Shepherd Cycles started July with 15 bicycles that cost $75 each. On July 16, Shepherd purchased 25 bicycles at $91 each. On July 31, Shepherd sold 20 bicycles for $110 each. Requirements 1. Prepare Shepherd Cycle's perpetual inventory record assuming the company uses the specific identification inventory costing method. Assume that Shepherd sold 10 bicycles that cost $75 each and 10 bicycles that cost $91 each. 2. Journalize the July 16 purchase of merchandise inventory on account and the July 31 sale of merchandise inventory on account. Requirement 1. Prepare Shepherd Cycle's perpetual inventory record assuming the company uses the specific identification inventory costing method. Assume that Shepherd sold 10 bicycles that cost $75 each and 10 bicycles that cost $91 each. Start by entering the beginning inventory balances. Enter the transactions in chronological order, calculating new inventory on hand balances after each transaction. Once all of the transactions have been entered into the perpetual record, calculate the quantity and total cost of inventory purchased, sold, and on hand at the end of the period. (Enter the oldest inventory layers first. Abbreviation used: QTY = Quantity; Tot. = Total) Shepherd Cycles Date Jul. 1 Purchases Unit Tot. QTY Cost Cost Cost of Goods Sold Unit Tot. QTY | Cost Cost Inventory on Hand Unit Tot. QTY Cost Cost
Shepherd Cycles started July with 15 bicycles that cost $75 each. On July 16, Shepherd purchased 25 bicycles at $91 each. On July 31, Shepherd sold 20 bicycles for $110 each. Requirements 1. Prepare Shepherd Cycle's perpetual inventory record assuming the company uses the specific identification inventory costing method. Assume that Shepherd sold 10 bicycles that cost $75 each and 10 bicycles that cost $91 each. 2. Journalize the July 16 purchase of merchandise inventory on account and the July 31 sale of merchandise inventory on account. Requirement 1. Prepare Shepherd Cycle's perpetual inventory record assuming the company uses the specific identification inventory costing method. Assume that Shepherd sold 10 bicycles that cost $75 each and 10 bicycles that cost $91 each. Start by entering the beginning inventory balances. Enter the transactions in chronological order, calculating new inventory on hand balances after each transaction. Once all of the transactions have been entered into the perpetual record, calculate the quantity and total cost of inventory purchased, sold, and on hand at the end of the period. (Enter the oldest inventory layers first. Abbreviation used: QTY = Quantity; Tot. = Total) Shepherd Cycles Date Jul. 1 Purchases Unit Tot. QTY Cost Cost Cost of Goods Sold Unit Tot. QTY | Cost Cost Inventory on Hand Unit Tot. QTY Cost Cost
Century 21 Accounting General Journal
11th Edition
ISBN:9781337680059
Author:Gilbertson
Publisher:Gilbertson
Chapter20: Accounting For Inventory
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 2AP
Related questions
Question
100%
Shepherd Cycles started July with
15
bicycles that cost
$75
each. On
July 16,
Shepherd
purchased
25
bicycles at
$91
each. On
July 31,
Shepherd
sold
20
bicycles for
$110
each.Requirements
|
1.
|
Prepare
Shepherd
Cycle's perpetual inventory record assuming the company uses the specific identification inventory costing method. Assume that
Shepherd
sold
10
bicycles that cost
$75
each and
10
bicycles that cost
$91
each. |
|
2.
|
Journalize the
July 16
purchase of merchandise inventory on account and the
July 31
