ric Circuits Objective: To observe connections between current, voltage and resistance as well as other measurements in circuit design. Website : GOTO the following we
ric Circuits Objective: To observe connections between current, voltage and resistance as well as other measurements in circuit design. Website : GOTO the following we
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student Edition
1st Edition
ISBN:9780078807213
Author:Paul W. Zitzewitz
Publisher:Paul W. Zitzewitz
Chapter23: Series And Parallel Circuits
Section23.1: Simple Circuits
Problem 7PP
Related questions
Question
Electric Circuits
Objective: To observe connections between current, voltage and resistance as well as other measurements in circuit design.
Website : GOTO the following website to accomplish the following tasks.
http://phet.colorado.edu/sims/html/circuit-construction-kit-dc-virtual-lab/latest/circuit- construction-kit-dc-virtual-lab_en.html
Transcribed Image Text:Visualization
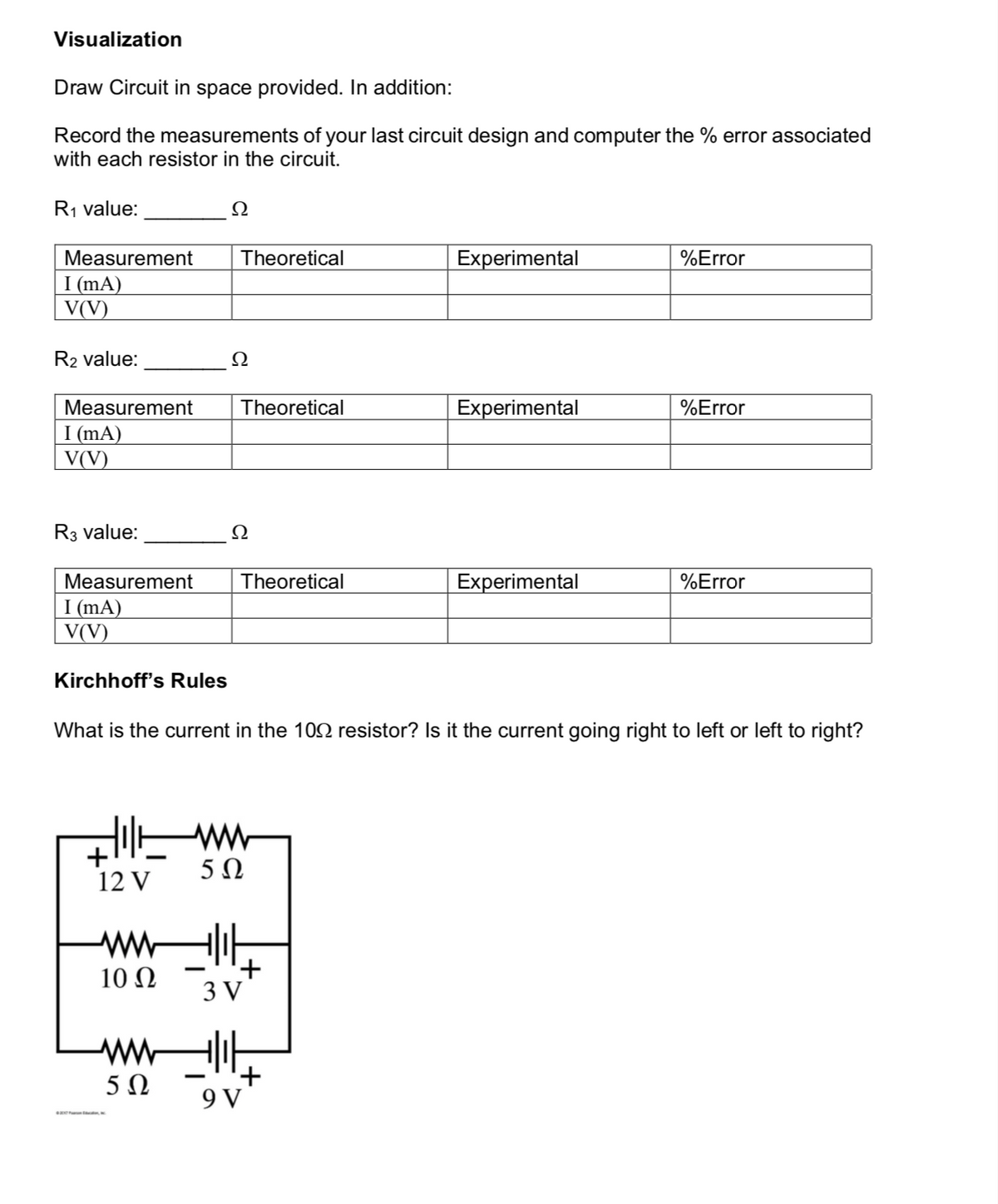
Draw Circuit in space provided. In addition:
Record the measurements of your last circuit design and computer the % error associated
with each resistor in the circuit.
R1 value:
Ω
Measurement
Theoretical
Experimental
%Error
I (mA)
V(V)
R2 value:
Ω
Measurement
Theoretical
Experimental
%Error
I (mA)
V(V)
R3 value:
Ω
Measurement
Theoretical
Experimental
%Error
I (mA)
V(V)
Kirchhoff's Rules
What is the current in the 102 resistor? Is it the current going right to left or left to right?
5Ω
12 V
ww
+
3 V
10 Ω
ww
+
9 V
5Ω

Transcribed Image Text:Tasks to Accomplish
Design circuits that demonstrate all of the principles listed below. Set up the circuits and
take measurements to show that the principle in question is indeed correct.
Principles of Series Circuits
1. The sum of the voltages across each circuit element equal that of the battery.
2. The current through each circuit element is the same.
3. Resistors with higher resistances have higher voltages across them.
4. Resistors added in series to any circuit increase the total resistance to current in
the circuit.
Principles of Parallel Circuits
1. Voltages across each circuit element are the same.
2. The sum of the currents through each parallel circuit element equal the current
through the battery.
3. Resistors with higher resistances have less current through them.
4. Resistors added in parallel to any circuit decrease the total resistance to current
in the circuit.
General Principles
1. A branch in a circuit that contains a short has no voltage across it.
2. A branch in a circuit that is open has the full voltage across it.
3. A battery is a constant voltage source.
4. A battery is not a constant current source.
5. Ammeters have very small internal resistance.
6. Voltmeters have very large internal resistance.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student…
Physics
ISBN:
9780078807213
Author:
Paul W. Zitzewitz
Publisher:
Glencoe/McGraw-Hill

Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student…
Physics
ISBN:
9780078807213
Author:
Paul W. Zitzewitz
Publisher:
Glencoe/McGraw-Hill