TABLE 5.1 Properties of the common amino acids found in proteins Name Alanine A, Ala Arginine R, Arg Asparagine N, Asn Abbreviations 1- and 3-letter codes Aspartic acid D, Asp C, Cys Q, Gln E, Glu Cysteine Glutamine Glutamic acid Glycine Histidine Isoleucine Leucine Lysine Proline Serine Threonine Tryptophan Tyrosine Valine G, Gly H, His I, Ile Methionine M, Met Phenylalanine F, Phe P, Pro S, Ser T, Thr W, Trp Y, Tyr V, Val L, Leu K, Lys Occurance in Proteins ( mol %) Residue Mass (daltons) 71.08 8.7 156.20 5.0 114.11 4.2 115.09 5.9 1.3 103.14 128.14 3.7 129.12 6.6 57.06 137.15 113.17 113.17 7.9 2.4 5.5 8.9 128.18 5.5 131.21 2.0 147.18 4.0 97.12 4.7 87.08 5.8 101.11 5.6 186.21 1.5 163.18 3.5 99.14 7.2 "To obtain the mass of the mass amino acids itself, add the mass of a molecule of water, 18.02 daltons. The values given are for neutral side chains; slightly different values will apply at pH values where protons have been gained or lost from the side chains. Average for a large number of proteins. Individual proteins can show large deviations from these values. Data from J. ▾ Part A Using the data in table 5.1, calculate the average amino acid residue weight in a protein of typical composition. This is a useful number to know for approximate calculations. Express your answer using one decimal place. IVE ΑΣΦ Submit Provide Feedback → Request Answer www. ? Next >
TABLE 5.1 Properties of the common amino acids found in proteins Name Alanine A, Ala Arginine R, Arg Asparagine N, Asn Abbreviations 1- and 3-letter codes Aspartic acid D, Asp C, Cys Q, Gln E, Glu Cysteine Glutamine Glutamic acid Glycine Histidine Isoleucine Leucine Lysine Proline Serine Threonine Tryptophan Tyrosine Valine G, Gly H, His I, Ile Methionine M, Met Phenylalanine F, Phe P, Pro S, Ser T, Thr W, Trp Y, Tyr V, Val L, Leu K, Lys Occurance in Proteins ( mol %) Residue Mass (daltons) 71.08 8.7 156.20 5.0 114.11 4.2 115.09 5.9 1.3 103.14 128.14 3.7 129.12 6.6 57.06 137.15 113.17 113.17 7.9 2.4 5.5 8.9 128.18 5.5 131.21 2.0 147.18 4.0 97.12 4.7 87.08 5.8 101.11 5.6 186.21 1.5 163.18 3.5 99.14 7.2 "To obtain the mass of the mass amino acids itself, add the mass of a molecule of water, 18.02 daltons. The values given are for neutral side chains; slightly different values will apply at pH values where protons have been gained or lost from the side chains. Average for a large number of proteins. Individual proteins can show large deviations from these values. Data from J. ▾ Part A Using the data in table 5.1, calculate the average amino acid residue weight in a protein of typical composition. This is a useful number to know for approximate calculations. Express your answer using one decimal place. IVE ΑΣΦ Submit Provide Feedback → Request Answer www. ? Next >
Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Course List)
11th Edition
ISBN:9781305251052
Author:Michael Cummings
Publisher:Michael Cummings
Chapter10: From Proteins To Phenotypes
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 14QP: If phenylalanine was not an essential amino acid, would diet therapy (the elimination of...
Related questions
Question
52.7
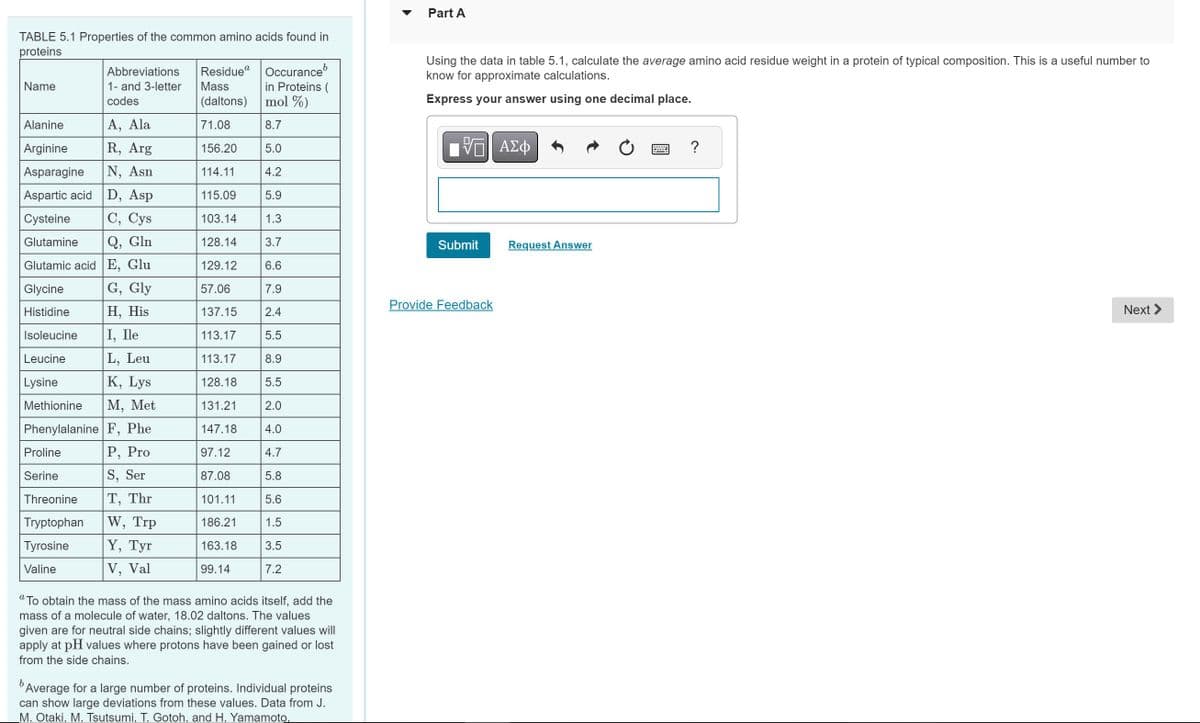
Transcribed Image Text:TABLE 5.1 Properties of the common amino acids found in
proteins
Name
Alanine
Arginine
Asparagine
Aspartic acid
Cysteine
Glutamine
Glutamic acid
Glycine
Histidine
Isoleucine
Leucine
Lysine
Methionine
Phenylalanine
Proline
Serine
Threonine
Tryptophan
Tyrosine
Valine
Abbreviations
1- and 3-letter
codes
A, Ala
R, Arg
N, Asn
D, Asp
C, Cys
Q, Gln
E, Glu
G, Gly
H, His
I, Ile
L, Leu
K, Lys
M, Met
F, Phe
P, Pro
S, Ser
T, Thr
W, Trp
Y, Tyr
V, Val
Residue Occurance
Mass
in Proteins (
mol %)
(daltons)
71.08
156.20
8.7
5.0
114.11
4.2
5.9
115.09
103.14
1.3
3.7
128.14
6.6
129.12
57.06
137.15
7.9
2.4
5.5
113.17
113.17
8.9
128.18
5.5
131.21
2.0
147.18
4.0
97.12
4.7
87.08
5.8
101.11
5.6
186.21
1.5
163.18
3.5
99.14
7.2
a
"To obtain the mass of the mass amino acids itself, add the
mass of a molecule of water, 18.02 daltons. The values
given are for neutral side chains; slightly different values will
apply at pH values where protons have been gained or lost
from the side chains.
b
Average for a large number of proteins. Individual proteins
can show large deviations from these values. Data from J.
M. Otaki, M. Tsutsumi, T. Gotoh, and H. Yamamoto.
Part A
Using the data in table 5.1, calculate the average amino acid residue weight in a protein of typical composition. This is a useful number to
know for approximate calculations.
Express your answer using one decimal place.
——| ΑΣΦ
Submit
Provide Feedback
Request Answer
?
Next >
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps

Recommended textbooks for you

Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co…
Biology
ISBN:
9781305251052
Author:
Michael Cummings
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co…
Biology
ISBN:
9781305251052
Author:
Michael Cummings
Publisher:
Cengage Learning