sale of merchandise inventory on account. |
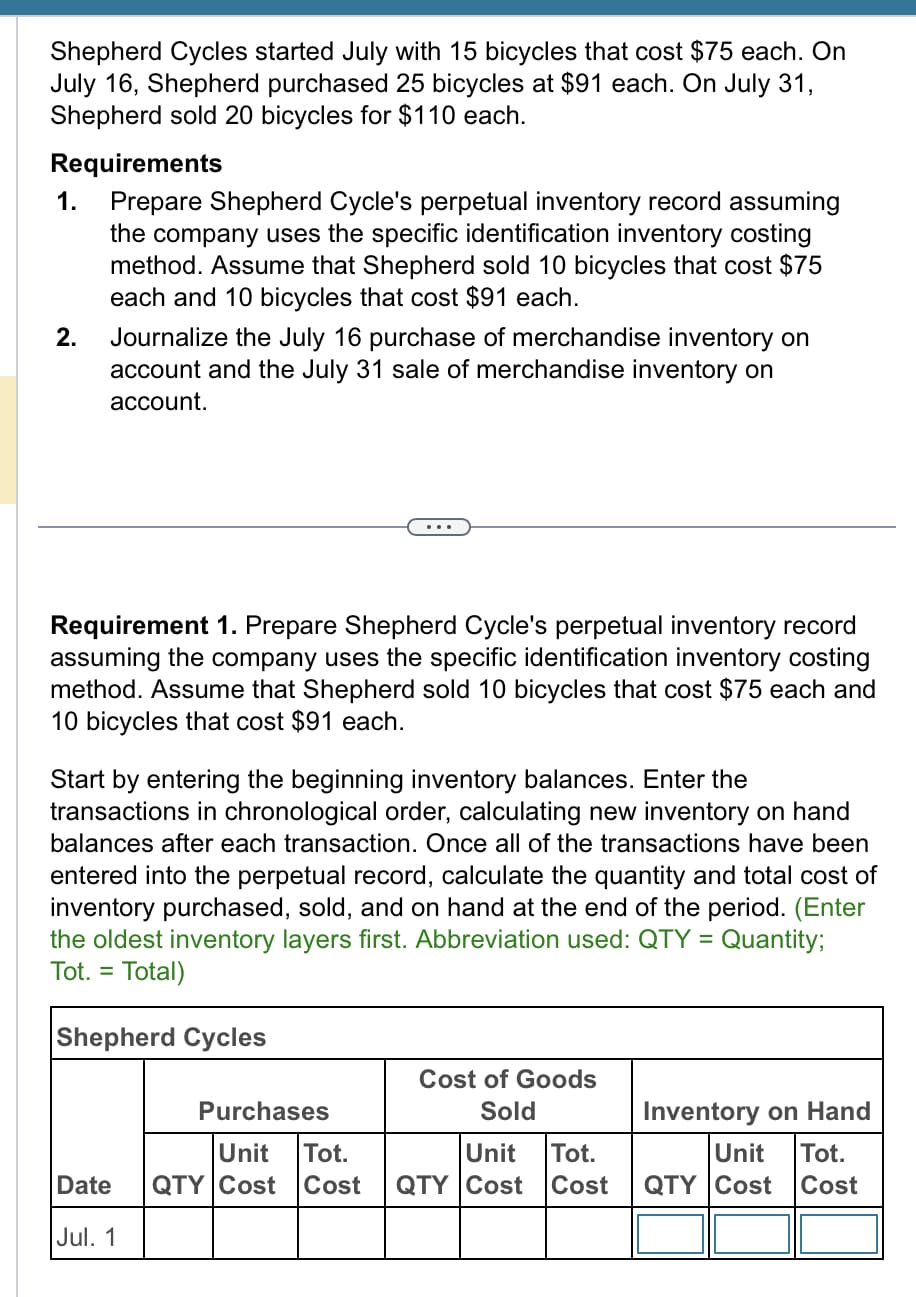
Transcribed Image Text:Shepherd Cycles started July with 15 bicycles that cost $75 each. On
July 16, Shepherd purchased 25 bicycles at $91 each. On July 31,
Shepherd sold 20 bicycles for $110 each.
Requirements
1. Prepare Shepherd Cycle's perpetual inventory record assuming
the company uses the specific identification inventory costing
method. Assume that Shepherd sold 10 bicycles that cost $75
each and 10 bicycles that cost $91 each.
2.
Journalize the July 16 purchase of merchandise inventory on
account and the July 31 sale of merchandise inventory on
account.
Requirement 1. Prepare Shepherd Cycle's perpetual inventory record
assuming the company uses the specific identification inventory costing
method. Assume that Shepherd sold 10 bicycles that cost $75 each and
10 bicycles that cost $91 each.
Start by entering the beginning inventory balances. Enter the
transactions in chronological order, calculating new inventory on hand
balances after each transaction. Once all of the transactions have been
ed into the perpetual record, calculate quantity and total cost of
inventory purchased, sold, and on hand at the end of the period. (Enter
the oldest inventory layers first. Abbreviation used: QTY = Quantity;
Tot. = Total)
Shepherd Cycles
Purchases
Unit
Tot.
Date QTY Cost Cost
Jul. 1
Cost of Goods
Sold
Inventory on Hand
Unit Tot.
Unit Tot.
QTY Cost Cost QTY Cost Cost
Expert Solution
Step 1
A perpetual inventory system is a system that tracks and keeps records of the inventory on a real-time basis electronically without the need for physical inventory. In this system, inventory gets updated automatically whenever the goods are purchased or sold, any purchase or sales return records are also immediately updated. This system is helpful in accurately recording the inventory data in comparison to the manual system of recording. Large businesses like grocery stores or departmental stores use a perpetual system of inventory recording.
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 4 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, accounting and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you


Cornerstones of Financial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:
9781337690881
Author:
Jay Rich, Jeff Jones
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Financial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:
9781337272124
Author:
Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan Duchac
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Cornerstones of Financial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:
9781337690881
Author:
Jay Rich, Jeff Jones
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Financial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:
9781337272124
Author:
Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan Duchac
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Financial Accounting: The Impact on Decision Make…
Accounting
ISBN:
9781305654174
Author:
Gary A. Porter, Curtis L. Norton
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

College Accounting, Chapters 1-27 (New in Account…
Accounting
ISBN:
9781305666160
Author:
James A. Heintz, Robert W. Parry
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Financial And Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:
9781337902663
Author:
WARREN, Carl S.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning,