Suppose that x,, X, ..., X and Y,, Y,, ..., Y, are independent random samples, with the variables x, normally distributed with mean u, and variance o,? and the variables Y, normally distributed with mean , and variance o,. The difference between the sample means, X - Y, is then a linear combination of m +n normally distributed random variables and, by this theorem, is itself normally distributed. (a) Find EX - (b) Find VX - ). (c) Suppose that o,? = 3, , = 6.5, and m = n. Find the minimum sample sizes so that (X -Y) will be within 1 unit of (4, - 42) with probability 0.95. (Round your answer up to the nearest integer.) m=n= You may need to use the appropriate appendix table technology to answer this question.
Suppose that x,, X, ..., X and Y,, Y,, ..., Y, are independent random samples, with the variables x, normally distributed with mean u, and variance o,? and the variables Y, normally distributed with mean , and variance o,. The difference between the sample means, X - Y, is then a linear combination of m +n normally distributed random variables and, by this theorem, is itself normally distributed. (a) Find EX - (b) Find VX - ). (c) Suppose that o,? = 3, , = 6.5, and m = n. Find the minimum sample sizes so that (X -Y) will be within 1 unit of (4, - 42) with probability 0.95. (Round your answer up to the nearest integer.) m=n= You may need to use the appropriate appendix table technology to answer this question.
Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
13th Edition
ISBN:9781133382119
Author:Swokowski
Publisher:Swokowski
Chapter10: Sequences, Series, And Probability
Section10.8: Probability
Problem 32E
Related questions
Question
Do asap and explain with proper steps
Answer should be correct
Thanks
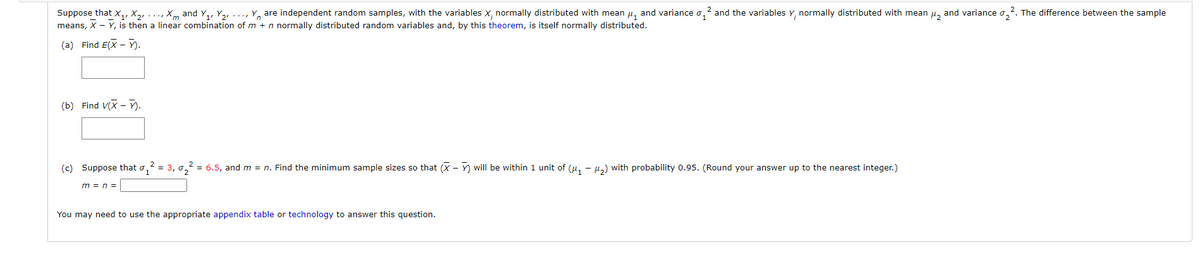
Transcribed Image Text:Suppose that x,, X2, ..., Xm and Y,, Y2, ..., Y, are independent random samples, with the variables X, normally distributed with mean µ, and variance o,
means, X - Y, is then a linear combination of m + n normally distributed random variables and, by this theorem, is itself normally distributed.
and the variables Y, normally distributed with mean u, and variance o,2.
The difference between the sample
(a) Find E(X - ).
(b) Find V(X - ).
(c) Suppose that o, = 3, o, = 6.5, and m = n. Find the minimum sample sizes so that (X - Y) will be within 1 unit of (u, - µ,) with probability 0.95. (Round your answer up to the nearest integer.)
m = n =
You may need to use the appropriate appendix table or technology to answer this question.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Recommended textbooks for you

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage