Small pieces of copper at 100.0°C are placed in 110.0 g of water at 25.0°C in a perfectly insulated calorimeter. The water and copper reach the same final temperature. The initial and final temperatures of the water are shown. Which of the following statements about thermal energy transfer in the experiment is correct? A B с D The temperature of the copper increases, so thermal energy must flow from the copper to the water. The temperature of the copper increases, so thermal energy must flow from the water to the copper. The temperature of the copper decreases, so thermal energy must flow from the copper to the water. The temperature of the copper decreases, so thermal energy must flow from the water to the copper. Su
Small pieces of copper at 100.0°C are placed in 110.0 g of water at 25.0°C in a perfectly insulated calorimeter. The water and copper reach the same final temperature. The initial and final temperatures of the water are shown. Which of the following statements about thermal energy transfer in the experiment is correct? A B с D The temperature of the copper increases, so thermal energy must flow from the copper to the water. The temperature of the copper increases, so thermal energy must flow from the water to the copper. The temperature of the copper decreases, so thermal energy must flow from the copper to the water. The temperature of the copper decreases, so thermal energy must flow from the water to the copper. Su
General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Course List)
11th Edition
ISBN:9781305580343
Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; Darrell
Publisher:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; Darrell
Chapter6: Thermochemisty
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 6.35QP: A 250-g sample of water at 20.0C is placed in a freezer that is held at a constant temperature of...
Related questions
Question
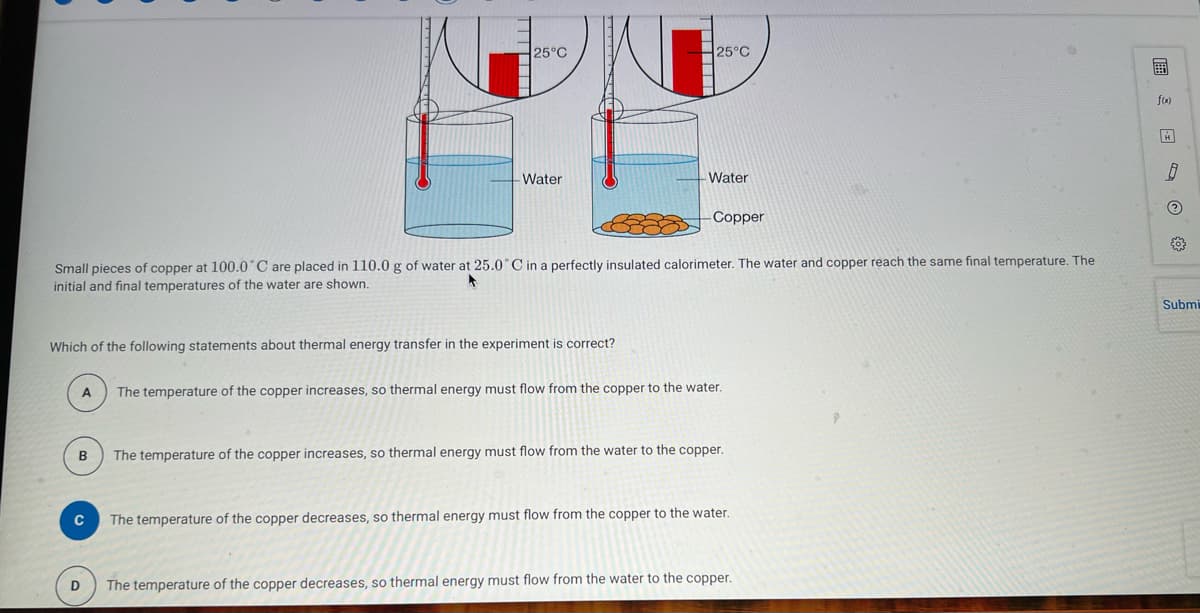
Transcribed Image Text:A
Which of the following statements about thermal energy transfer in the experiment is correct?
B
25°C
с
Water
Small pieces of copper at 100.0°C are placed in 110.0 g of water at 25.0°C in a perfectly insulated calorimeter. The water and copper reach the same final temperature. The
initial and final temperatures of the water are shown.
D
25°C
- Water
-Copper
The temperature of the copper increases, so thermal energy must flow from the copper to the water.
The temperature of the copper increases, so thermal energy must flow from the water to the copper.
The temperature of the copper decreases, so thermal energy must flow from the copper to the water.
The temperature of the copper decreases, so thermal energy must flow from the water to the copper.
f(x)
8
?
{0}
Submi
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour…
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305580343
Author:
Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; Darrell
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry for Engineering Students
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337398909
Author:
Lawrence S. Brown, Tom Holme
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: An Atoms First Approach
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079243
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour…
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305580343
Author:
Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; Darrell
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry for Engineering Students
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337398909
Author:
Lawrence S. Brown, Tom Holme
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: An Atoms First Approach
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079243
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781133949640
Author:
John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337399074
Author:
John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning