The driver of an SUV (m= 1800 kg) moving at a velocity of 3.50 m/s isn't paying attention and rear ends a car (m = 1200 kg) that is at rest as it waits for the red light to turn green. On impact, both drivers lock their brakes. The SUV and car stick together and travel beyond the line. What is the velocity of the cars after the collision?
The driver of an SUV (m= 1800 kg) moving at a velocity of 3.50 m/s isn't paying attention and rear ends a car (m = 1200 kg) that is at rest as it waits for the red light to turn green. On impact, both drivers lock their brakes. The SUV and car stick together and travel beyond the line. What is the velocity of the cars after the collision?
Chapter10: Atomic Physics
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 19Q
Related questions
Question
please see the attached photos, thank you!
Transcribed Image Text:WPS Office
PETA4 Conserv.n of Momentum Q X
+
O Franci.
O Go Premium
Menu v
Page Layout
References
Q Click to find commands
Home
Insert
Review
View
Section
Tools
E E A. AL - D
A* A Q I -
BI U- A- X² X2 A- ak - A- A
X Cut
AaBbCcDd AaBb AaBbC AaBbC AaBbCcl
Times New Roman
11
L Copy Format
Painter
Paste
Normal
Heading 1 Heading 2 Heading 3 Heading 4
New Style
Text Tools"
Find and Select
Replace
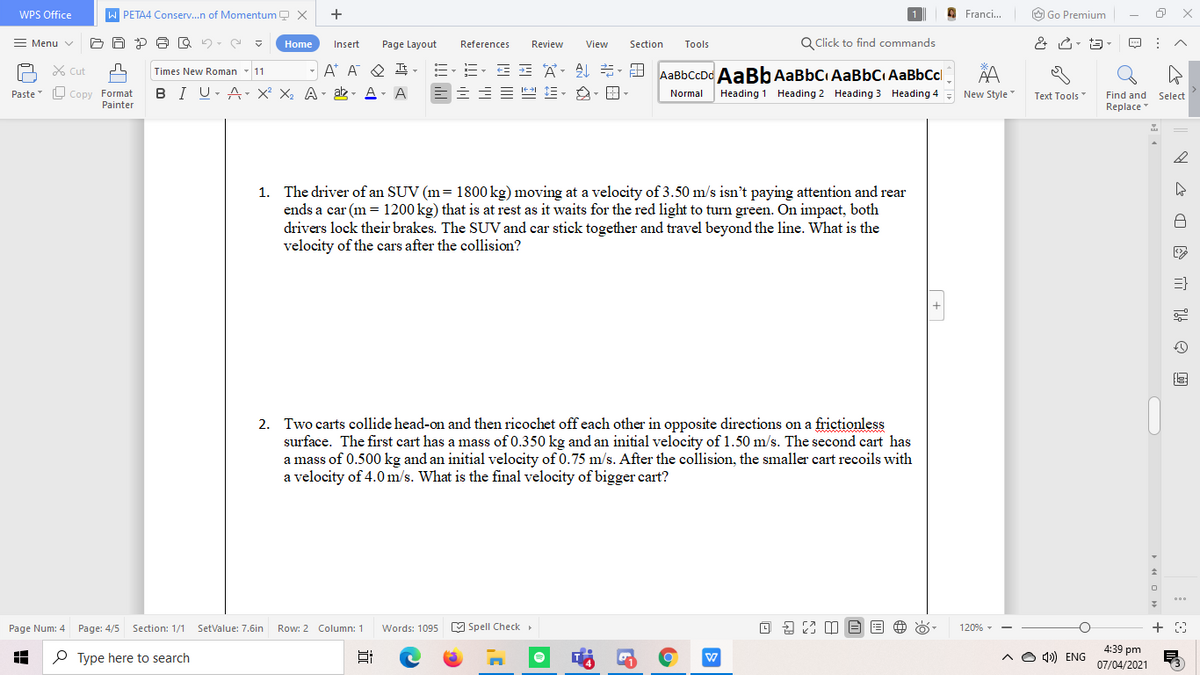
1. The driver of an SUV (m= 1800 kg) moving at a velocity of 3.50 m/s isn't paying attention and rear
ends a car (m = 1200 kg) that is at rest as it waits for the red light to turn green. On impact, both
drivers lock their brakes. The SUV and car stick together and travel beyond the line. What is the
velocity of the cars after the collision?
2. Two carts collide head-on and then ricochet off each other in opposite directions on a frictionless
surface. The first cart has a mass of 0.350 kg and an initial velocity of 1.50 m/s. The second cart has
a mass of 0.500 kg and an initial velocity of 0.75 m/s. After the collision, the smaller cart recoils with
a velocity of 4.0 m/s. What is the final velocity of bigger cart?
Page Num: 4 Page: 4/5 Section: 1/1 SetvValue: 7.6in
Words: 1095
M Spell Check
120%
Row: 2 Column: 1
4:39 pm
P Type here to search
A O 4) ENG
07/04/2021
Transcribed Image Text:WPS Office
PETA4 Conserv.n of Momentum Q X
+
O Franci.
O Go Premium
Menu v
Table Tools
Table Style
Q Click to find commands
Home
Insert
Page Layout
References
Review
View
Section
Tools
X Cut
A* A O E,
AaBbCcDd AaBb AaBbC AaBbC AaBbCcl
Times New Roman
12
L Copy Format
Painter
B I U- A X² X2 A- ab - A- A
Normal
Heading 1 Heading 2 Heading 3 Heading 4
New Style
Find and Select
Replace
Paste
Text Tools"
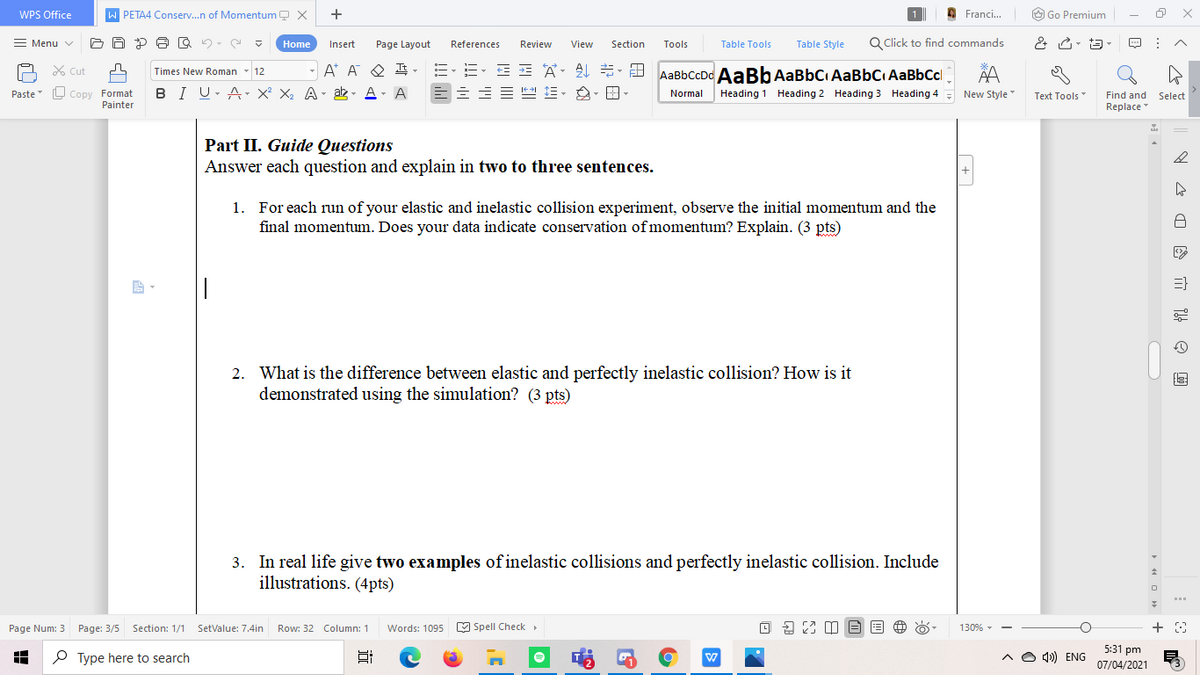
Part II. Guide Questions
Answer each question and explain in two to three sentences.
1. For each run of your elastic and inelastic collision experiment, observe the initial momentum and the
final momentum. Does your data indicate conservation of momentum? Explain. (3 pts)
2. What is the difference between elastic and perfectly inelastic collision? How is it
demonstrated using the simulation? (3 pts)
3. In real life give two examples of inelastic collisions and perfectly inelastic collision. Include
illustrations. (4pts)
Page Num: 3 Page: 3/5 Section: 1/1
SetValue: 7.4in
Row: 32 Column: 1
Words: 1095
M Spell Check
130% -
5:31 pm
P Type here to search
A O 4) ENG
07/04/2021
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you


Foundations of Astronomy (MindTap Course List)
Physics
ISBN:
9781337399920
Author:
Michael A. Seeds, Dana Backman
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Foundations of Astronomy (MindTap Course List)
Physics
ISBN:
9781337399920
Author:
Michael A. Seeds, Dana Backman
Publisher:
Cengage Learning