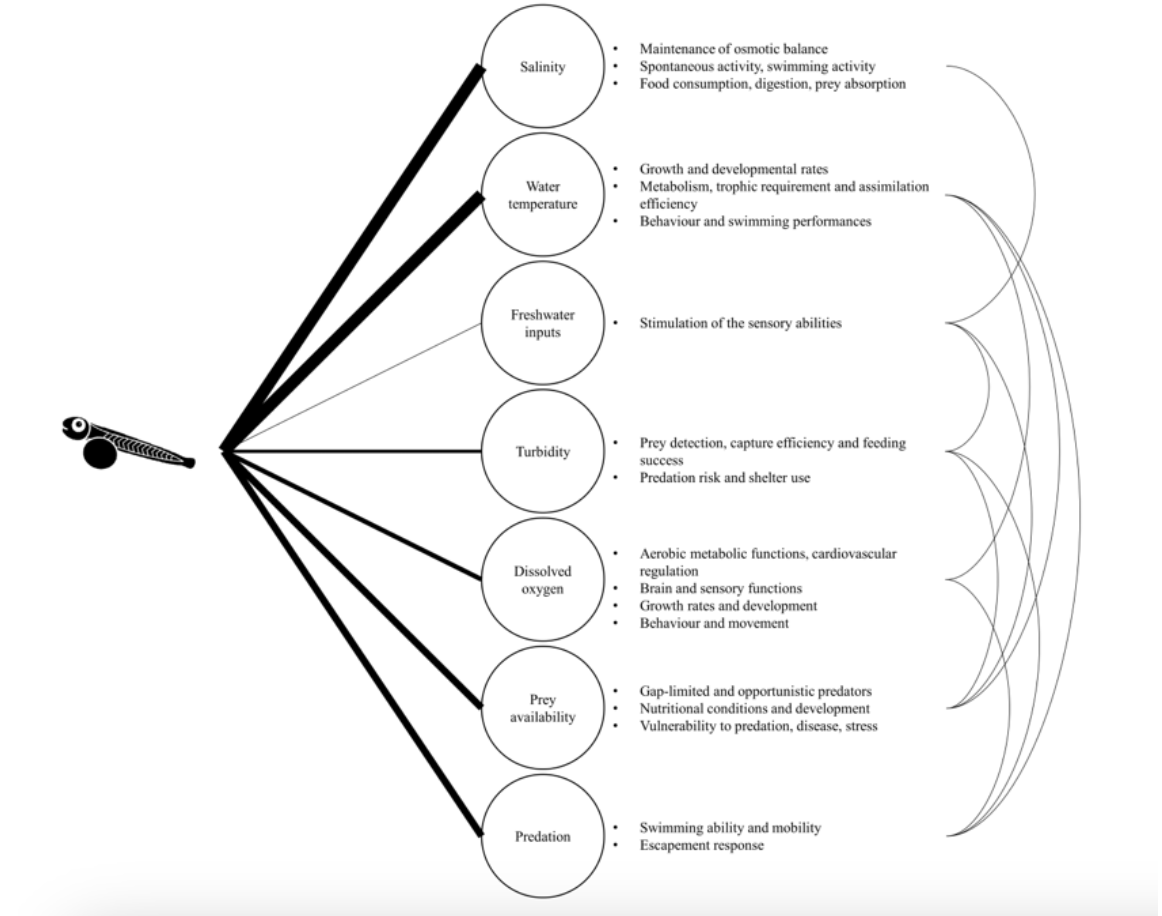
Salinity Maintenance of osmotic balance Spontaneous activity, swimming activity Food consumption, digestion, prey absorption Water temperature Growth and developmental rates Metabolism, trophic requirement and assimilation efficiency Behaviour and swimming performances Freshwater inputs Stimulation of the sensory abilities Turbidity Prey detection, capture efficiency and feeding success Predation risk and shelter use Aerobic metabolic functions, cardiovascular regulation Brain and sensory functions Growth rates and development Behaviour and movement Dissolved oxygen Gap-limited and opportunistic predators Nutritional conditions and development Vulnerability to predation, disease, stress Prey availability 000004 Predation Swimming ability and mobility Escapement response
The figure above shows main abiotic and biotic factors influencing the physiology and behavior of fish larvae in estuaries. The more important the factors are for the larvae, the thicker the lines. Suppose changes from question 1 take place. Draw a new figure and redefine the thickness of the lines and new factor interactions.
This is from question 1 :
A proposal is made to deepen the entrance and main channel of an estuary. What do you suppose will happen to the salt marshes that surround the channel? What do you predict will happen to the productivity of the estuary?
Deeper channels would probably change the mixing of the fresh and saltwater and lead to increased salinity and changes in the salt wedges in the channel. This would probably negatively impact the plants on the edges of the channel, as they would have to deal with higher salt levels than they are adapted to. The strain that would be put on the plants (like cordgrasses) in the marshes, would most likely lead to a decline in productivity in the estuary.
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 1 steps


