Salivary amylase is an enzyme in the human body that digests carbohydrates from food. When food mixed with saliva enters the stomach, the action of salivary amylase slows dramatically. Which causes salivary amylase enzyme to stop digesting food?
Salivary amylase is an enzyme in the human body that digests carbohydrates from food. When food mixed with saliva enters the stomach, the action of salivary amylase slows dramatically. Which causes salivary amylase enzyme to stop digesting food?
Anatomy & Physiology
1st Edition
ISBN:9781938168130
Author:Kelly A. Young, James A. Wise, Peter DeSaix, Dean H. Kruse, Brandon Poe, Eddie Johnson, Jody E. Johnson, Oksana Korol, J. Gordon Betts, Mark Womble
Publisher:Kelly A. Young, James A. Wise, Peter DeSaix, Dean H. Kruse, Brandon Poe, Eddie Johnson, Jody E. Johnson, Oksana Korol, J. Gordon Betts, Mark Womble
Chapter2: The Chemical Level Of Organization
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 13RQ: Which of the following statements about chemical bonds is true? Covalent bonds are stronger than...
Related questions
Question
Transcribed Image Text:* vbschools schoology.com
6 Schoology
Eayside Home Page 6 Schoology
Eayside Home Page ts Elemuta-Ele
Fertauass
HBY-BIO-U2-TEST BIOCHEMISTRY-SY 20-21
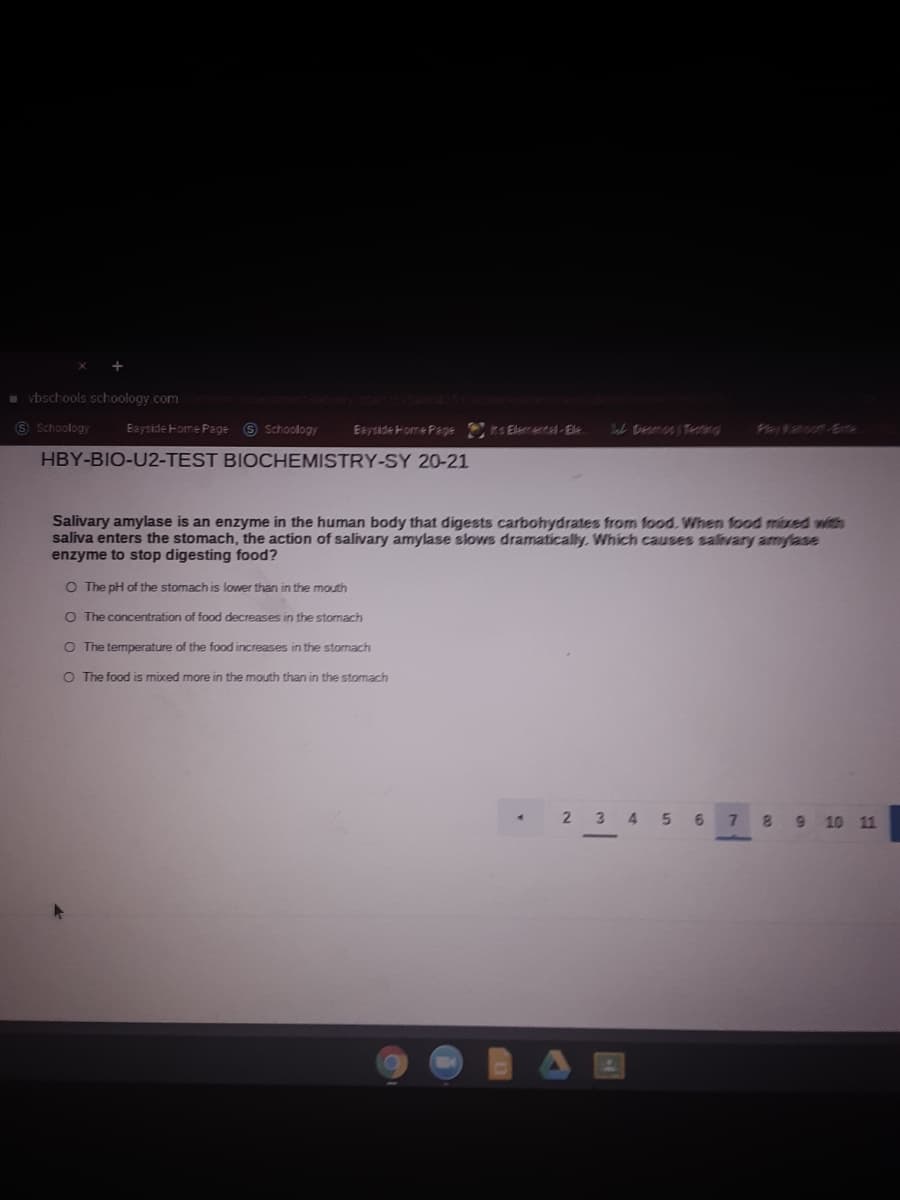
Salivary amylase is an enzyme in the human body that digests carbohydrates from food. When fod mixed with
saliva enters the stomach, the action of salivary amylase slows dramatically. Which causes salivary amylase
enzyme to stop digesting food?
O The pH of the stomach is lower than in the mouth
O The concentration of food decreases in the stormach
O The temperature of the food increases in the stomach
O The food is mixed more in the mouth than in the stomach
2 34 5 6 7
89 10 11
Transcribed Image Text:El - El-
HBY-BIO-U2-TEST BIOCHEMISTRY-SY 20-21
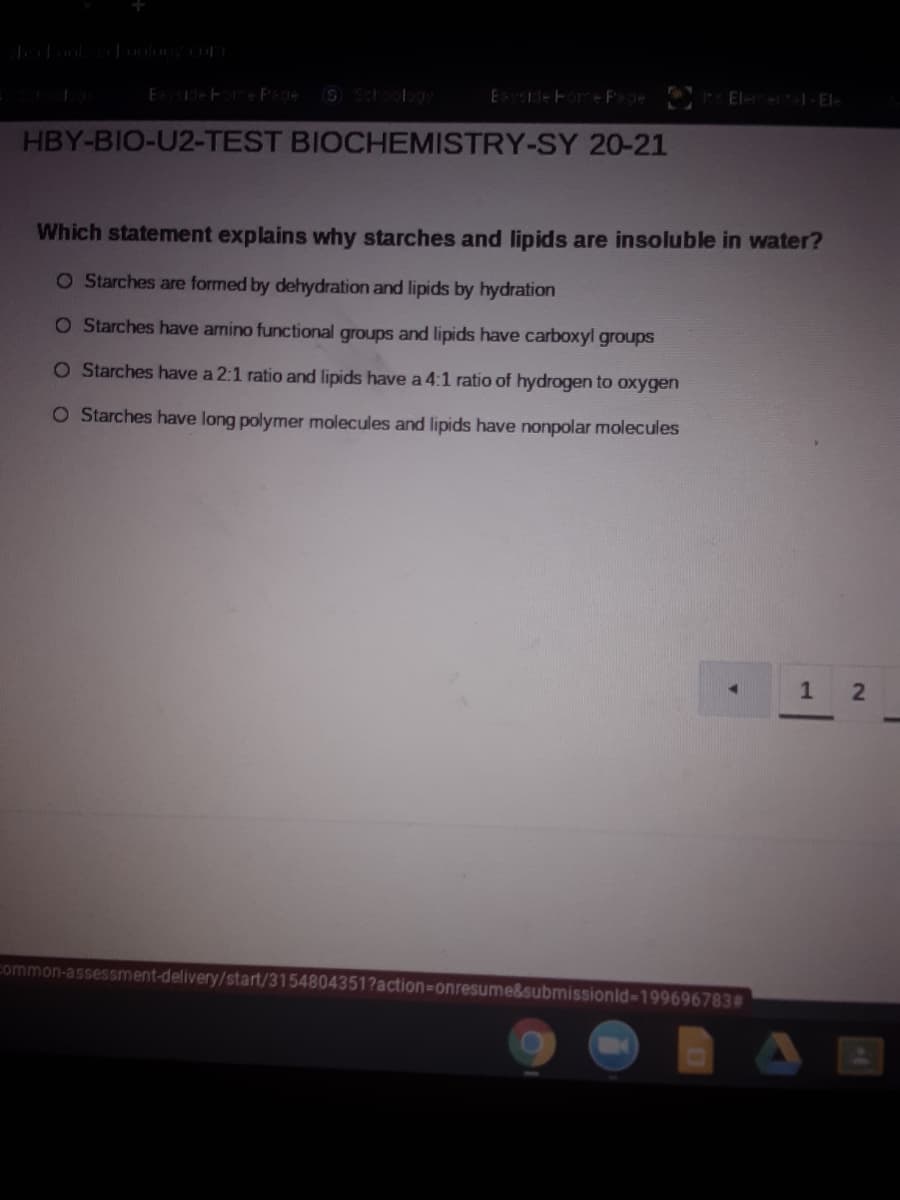
Which statement explains why starches and lipids are insoluble in water?
O S tarches are formed by dehydration and lipids by hydration
O Starches have amino functional groups and lipids have carboxyl groups
O Starches have a 2:1 ratio and lipids have a 4:1 ratio of hydrogen to oxygen
O Starches have long polymer molecules and lipids have nonpolar molecules
1
common-assessment-delivery/start/3154804351?action-Donresume&submissionid-199696783#
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biochemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:
9781938168130
Author:
Kelly A. Young, James A. Wise, Peter DeSaix, Dean H. Kruse, Brandon Poe, Eddie Johnson, Jody E. Johnson, Oksana Korol, J. Gordon Betts, Mark Womble
Publisher:
OpenStax College

Biology: The Unity and Diversity of Life (MindTap…
Biology
ISBN:
9781305073951
Author:
Cecie Starr, Ralph Taggart, Christine Evers, Lisa Starr
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:
9781947172517
Author:
Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:
OpenStax

Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:
9781938168130
Author:
Kelly A. Young, James A. Wise, Peter DeSaix, Dean H. Kruse, Brandon Poe, Eddie Johnson, Jody E. Johnson, Oksana Korol, J. Gordon Betts, Mark Womble
Publisher:
OpenStax College

Biology: The Unity and Diversity of Life (MindTap…
Biology
ISBN:
9781305073951
Author:
Cecie Starr, Ralph Taggart, Christine Evers, Lisa Starr
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:
9781947172517
Author:
Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:
OpenStax