The buying and selling commission schedule shown in the table is from an online discount brokerage firm. Taking into consideration the buying and selling commissions in this schedule, find the annual compound rate of interest earned on the investment. Transaction Size Commission Rate $0 - $1,500 $1,501 - $6,000 $29 + 2.5% of principal $57 + 0.6% of principal $6,001 - $22,000 $75 + 0.30% of principal $97 +0.20% of principal $147 +0.10% of principal $247 + 0.08% of principal An investor purchases 125 shares of stock at $50 per share, holds the stock for 5 years, and then sells the stock for $22,001 - $50,000 $50,001 - $500,000 $500,001 + $115 a share. क O A. I-Prt, where I is the interest, Pis the principal, r is the annual simple interest rate, and t is the time in years OB. A-P(1+ rt), where A is the amount, Pis the principal, r is the annual simple interest rate, and tis the time in years O C. A-Pe" where A is the amount at the end of t years if P is the principal invested at an annual rate r compounded continuously OD. A P(1+)", where i- nominal rate, m is number of compounding periods per year, i is rate per compounding period, and n is total number of compounding periods and A is the amount at the end of n periods, P is the principal value, r is the annual The annual rate of interest is%.
The buying and selling commission schedule shown in the table is from an online discount brokerage firm. Taking into consideration the buying and selling commissions in this schedule, find the annual compound rate of interest earned on the investment. Transaction Size Commission Rate $0 - $1,500 $1,501 - $6,000 $29 + 2.5% of principal $57 + 0.6% of principal $6,001 - $22,000 $75 + 0.30% of principal $97 +0.20% of principal $147 +0.10% of principal $247 + 0.08% of principal An investor purchases 125 shares of stock at $50 per share, holds the stock for 5 years, and then sells the stock for $22,001 - $50,000 $50,001 - $500,000 $500,001 + $115 a share. क O A. I-Prt, where I is the interest, Pis the principal, r is the annual simple interest rate, and t is the time in years OB. A-P(1+ rt), where A is the amount, Pis the principal, r is the annual simple interest rate, and tis the time in years O C. A-Pe" where A is the amount at the end of t years if P is the principal invested at an annual rate r compounded continuously OD. A P(1+)", where i- nominal rate, m is number of compounding periods per year, i is rate per compounding period, and n is total number of compounding periods and A is the amount at the end of n periods, P is the principal value, r is the annual The annual rate of interest is%.
Financial Accounting: The Impact on Decision Makers
10th Edition
ISBN:9781305654174
Author:Gary A. Porter, Curtis L. Norton
Publisher:Gary A. Porter, Curtis L. Norton
Chapter9: Current Liabilities, Contingencies, And The Time Value Of Money
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 9.6E
Related questions
Question
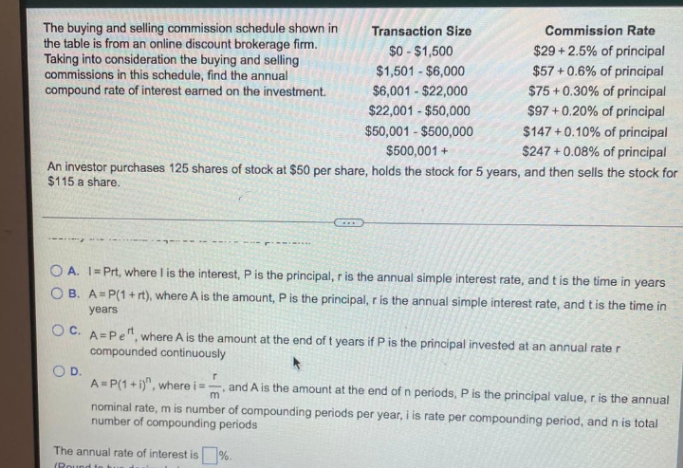
Transcribed Image Text:The buying and selling commission schedule shown in
the table is from an online discount brokerage firm.
Taking into consideration the buying and selling
commissions in this schedule, find the annual
compound rate of interest earned on the investment.
Transaction Size
Commission Rate
$0 - $1,500
$29 +2.5% of principal
$57 + 0.6% of principal
$1,501 - $6,000
$6,001 - $22,000
$75 + 0.30% of principal
$97 + 0.20% of principal
$147 +0.10% of principal
$247 + 0.08% of principal
An investor purchases 125 shares of stock at $50 per share, holds the stock for 5 years, and then sells the stock for
$22,001 - $50,000
$50,001 - $500,000
$500,001 +
$115 a share.
O A. I= Prt, where I is the interest, P is the principal, r is the annual simple interest rate, and t is the time in years
O B. A=P(1+ rt), where A is the amount, P is the principal, r is the annual simple interest rate, and t is the time in
years
OC. A=Pe", where A is the amount at the end of t years if P is the principal invested at an annual rate r
compounded continuously
OD.
A= P(1 + i)", where is
-, and A is the amount at the end of n periods, P is the principal value, r is the annual
nominal rate, m is number of compounding periods per year, i is rate per compounding period, and n is total
number of compounding periods
The annual rate of interest is %.
(Round
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps

Recommended textbooks for you

Financial Accounting: The Impact on Decision Make…
Accounting
ISBN:
9781305654174
Author:
Gary A. Porter, Curtis L. Norton
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Accounting Volume 1
Accounting
ISBN:
9781947172685
Author:
OpenStax
Publisher:
OpenStax College

Cornerstones of Financial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:
9781337690881
Author:
Jay Rich, Jeff Jones
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Financial Accounting: The Impact on Decision Make…
Accounting
ISBN:
9781305654174
Author:
Gary A. Porter, Curtis L. Norton
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Accounting Volume 1
Accounting
ISBN:
9781947172685
Author:
OpenStax
Publisher:
OpenStax College

Cornerstones of Financial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:
9781337690881
Author:
Jay Rich, Jeff Jones
Publisher:
Cengage Learning