Solar power towers (also called 'central tower' power plants or 'heliostat' power plants), allow solar irradiation to be concentrated into a single receiver by a series of reflectors (mirrors) to maximize the amount of heat flux being used to make clean, renewable energy. Here's the Ivanpah Solar Power Facility pictured below (https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ivanpah Solar Power Facility). It is located in the Mojave desert by the border of California and Nevada, where irradiation from sunlight is high due to lack of cloud cover and interference from moisture in the air. In this problem, we'll study a simplified solar power plant model to understand how the properties of thermal radiation affect its ability to take in and use energy from the sun. Let's assume that the solar reflectors provide G₁ = 80,000 W/m² of solar heat flux to the receiver (white glowing cylinder at the top of the tower). (Keep in mind that solar irradiation onto the Earth's surface is typically around 1400W/m². The reflectors are what can increase this typical heat flux by "bouncing "/reflecting and concentrating this solar flux into the receiver. This is what makes this a much higher concentration of solar power than something like a solar panel would see from the sun alone. The downside is that the high magnitude of solar radiation power all being localized in this tower can be deadly for both people and wildlife if they get in the way of the concentrators - another reason to put these deep in the middle of the desert. This assignment will help us see just how much power that is!) For now, assume that the receiver at the top of the tower has a steady-state temperature of T, = 800 K. Not only is the receiver exposed to solar irradiation from the reflectors, but it also is exposed to surrounding air. Assume that the air is at an average temperature of T = 300 K with a convective heat transfer coefficient of 7 W/m² K due to natural convection (no wind). The outer surface of the receiver can be treated as diffuse and opaque. The spectral absorptivity of the coating at the surface of the receiver is given in the figure below: 0.9 az 0.2 2. (μm) 3 Assume that we'll be studying just the receiver at the top of the tower, which can be modeled as a very large cylinder with a diameter of 7m and a height of 12 m. Only the sides of the cylinder are exposed to the air/solar radiation, as the top/bottom have other equipment and mounting structure attached to them. This exposed surface area is represented as A,.
Solar power towers (also called 'central tower' power plants or 'heliostat' power plants), allow solar irradiation to be concentrated into a single receiver by a series of reflectors (mirrors) to maximize the amount of heat flux being used to make clean, renewable energy. Here's the Ivanpah Solar Power Facility pictured below (https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ivanpah Solar Power Facility). It is located in the Mojave desert by the border of California and Nevada, where irradiation from sunlight is high due to lack of cloud cover and interference from moisture in the air. In this problem, we'll study a simplified solar power plant model to understand how the properties of thermal radiation affect its ability to take in and use energy from the sun. Let's assume that the solar reflectors provide G₁ = 80,000 W/m² of solar heat flux to the receiver (white glowing cylinder at the top of the tower). (Keep in mind that solar irradiation onto the Earth's surface is typically around 1400W/m². The reflectors are what can increase this typical heat flux by "bouncing "/reflecting and concentrating this solar flux into the receiver. This is what makes this a much higher concentration of solar power than something like a solar panel would see from the sun alone. The downside is that the high magnitude of solar radiation power all being localized in this tower can be deadly for both people and wildlife if they get in the way of the concentrators - another reason to put these deep in the middle of the desert. This assignment will help us see just how much power that is!) For now, assume that the receiver at the top of the tower has a steady-state temperature of T, = 800 K. Not only is the receiver exposed to solar irradiation from the reflectors, but it also is exposed to surrounding air. Assume that the air is at an average temperature of T = 300 K with a convective heat transfer coefficient of 7 W/m² K due to natural convection (no wind). The outer surface of the receiver can be treated as diffuse and opaque. The spectral absorptivity of the coating at the surface of the receiver is given in the figure below: 0.9 az 0.2 2. (μm) 3 Assume that we'll be studying just the receiver at the top of the tower, which can be modeled as a very large cylinder with a diameter of 7m and a height of 12 m. Only the sides of the cylinder are exposed to the air/solar radiation, as the top/bottom have other equipment and mounting structure attached to them. This exposed surface area is represented as A,.
Principles of Heat Transfer (Activate Learning with these NEW titles from Engineering!)
8th Edition
ISBN:9781305387102
Author:Kreith, Frank; Manglik, Raj M.
Publisher:Kreith, Frank; Manglik, Raj M.
Chapter11: Heat Transfer By Radiation
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 11.15P
Related questions
Question
a)
b) Find the overall emissivity of the receiver's surface at its steady-state temperature.

Transcribed Image Text:What is true about the relationship between the emissivity and absorptivity of the receiver's
surface?
○ It can only be said that e(0, 0, X) = a(0, 0, X) since this is the only relationship that is always true.
The overall emissivity and absorptivity are equal to each other because the irradiation source is diffuse.
They are equal only spectrally, because the surface of the receiver is diffuse and the source of irradiation is
diffuse. BOTH of these MUST be true for the spectral emissivity and absorptivity to be equal to one another.
The overall emissivity and absorptivity are equal to each other because the receiver surface is diffuse.
O It can only be said that c(0, 0, X) = a(0, 0, X) since the surface of the receiver is diffuse but the source of
irradiation is not specifically stated to be a diffuse source.
They are equal only spectrally, because the surface of the receiver is diffuse and the source of irradiation is
diffuse. Only one of these needs to be true for the spectral emissivity and absorptivity to be equal to one
another.
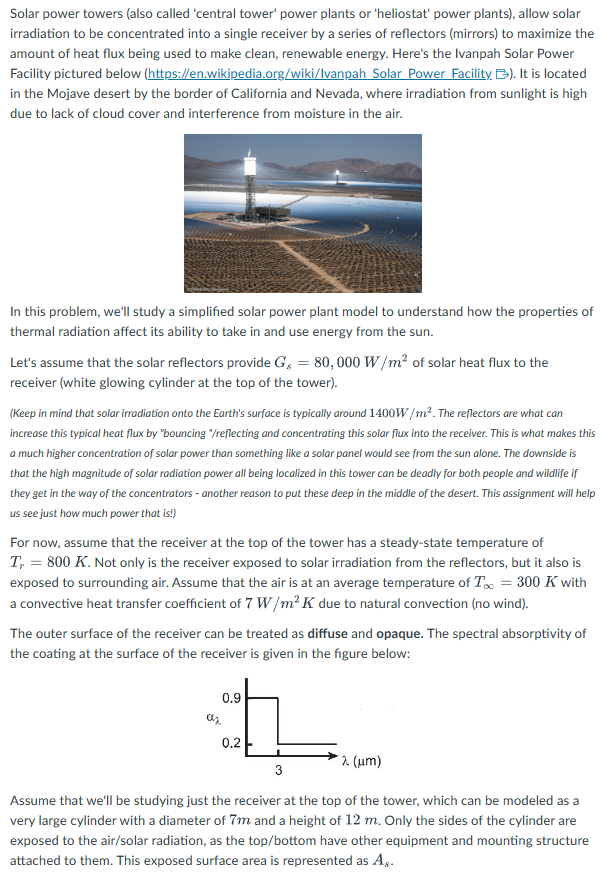
Transcribed Image Text:Solar power towers (also called 'central tower' power plants or 'heliostat' power plants), allow solar
irradiation to be concentrated into a single receiver by a series of reflectors (mirrors) to maximize the
amount of heat flux being used to make clean, renewable energy. Here's the Ivanpah Solar Power
Facility pictured below (https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ivanpah Solar Power Facility B). It is located
in the Mojave desert by the border of California and Nevada, where irradiation from sunlight is high
due to lack of cloud cover and interference from moisture in the air.
In this problem, we'll study a simplified solar power plant model to understand how the properties of
thermal radiation affect its ability to take in and use energy from the sun.
Let's assume that the solar reflectors provide G = 80,000 W/m² of solar heat flux to the
receiver (white glowing cylinder at the top of the tower).
(Keep in mind that solar irradiation onto the Earth's surface is typically around 1400W/m². The reflectors are what can
increase this typical heat flux by "bouncing "/reflecting and concentrating this solar flux into the receiver. This is what makes this
a much higher concentration of solar power than something like a solar panel would see from the sun alone. The downside is
that the high magnitude of solar radiation power all being localized in this tower can be deadly for both people and wildlife if
they get in the way of the concentrators - another reason to put these deep in the middle of the desert. This assignment will help
us see just how much power that is!)
For now, assume that the receiver at the top of the tower has a steady-state temperature of
T, = 800 K. Not only is the receiver exposed to solar irradiation from the reflectors, but it also is
exposed to surrounding air. Assume that the air is at an average temperature of T∞ = 300 K with
a convective heat transfer coefficient of 7 W/m² K due to natural convection (no wind).
The outer surface of the receiver can be treated as diffuse and opaque. The spectral absorptivity of
the coating at the surface of the receiver is given in the figure below:
0.9
az
0.2
λ (μm)
3
Assume that we'll be studying just the receiver at the top of the tower, which can be modeled as a
very large cylinder with a diameter of 7m and a height of 12 m. Only the sides of the cylinder are
exposed to the air/solar radiation, as the top/bottom have other equipment and mounting structure
attached to them. This exposed surface area is represented as A,.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Principles of Heat Transfer (Activate Learning wi…
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781305387102
Author:
Kreith, Frank; Manglik, Raj M.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Heat Transfer (Activate Learning wi…
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781305387102
Author:
Kreith, Frank; Manglik, Raj M.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning