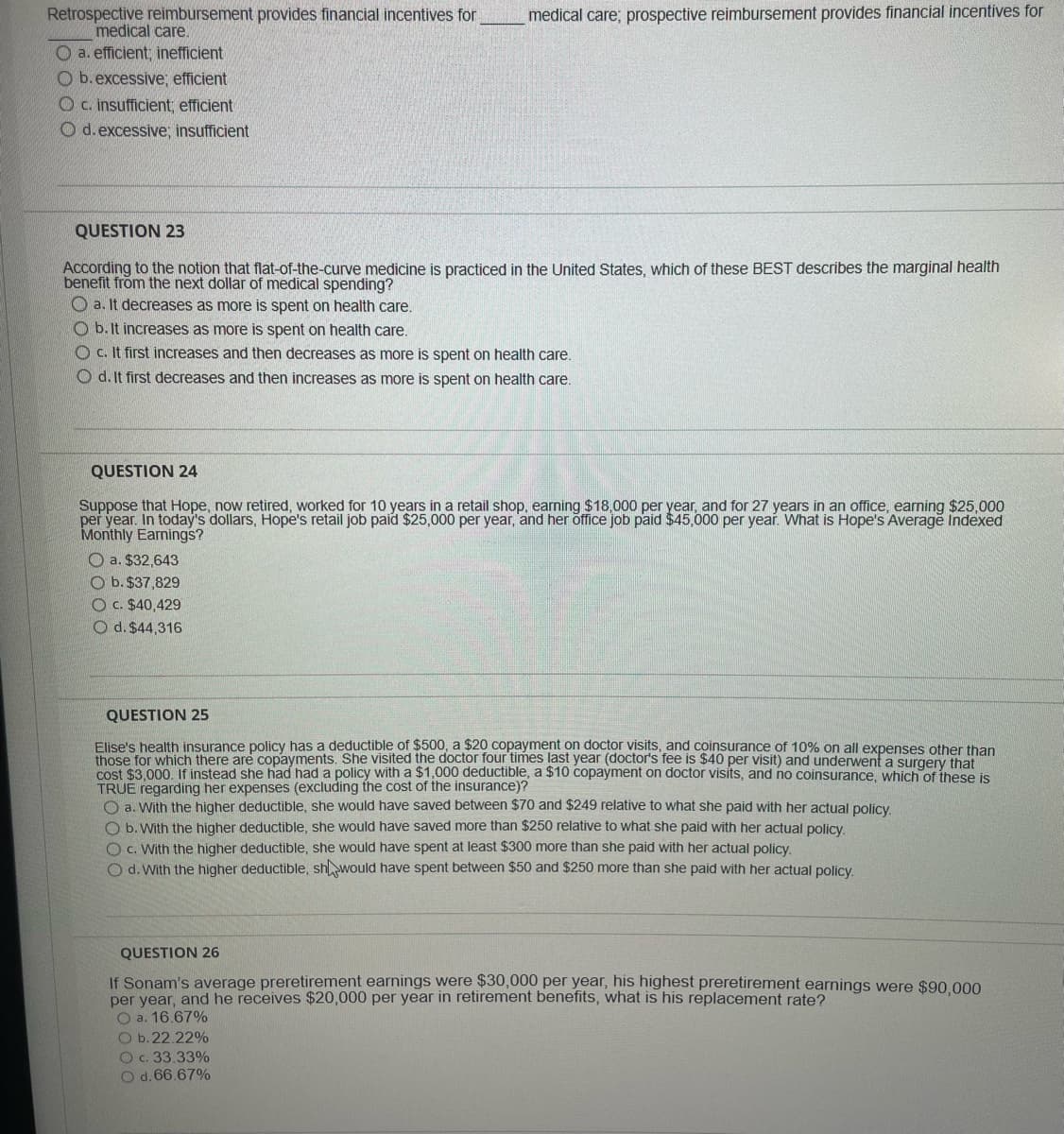
Transcribed Image Text:Retrospective reimbursement provides financial incentives for
medical care.
O a. efficient, inefficient
Ob. excessive; efficient
Oc. insufficient; efficient
O d. excessive; insufficient
medical care; prospective reimbursement provides financial incentives for
QUESTION 23
According to the notion that flat-of-the-curve medicine is practiced in the United States, which of these BEST describes the marginal health
benefit from the next dollar of medical spending?
a. It decreases as more is spent on health care.
Ob. It increases as more is spent on health care.
Oc. It first increases and then decreases as more is spent on health care.
Od. It first decreases and then increases as more is spent on health care.
QUESTION 24
Suppose that Hope, now retired, worked for 10 years in a retail shop, earning $18,000 per year, and for 27 years in an office, earning $25,000
per year. In today's dollars, Hope's retail job paid $25,000 per year, and her office job paid $45,000 per year. What is Hope's Average Indexed
Monthly Earnings?
a. $32,643
Ob. $37,829
O c. $40,429
O d. $44,316
QUESTION 25
Elise's health insurance policy has a deductible of $500, a $20 copayment on doctor visits, and coinsurance of 10% on all expenses other than
those for which there are copayments. She visited the doctor four times last year (doctor's fee is $40 per visit) and underwent a surgery that
cost $3,000. If instead she had had a policy with a $1,000 deductible, a $10 copayment on doctor visits, and no coinsurance, which of these is
TRUE regarding her expenses (excluding the cost of the insurance)?
O a. With the higher deductible, she would have saved between $70 and $249 relative to what she paid with her actual policy.
have aved more than $250 relative to what she paid with her actual policy.
O b. With the higher deductible, she
O c. With the higher deductible, she would have spent at least $300 more than she paid with her actual policy.
d. With the higher deductible, sh would have spent between $50 and $250 more than she paid with her actual policy.
QUESTION 26
If Sonam's average preretirement earnings were $30,000 per year, his highest preretirement earnings were $90,000
per year, and he receives $20,000 per year in retirement benefits, what is his replacement rate?
O a. 16.67%
O b. 22.22%
O c. 33.33%
O d. 66.67%
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

