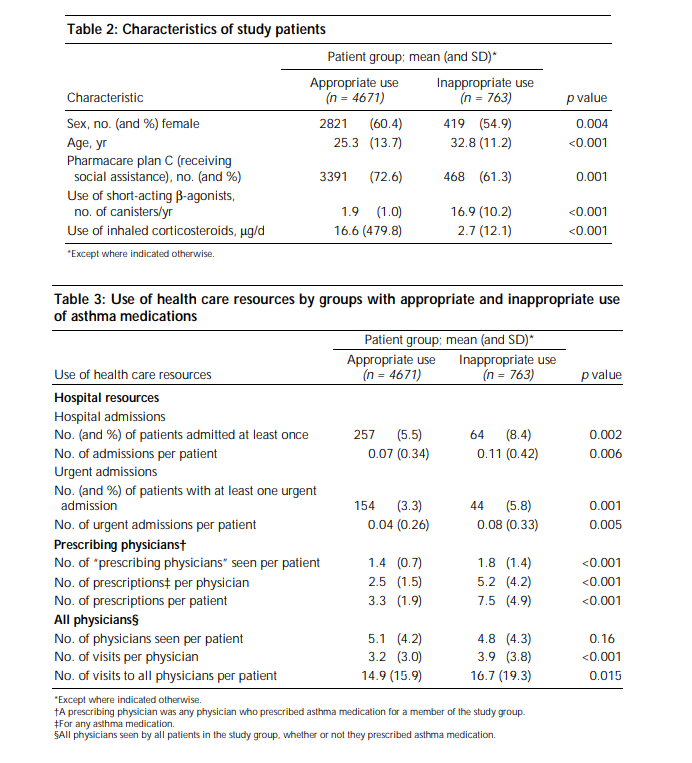
Table 2: Characteristics of study patients Patient group; mean (and SD)* Appropriate use (n = 4671) Inappropriate use (n = 763) p value Characteristic Sex, no. (and %) female 2821 (60.4) 419 (54.9) 0.004 25.3 (13.7) 32.8 (11.2) Age, yr Pharmacare plan C (receiving social assistance), no. (and %) <0.001 3391 (72.6) 468 (61.3) 0.001
Please explain the Data in the graphs
Standard Deviation in Population --The standard deviation is a statistics which measure the dispersion of a dataset relative to mean and is calculated as the square root of the variance .
The standard deviation is calculated as the square root of variance by determining each data points deviation relative to mean .
If data points are farther from the mean there is a higher deviation with in the data set , thus the more spread out the data ,the higher the standard deviation.
Calculation of Standard Deviation --Standard Deviation is calculated as ---
1- The mean value is calculated by adding all the data points and dividing them by number of data points .
2 - The variance for each data point is calculated by subtracting the mean from the value of the data point .
Each of the values is then squared and the results summed .
The result is then divided by the number of data points less one .
3 - The square root of the variance - result from no.2 - is then used to find the standard deviation .
Importance of the Standard Deviation --
High Standard Deviation Mean -- A large standard deviation indicates that there is a lot of variance in the observed data around the mean .
This indicates that the data observed is quite spread out .
Small Standard Deviation Mean -- A small or low standard deviation indicates instead that much of the data observed is clustered tightly around the mean .
Standard Error --The standard error is a standard deviation of its sampling distribution or an estimate of that standard deviation .
Standard error explains how accurate the mean of any given sample from that population is likely to be compared to the true population mean .
When standard error increases i.e. it becomes more likely that any given mean is an inaccurate representation of the true population mean .
Hypothesis-- Generation of hypothesis is the beginning of a scientific process ,refers to a supposition based on reasoning and evidence .
Hypothesis is tested on the basis of observations and experiments which then provide facts and forecast possible out comes .
Types of Hypothesis -Hypothesis can be inductive or deductive , simple or complex , null or alternative .
1 - Null Hypothesis -- Null hypothesis is the hypothesis which is to be actually tested .There is no significant difference between the heights of the sample compared with the rational average .
It denote certain value of population parameters. Null hypothesis can be rejected but it can not be accepted just on the basis of a single test , a hypothesis in which there is no significant difference exists between the set of variables .
It is the original or default statement with no effect .
Represented by H0 ( H - 0 )
It is always hypothesis that is tested .
It denotes certain value of population parameter
2 - Alternative Hypothesis -- There is a significant difference between the heights of the sample , compared with the national average .
It is often referred to as the hypothesis other than the null hypothesis often denoted by
H1 ( H - one ) .
Researcher seeks to prove in an indirect way , by using the test , refers to a certain value of sample statistic .
The acceptance of alternative hypothesis depends on the rejection of null hypothesis means until and unless null hypothesis is rejected an alternative hypothesis can not be accepted .
On Tailed and Two Tailed Hypothesis Test ---
One Tailed Test of Hypothesis -- A one tailed test has the entire 5% of the alpha level in one tail , either in left tail or right tail .
Two Tailed Test of Hypothesis -- A two tailed test splits the alpha level in half.
Indication of Use of One Tailed or Two Tailed Testing of Hypothesis -- In medical testing , one is generally interested in whether a treatment results in out comes which are better than chance ,thus a one tailed test should be performed .A worse outcome is also interesting for the scientific field , there fore one should use a two tailed test which corresponds instead to testing .
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps






