Simon Company's year-end balance sheets follow. At December 31 2017 2016 2015 Assets $ 30,510 $ 36,391 $ 88,428 113,450 10,126 285,160 $ 527,674 $ 454,891 $ 390,800 Cash Accounts receivable, net Merchandise inventory Prepaid expenses 64,322 84,996 9,648 259,534 37,915 51,586 54,939 4,428 241,932 Plant assets, net Total assets Liabilities and Equity Accounts payable Long-term notes payable secured by mortgages on plant assets Common stock, $10 par value Retained earnings $ 132,705 $ 76,877 $ 50,554 102,179 162,500 105,671 162,500 109,843 $ 527,674 $ 454,891 $ 390,800 84,639 162,500 93,107 130,290 Total liabilities and equity 1. Compute the current ratio for the year ended 2017, 2016, and 2015. 2. Compute the acid-test ratio for the year ended 2017, 2016, and 2015.
Simon Company's year-end balance sheets follow. At December 31 2017 2016 2015 Assets $ 30,510 $ 36,391 $ 88,428 113,450 10,126 285,160 $ 527,674 $ 454,891 $ 390,800 Cash Accounts receivable, net Merchandise inventory Prepaid expenses 64,322 84,996 9,648 259,534 37,915 51,586 54,939 4,428 241,932 Plant assets, net Total assets Liabilities and Equity Accounts payable Long-term notes payable secured by mortgages on plant assets Common stock, $10 par value Retained earnings $ 132,705 $ 76,877 $ 50,554 102,179 162,500 105,671 162,500 109,843 $ 527,674 $ 454,891 $ 390,800 84,639 162,500 93,107 130,290 Total liabilities and equity 1. Compute the current ratio for the year ended 2017, 2016, and 2015. 2. Compute the acid-test ratio for the year ended 2017, 2016, and 2015.
Financial Accounting
15th Edition
ISBN:9781337272124
Author:Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan Duchac
Publisher:Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan Duchac
Chapter7: Inventories
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 8PEA: Financial statement data for years ending December 31 for Holland Company follow: a. Determine the...
Related questions
Topic Video
Question
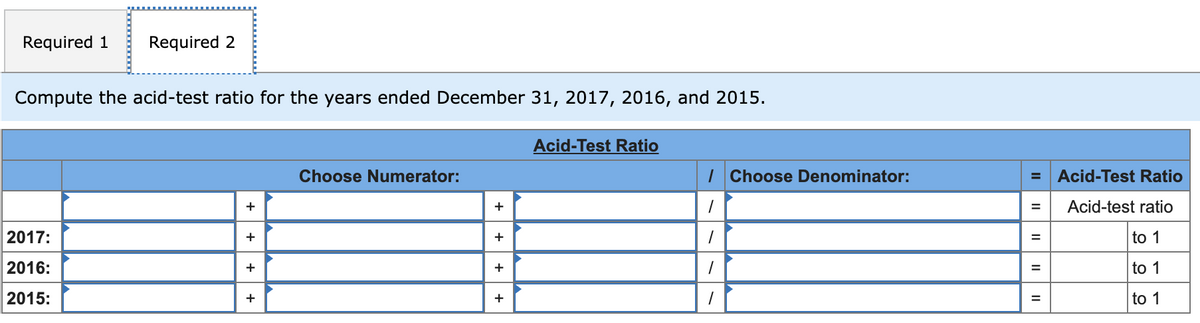
Transcribed Image Text:Required 1
Required 2
Compute the acid-test ratio for the years ended December 31, 2017, 2016, and 2015.
Acid-Test Ratio
Choose Numerator:
I Choose Denominator:
Acid-Test Ratio
+
+
Acid-test ratio
2017:
+
+
to 1
%3D
2016:
+
+
to 1
%3D
2015:
+
+
to 1
II
II
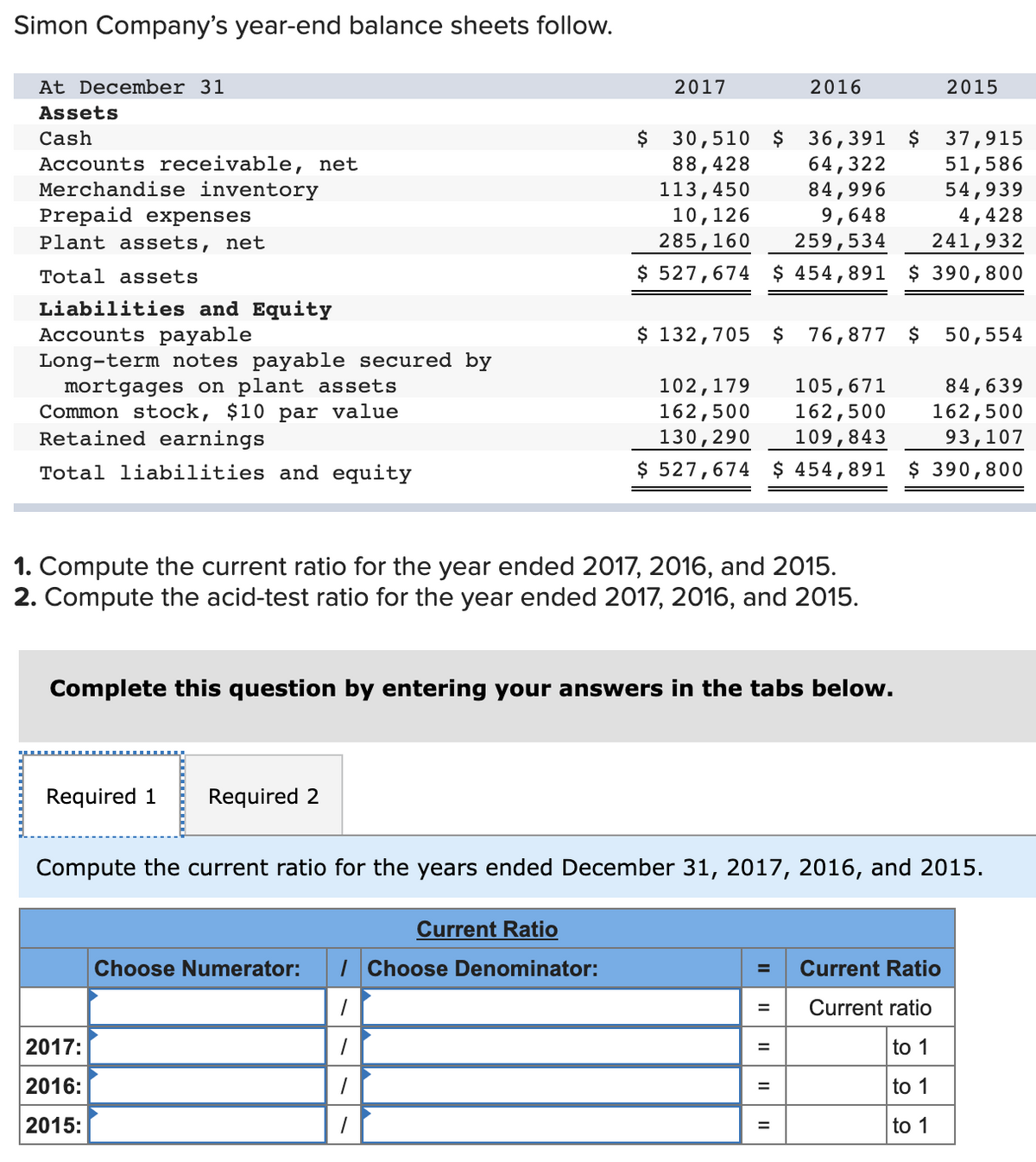
Transcribed Image Text:Simon Company's year-end balance sheets follow.
At December 31
2017
2016
2015
Assets
$ 30,510 $ 36,391 $
88,428
113,450
10,126
285,160
37,915
51,586
54,939
4,428
241,932
Cash
Accounts receivable, net
Merchandise inventory
64,322
84,996
9,648
259,534
Prepaid expenses
Plant assets, net
Total assets
$ 527,674 $ 454,891 $ 390,800
Liabilities and Equity
Accounts payable
Long-term notes payable secured by
mortgages on plant assets
Common stock, $10 par value
Retained earnings
$ 132,705 $
76,877 $
50,554
102,179
162,500
130,290
105,671
162,500
109,843
84,639
162,500
93,107
$ 527,674 $ 454,891 $ 390,800
Total liabilities and equity
1. Compute the current ratio for the year ended 2017, 2016, and 2015.
2. Compute the acid-test ratio for the year ended 2017, 2016, and 2015.
Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below.
Required 1
Required 2
Compute the current ratio for the years ended December 31, 2017, 2016, and 2015.
Current Ratio
Choose Numerator:
| Choose Denominator:
Current Ratio
%3D
Current ratio
2017:
to 1
%3D
2016:
to 1
2015:
to 1
%3D
II
Expert Solution
Step 1
The current ratio is the measure of a company's ability to pay back its short-term debts. It is calculated by dividing the current assets of the company by the current liabilities.
The acid-test ratio is a more conservative measure of a company's ability to pay back its short-term debts. It is calculated by dividing the current assets less inventory by the current liabilities.
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, finance and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Financial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:
9781337272124
Author:
Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan Duchac
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Financial And Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:
9781337902663
Author:
WARREN, Carl S.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning,

Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines…
Accounting
ISBN:
9781337115773
Author:
Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. Heitger
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Financial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:
9781337272124
Author:
Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan Duchac
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Financial And Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:
9781337902663
Author:
WARREN, Carl S.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning,

Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines…
Accounting
ISBN:
9781337115773
Author:
Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. Heitger
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And Analysis
Accounting
ISBN:
9781337788281
Author:
James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald Pagach
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Survey of Accounting (Accounting I)
Accounting
ISBN:
9781305961883
Author:
Carl Warren
Publisher:
Cengage Learning
