Sales (35,000 tires at $90 each) Variable costs (35,000 tires at $45) Fixed costs Earnings before interest and taxes (EBIT) Interest expense Earnings before taxes (EBT) Income tax expense (30%) Earnings after taxes (EAT) a. Compute the degree of operating leverage. Note: Round your answer to 2 decimal places. Degree of operating leverage b. Compute the degree of financial leverage. Note: Round your answer to 2 decimal places. Degree of financial leverage c. Compute the degree of combined leverage. Note: Round your answer to 2 decimal places. Degree of combined leverage $ 3,150,000 1,575,000 550,000 $ 1,025,000 57,500 $ 967,500 290, 250 $ 677,250 d. Compute the break-even point in units. Note: Round your answer to the nearest whole number.
Sales (35,000 tires at $90 each) Variable costs (35,000 tires at $45) Fixed costs Earnings before interest and taxes (EBIT) Interest expense Earnings before taxes (EBT) Income tax expense (30%) Earnings after taxes (EAT) a. Compute the degree of operating leverage. Note: Round your answer to 2 decimal places. Degree of operating leverage b. Compute the degree of financial leverage. Note: Round your answer to 2 decimal places. Degree of financial leverage c. Compute the degree of combined leverage. Note: Round your answer to 2 decimal places. Degree of combined leverage $ 3,150,000 1,575,000 550,000 $ 1,025,000 57,500 $ 967,500 290, 250 $ 677,250 d. Compute the break-even point in units. Note: Round your answer to the nearest whole number.
Chapter3: Cost-volume-profit Analysis
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 7EB: Delta Co. sells a product for $150 per unit. The variable cost per unit is $90 and fixed costs are...
Related questions
Question
100%
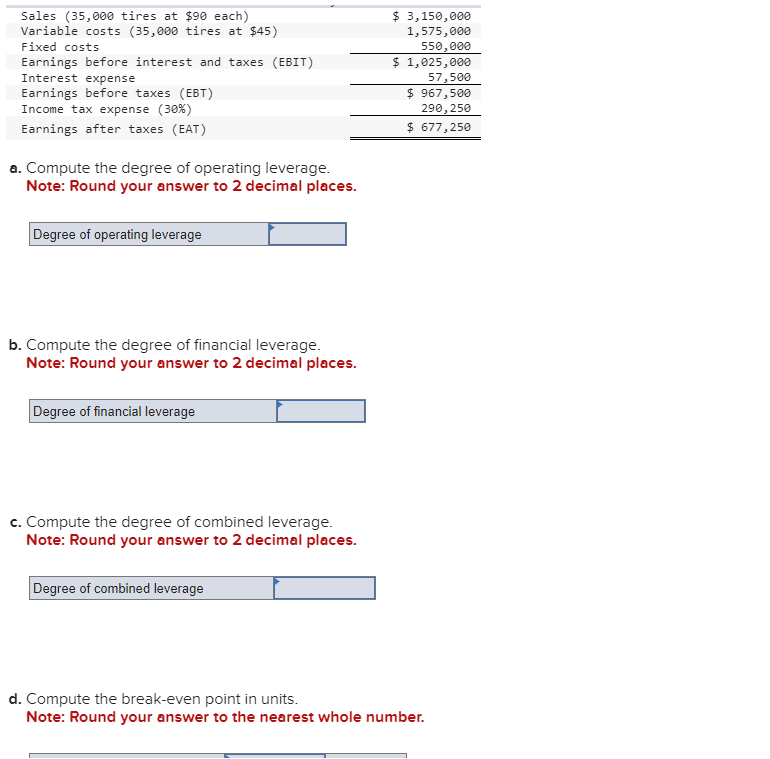
Transcribed Image Text:Sales (35,000 tires at $90 each)
Variable costs (35,000 tires at $45)
Fixed costs
Earnings before interest and taxes (EBIT)
Interest expense
Earnings before taxes (EBT)
Income tax expense (30%)
Earnings after taxes (EAT)
a. Compute the degree of operating leverage.
Note: Round your answer to 2 decimal places.
Degree of operating leverage
b. Compute the degree of financial leverage.
Note: Round your answer to 2 decimal places.
Degree of financial leverage
c. Compute the degree of combined leverage.
Note: Round your answer to 2 decimal places.
Degree of combined leverage
$ 3,150,000
1,575,000
550,000
$ 1,025,000
57,500
$ 967,500
290,250
$ 677,250
d. Compute the break-even point in units.
Note: Round your answer to the nearest whole number.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, finance and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Principles of Accounting Volume 2
Accounting
ISBN:
9781947172609
Author:
OpenStax
Publisher:
OpenStax College

Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:
9781337912020
Author:
Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. Tayler
Publisher:
South-Western College Pub

Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser…
Accounting
ISBN:
9781305970663
Author:
Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. Mowen
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Accounting Volume 2
Accounting
ISBN:
9781947172609
Author:
OpenStax
Publisher:
OpenStax College

Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:
9781337912020
Author:
Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. Tayler
Publisher:
South-Western College Pub

Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser…
Accounting
ISBN:
9781305970663
Author:
Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. Mowen
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines…
Accounting
ISBN:
9781337115773
Author:
Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. Heitger
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

EBK CONTEMPORARY FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT
Finance
ISBN:
9781337514835
Author:
MOYER
Publisher:
CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT