Suppose student Ana is running for a charity and asks her friend to chip in the donation. Suppose each friend donates independently, and the donated value T is a random variable with the following probability density: c ti € [5, 10] dollars с t € [35, 40] dollars. otherwise 0 Let's assume Te's are mutually independent and each donation is a continuous random variable given they're using electronic transfer. Ana requested from 150 friends for the Lot bo looted from thooo 150 friendo You p(Ti = ts) : = in de
Suppose student Ana is running for a charity and asks her friend to chip in the donation. Suppose each friend donates independently, and the donated value T is a random variable with the following probability density: c ti € [5, 10] dollars с t € [35, 40] dollars. otherwise 0 Let's assume Te's are mutually independent and each donation is a continuous random variable given they're using electronic transfer. Ana requested from 150 friends for the Lot bo looted from thooo 150 friendo You p(Ti = ts) : = in de
Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
13th Edition
ISBN:9781133382119
Author:Swokowski
Publisher:Swokowski
Chapter10: Sequences, Series, And Probability
Section10.8: Probability
Problem 32E
Related questions
Question
Statistics CS
![Suppose student Ana is running for a charity and asks her friend to
chip in the donation. Suppose each friend donates independently, and the donated
value T is a random variable with the following probability density:
te [5, 10] dollars
C
t€ [35, 40] dollars.
0
otherwise
Let's assume It's are mutually independent and each donation is a continuous random
variable given they're using electronic transfer. Ana requested from 150 friends for the
donation. Let X be the total amount in dollar Ana collected from these 150 friends. You
need to simplify for this problem.
p(T} = t₁) :
=](/v2/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fcontent.bartleby.com%2Fqna-images%2Fquestion%2F1784d6b6-d0da-4ca6-88bb-f1a2aff3fb92%2F8df9b068-0755-4e4b-8cf2-b10f3cff564c%2Frwo9s_processed.png&w=3840&q=75)
Transcribed Image Text:Suppose student Ana is running for a charity and asks her friend to
chip in the donation. Suppose each friend donates independently, and the donated
value T is a random variable with the following probability density:
te [5, 10] dollars
C
t€ [35, 40] dollars.
0
otherwise
Let's assume It's are mutually independent and each donation is a continuous random
variable given they're using electronic transfer. Ana requested from 150 friends for the
donation. Let X be the total amount in dollar Ana collected from these 150 friends. You
need to simplify for this problem.
p(T} = t₁) :
=
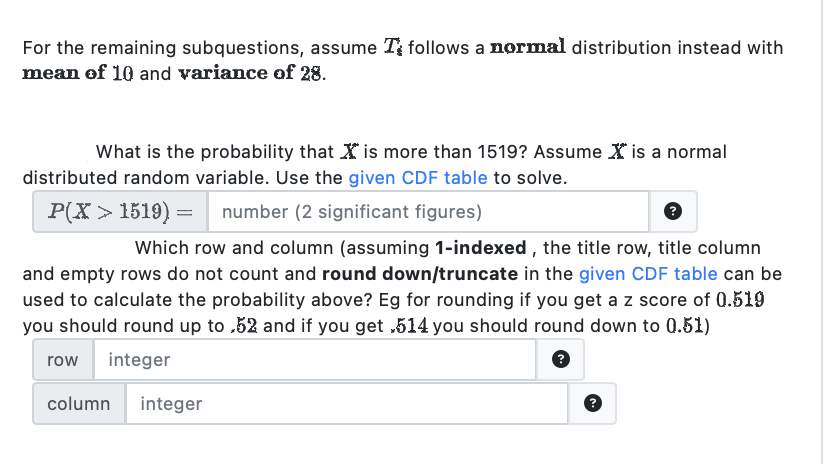
Transcribed Image Text:For the remaining subquestions, assume T follows a normal distribution instead with
mean of 10 and variance of 28.
What is the probability that is more than 1519? Assume is a normal
distributed random variable. Use the given CDF table to solve.
P(X> 1519) =
number (2 significant figures)
?
Which row and column (assuming 1-indexed, the title row, title column
and empty rows do not count and round down/truncate in the given CDF table can be
used to calculate the probability above? Eg for rounding if you get a z score of 0.519
you should round up to.52 and if you get ,514 you should round down to 0.51)
row integer
?
column
integer
?
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 4 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage