Suppose (X, d) is a metric space and let r> 0. Show that p: X2 → [0, c0) defined by p(x, y) = r· d(x, y) is a metric on X.
Suppose (X, d) is a metric space and let r> 0. Show that p: X2 → [0, c0) defined by p(x, y) = r· d(x, y) is a metric on X.
Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
13th Edition
ISBN:9781133382119
Author:Swokowski
Publisher:Swokowski
Chapter8: Applications Of Trigonometry
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 17RE
Related questions
Question
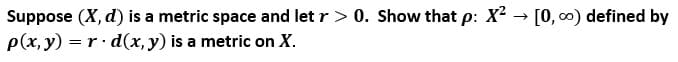
Transcribed Image Text:Suppose (X, d) is a metric space and let r> 0. Show that p: X2 → [0, 0) defined by
p(x, y) = r· d(x, y) is a metric on X.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, advanced-math and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage

Elements Of Modern Algebra
Algebra
ISBN:
9781285463230
Author:
Gilbert, Linda, Jimmie
Publisher:
Cengage Learning,

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage

Elements Of Modern Algebra
Algebra
ISBN:
9781285463230
Author:
Gilbert, Linda, Jimmie
Publisher:
Cengage Learning,