SOLVE Use the conditions for equilibrium to determine the tensions in the two ropes. Part D Find the value of T, the magnitude of the tension in either of the ropes. Express your answer in newtons. • View Available Hint(s) ? T = N
SOLVE Use the conditions for equilibrium to determine the tensions in the two ropes. Part D Find the value of T, the magnitude of the tension in either of the ropes. Express your answer in newtons. • View Available Hint(s) ? T = N
College Physics
1st Edition
ISBN:9781938168000
Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger Hinrichs
Publisher:Paul Peter Urone, Roger Hinrichs
Chapter4: Dynamics: Force And Newton's Laws Of Motion
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 49PE: Integrated Concepts An elevator filled with passengers has a mass of 1700 kg. (a) The elevator...
Related questions
Topic Video
Question
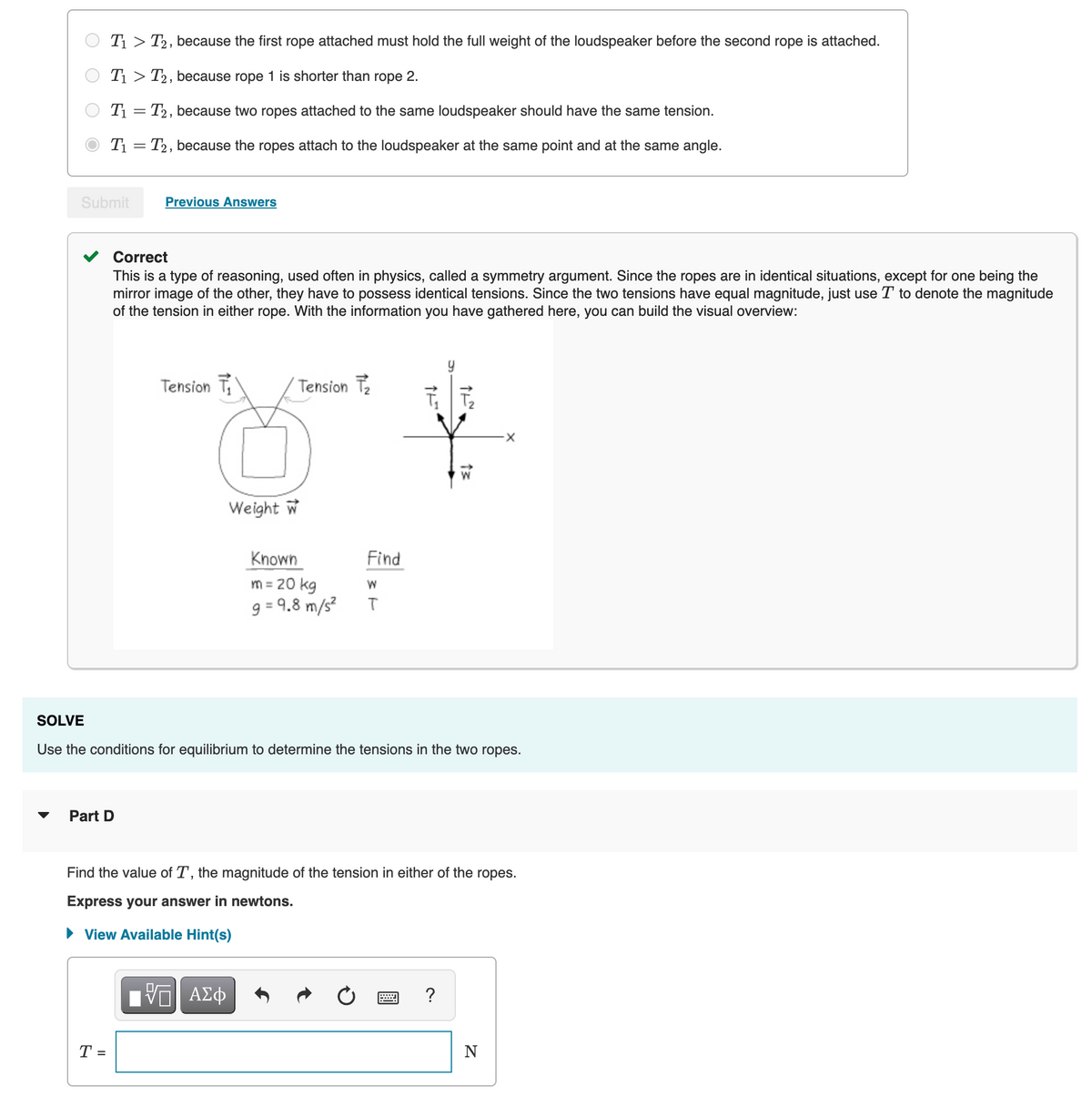
Transcribed Image Text:T1 > T2, because the first rope attached must hold the full weight of the loudspeaker before the second rope is attached.
T1 > T2, because rope 1 is shorter than rope 2.
T1 = T2, because two ropes attached to the same loudspeaker should have the same tension.
T1 = T2, because the ropes attach to the loudspeaker at the same point and at the same angle.
Submit
Previous Answers
Correct
This is a type of reasoning, used often in physics, called a symmetry argument. Since the ropes are in identical situations, except for one being the
mirror image of the other, they have to possess identical tensions. Since the two tensions have equal magnitude, just use T to denote the magnitude
of the tension in either rope. With the information you have gathered here, you can build the visual overview:
Tension T
Tension Te
W
Weight w
Known
Find
m = 20 kg
9 = 9,8 m/s?
SOLVE
Use the conditions for equilibrium to determine the tensions in the two ropes.
Part D
Find the value of T, the magnitude of the tension in either of the ropes.
Express your answer in newtons.
• View Available Hint(s)
T =
N
%D
O O
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:
9781938168000
Author:
Paul Peter Urone, Roger Hinrichs
Publisher:
OpenStax College

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:
9781337553278
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern …
Physics
ISBN:
9781337553292
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:
9781938168000
Author:
Paul Peter Urone, Roger Hinrichs
Publisher:
OpenStax College

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:
9781337553278
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern …
Physics
ISBN:
9781337553292
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:
9781305952300
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:
9781285737027
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology …
Physics
ISBN:
9781305116399
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning