Show that the line y x-1 is an oblique asymptote for the graph of y f(x), summarize all pertinent information obtained by applying the graphing strategy, and sketch the graph of y f(x). () -x- 1+ In the limit, becomes negligibly small, and ignoring this term results in the equation. which implies that yx-1 is an oblique asymptote for the given function To show that y x- 1 is an oblique asymptote for the given function, take the limit of f(x) as x approaches (Type an equation using x as the variable. Simplify your answer.) Find the domain of f(x). Select the correct choice below and, if necessary, fill in the answer box to complete your cholce O A. The domain is all real x, except x (Type an integer or a decimal. Use a comma to separate answers as needed.) O B. The domain is all real x Find the x-intercepts of f(x). Select the correct choice below and, If necessary, fill in the answer box to complete your cholce. O A The x-intercept(s) is/are at x (Type an integer or a decimal. Use a comma separate answers as needed.) OB. There are no x-intercepts Find the y-intercepts of f(x). Select the correct choice below and, if necessary, fill in the answer box to complete your choice. OA. The y-intercept(s) islare at y (Type an integer or a decimal. Use a comma to separate answers as needed.) O B. There are no y-intercepts.
Show that the line y x-1 is an oblique asymptote for the graph of y f(x), summarize all pertinent information obtained by applying the graphing strategy, and sketch the graph of y f(x). () -x- 1+ In the limit, becomes negligibly small, and ignoring this term results in the equation. which implies that yx-1 is an oblique asymptote for the given function To show that y x- 1 is an oblique asymptote for the given function, take the limit of f(x) as x approaches (Type an equation using x as the variable. Simplify your answer.) Find the domain of f(x). Select the correct choice below and, if necessary, fill in the answer box to complete your cholce O A. The domain is all real x, except x (Type an integer or a decimal. Use a comma to separate answers as needed.) O B. The domain is all real x Find the x-intercepts of f(x). Select the correct choice below and, If necessary, fill in the answer box to complete your cholce. O A The x-intercept(s) is/are at x (Type an integer or a decimal. Use a comma separate answers as needed.) OB. There are no x-intercepts Find the y-intercepts of f(x). Select the correct choice below and, if necessary, fill in the answer box to complete your choice. OA. The y-intercept(s) islare at y (Type an integer or a decimal. Use a comma to separate answers as needed.) O B. There are no y-intercepts.
Intermediate Algebra
10th Edition
ISBN:9781285195728
Author:Jerome E. Kaufmann, Karen L. Schwitters
Publisher:Jerome E. Kaufmann, Karen L. Schwitters
Chapter7: Equations And Inequalities In Two Variables
Section7.1: Rectangular Coordinate System And Linear Equations
Problem 59PS: Now lets use a graphing calculator to get a graph of C=59(F32). By letting F=x and C=y, we obtain...
Related questions
Question
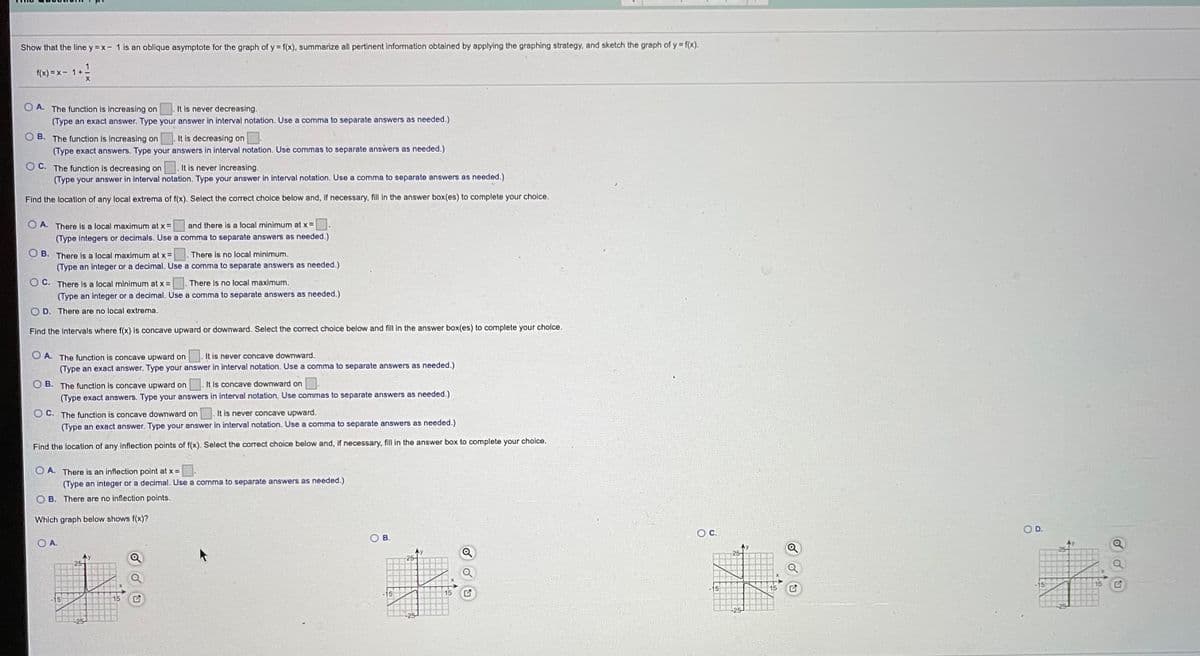
Transcribed Image Text:Show that the line y = x- 1 is an oblique asymptote for the graph of y = f(x), summarize all pertinent information obtained by applying the graphing strategy, and sketch the graph of y f(x).
f(x) = x- 1+.
O A. The function is increasing on
It is never decreasing.
(Type an exact answer. Type your answer in interval notation. Use a comma to separate answers as needed.)
B. The function is increasing on
It is decreasing on .
(Type exact answers. Type your answers in interval notation. Use commas to separate answers as needed.)
O C. The function is decreasing on .It is never increasing.
(Type your answer in interval notation. Type your answer in interval notation. Use a comma to separate answers as needed.)
Find the location of any local extrema of f(x). Select the correct cholce below and, if necessary, fill in the answer box(es) to complete your choice.
O A. There is a local maximum at x =
and there is a local minimum at x =
(Type integers or decimals. Use a comma to separate answers as needed.)
There is no local minimum.
O B. There is a local maximum at x =
(Type an integer or a decimal. Use a comma to separate answers as needed.)
O C. There is a local minimum at x =
There is no local maximum.
(Type an integer or a decimal. Use a comma to separate answers as needed.)
O D. There are no local extrema.
Find the intervals where f(x) is concave upward or downward. Select the correct choice below and fill in the answer box(es) to complete your choice.
O A. The function is concave upward on
It is never concave downward.
(Type an exact answer. Type your answer in interval notation. Use a comma to separate answers as needed.)
O B. The function is concave upward on
It is concave downward on
(Type exact answers. Type your answers in interval notation. Use commas to separate answers as needed.)
C. The function is concave downward on
It is never concave upward.
(Type an exact answer. Type your answer in interval notation. Use a comma to separate answers as needed.)
Find the location of any inflection points of f(x). Select the correct choice below and, if necessary, fill in the answer box to complete your choice.
O A. There is an inflection point at x =
(Type an integer or a decimal. Use a comma to separate answers as needed.)
B. There are no inflection points.
Which graph below shows f(x)?
D.
c.
OB.
OA.
Ay
26
25
26-
25-
-15
15
15
-15
15
25
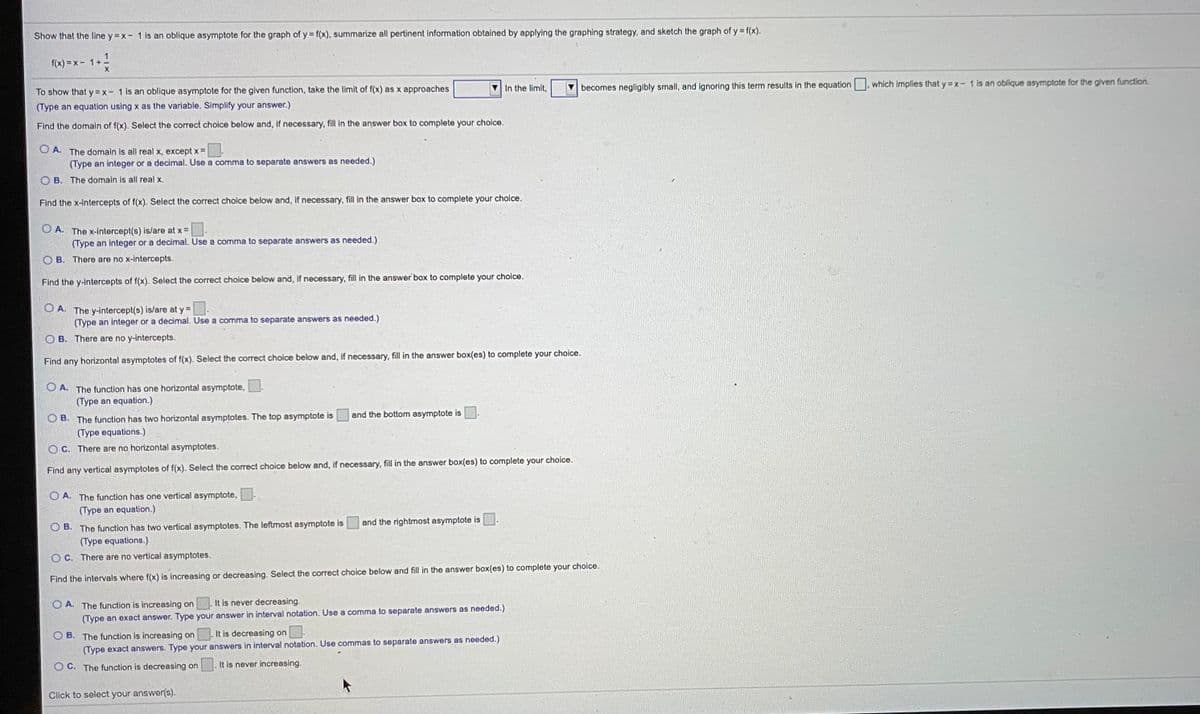
Transcribed Image Text:Show that the line y = x- 1 is an oblique asymptote for the graph of y= f(x), summarize all pertinent information obtained by applying the graphing strategy, and sketch the graph of y = f(x).
f(x) = x - 1+
In the limit,
becomes negligibly small, and ignoring this term results in the equation , which implies that y =x- 1 is an oblique asymptote for the given function.
To show that y=x- 1 is an oblique asymptote for the given function, take the limit of f(x) as x approaches
(Type an equation using x as the variable. Slmplify your answer.)
Find the domain of f(x). Select the correct choice below and, if necessary, fill in the answer box to complete your choice.
O A. The domain is all real x, except x =
(Type an integer or a decimal. Use a comma to separate answers as needed.)
B. The domain is all real x.
Find the x-intercepts of f(x). Select the correct choice below and, If necessary, fill in the answer box to complete your cholce.
O A. The x-intercept(s) is/are at x =.
(Type an integer or a decimal. Use a comma to separate answers as needed.)
O B. There are no x-intercepts.
Find the y-intercepts of f(x). Select the correct choice below and, if necessary, fill in the answer box to complete your choice.
O A. The y-intercept(s) is/are at y =.
(Type an integer or a decimal. Use a comma to separate answers as needed.)
O B. There are no y-intercepts.
Find any horizontal asymptotes of f(x). Select the correct choice below and, if necessary, fill in the answer box(es) to complete your choice.
O A. The function has one horizontal asymptote,
(Type an equation.)
and the bottom asymptote is
O B. The function has two horizontal asymptotes. The top asymptote is
(Type equations.)
O C. There are no horizontal asymptotes.
Find any vertical asymptotes of f(x). Select the correct choice below and, if necessary, fill in the answer box(es) to complete your choice.
O A. The function has one vertical asymptote,
(Type an equation.)
and the rightmost asymptote is
O B. The function has two vertical asymptotes. The leftmost asymptote is
(Type equations.)
O C. There are no vertical asymptotes.
Find the intervals where f(x) is increasing or decreasing. Select the correct choice below and fill in the answer box(es) to complete your choice.
It is never decreasing.
O A. The function is increasing on
(Type an exact answer. Type your answer in interval notation. Use a comma to separate answers as needed.)
It is decreasing on
O B. The function is increasing on
(Type exact answers. Type your answers in interval notation. Use commas to separate answers as needed.)
O C. The function is decreasing on
It is never increasing.
Click to select your answer(s).
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 12 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, calculus and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Intermediate Algebra
Algebra
ISBN:
9781285195728
Author:
Jerome E. Kaufmann, Karen L. Schwitters
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Algebra for College Students
Algebra
ISBN:
9781285195780
Author:
Jerome E. Kaufmann, Karen L. Schwitters
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Intermediate Algebra
Algebra
ISBN:
9781285195728
Author:
Jerome E. Kaufmann, Karen L. Schwitters
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Algebra for College Students
Algebra
ISBN:
9781285195780
Author:
Jerome E. Kaufmann, Karen L. Schwitters
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage

College Algebra
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305115545
Author:
James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem Watson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning