Table 11.3 Thermocouple Voltage (in millivolts) versus Temperature (in °C) for an Iron-Constantan Thermocouple 0 1 2 4 5 6 7 8 9 3 °C Millivolts 0.00 0.05 0.10 0.15 0.20 0.25 0.30 0.35 0.40 0.45 10 0.50 0.56 0.61 0.66 0.71 0.76 0.81 0.86 0.91 0.97 20 1.02 1.07 1.12 1.17 1.22 1.28 1.33 1.38 1.43 1.48 30 1.54 1.59 1.64 1.69 1.74 1.80 1.85 1.90 1.95 2.00 40 2.06 2.11 2.16 2.22 2.27 2.32 2.37 2.42 2.48 2.53 50 2.58 2.64 2.69 2.74 2.80 2.85 2.90 2.96 3.01 3.06 60 3.11 3.17 3.22 3.27 3.33 3.38 3.43 3.49 3.54 3.60 70 3.65 3.70 3.76 3.81 3.86 3.92 3.97 4.02 4.08 4.13 80 4.19 4.24 4.29 4.35 4.40 4.46 4.51 4.56 4.62 4.67 90 4.73 4.78 4.83 4.89 4.94 5.00 5.05 5.11 5.16 5.21 100 5.27 5.32 5.38 5.43 5.48 5.54 5.59 5.65 5.70 5.76 From CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics, 55th ed., Cleveland: CRC Press (1974), р. Е-109.
Table 11.3 Thermocouple Voltage (in millivolts) versus Temperature (in °C) for an Iron-Constantan Thermocouple 0 1 2 4 5 6 7 8 9 3 °C Millivolts 0.00 0.05 0.10 0.15 0.20 0.25 0.30 0.35 0.40 0.45 10 0.50 0.56 0.61 0.66 0.71 0.76 0.81 0.86 0.91 0.97 20 1.02 1.07 1.12 1.17 1.22 1.28 1.33 1.38 1.43 1.48 30 1.54 1.59 1.64 1.69 1.74 1.80 1.85 1.90 1.95 2.00 40 2.06 2.11 2.16 2.22 2.27 2.32 2.37 2.42 2.48 2.53 50 2.58 2.64 2.69 2.74 2.80 2.85 2.90 2.96 3.01 3.06 60 3.11 3.17 3.22 3.27 3.33 3.38 3.43 3.49 3.54 3.60 70 3.65 3.70 3.76 3.81 3.86 3.92 3.97 4.02 4.08 4.13 80 4.19 4.24 4.29 4.35 4.40 4.46 4.51 4.56 4.62 4.67 90 4.73 4.78 4.83 4.89 4.94 5.00 5.05 5.11 5.16 5.21 100 5.27 5.32 5.38 5.43 5.48 5.54 5.59 5.65 5.70 5.76 From CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics, 55th ed., Cleveland: CRC Press (1974), р. Е-109.
Related questions
Question
Assuming that the potential corresponding to any temperature T in Table could be known (say, through a computer model) to at least fi ve signifi cant digits, what maximum uncertainty would be allowed in your voltmeter if you were to use an iron-constantan thermocouple to measure temperatures to within 0.01°C?
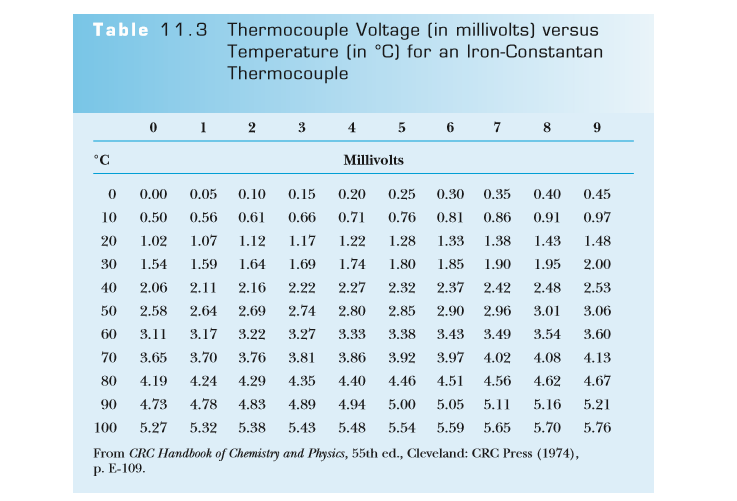
Transcribed Image Text:Table 11.3
Thermocouple Voltage (in millivolts) versus
Temperature (in °C) for an Iron-Constantan
Thermocouple
0 1
2
4 5 6 7 8 9
3
°C
Millivolts
0.00
0.05
0.10
0.15
0.20
0.25
0.30
0.35
0.40
0.45
10
0.50
0.56
0.61
0.66
0.71
0.76
0.81
0.86
0.91
0.97
20
1.02
1.07
1.12
1.17
1.22
1.28
1.33
1.38
1.43
1.48
30
1.54
1.59
1.64
1.69
1.74
1.80
1.85
1.90
1.95
2.00
40
2.06
2.11
2.16
2.22
2.27
2.32
2.37
2.42
2.48
2.53
50
2.58
2.64
2.69
2.74
2.80
2.85
2.90
2.96
3.01
3.06
60
3.11
3.17
3.22
3.27
3.33
3.38
3.43
3.49
3.54
3.60
70
3.65
3.70
3.76
3.81
3.86
3.92
3.97
4.02
4.08
4.13
80
4.19
4.24
4.29
4.35
4.40
4.46
4.51
4.56
4.62
4.67
90
4.73
4.78
4.83
4.89
4.94
5.00
5.05
5.11
5.16
5.21
100
5.27
5.32
5.38
5.43
5.48
5.54
5.59
5.65
5.70
5.76
From CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics, 55th ed., Cleveland: CRC Press (1974),
р. Е-109.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 4 images
