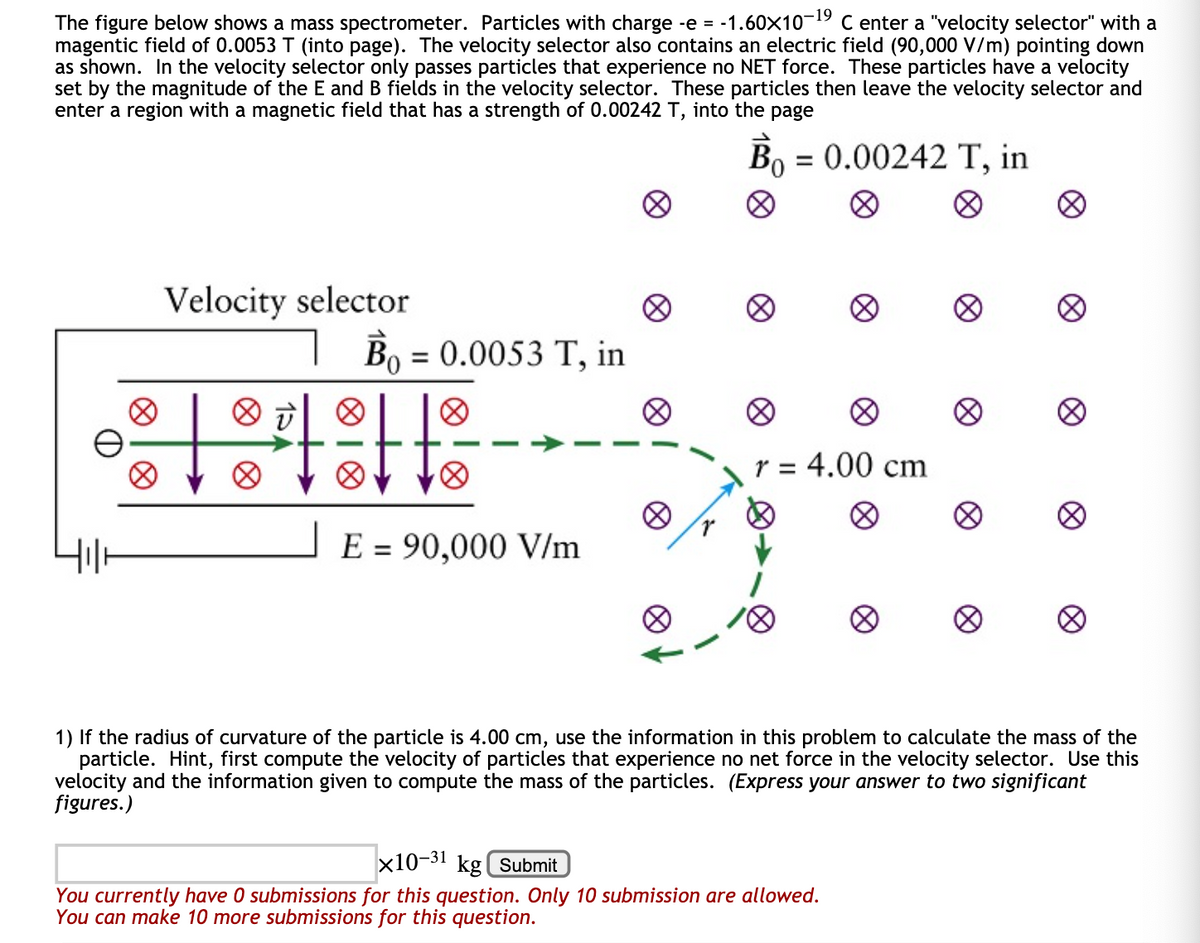
The figure below shows a mass spectrometer. Particles with charge -e = -1.60×10¬19 C enter a "velocity selector" with a magentic field of 0.0053 T (into page). The velocity selector also contains an electric field (90,000 V/m) pointing down as shown. In the velocity selector only passes particles that experience no NET force. These particles have a velocity set by the magnitude of the E and B fields in the velocity selector. These particles then leave the velocity selector and enter a region with a magnetic field that has a strength of 0.00242 T, into the page Bo = 0.00242 T, in %3D Velocity selector Bo = 0.0053 T, in - r = 4.00 cm E = 90,000 V/m 1) If the radius of curvature of the particle is 4.00 cm, use the information in this problem to calculate the mass of the particle. Hint, first compute the velocity of particles that experience no net force in the velocity selector. Use this velocity and the information given to compute the mass of the particles. (Express your answer to two significant figures.) x10-31 kg( Submit
The figure below shows a mass spectrometer. Particles with charge -e = -1.60×10^−19 C enter a "velocity selector" with a magentic field of 0.0053 T (into page). The velocity selector also contains an electric field (90,000 V/m) pointing down as shown. In the velocity selector only passes particles that experience no NET force. These particles have a velocity set by the magnitude of the E and B fields in the velocity selector. These particles then leave the velocity selector and enter a region with a magnetic field that has a strength of 0.00242 T, into the page
1)If the radius of curvature of the particle is 4.00 cm, use the information in this problem to calculate the mass of the particle. Hint, first compute the velocity of particles that experience no net force in the velocity selector. Use this velocity and the information given to compute the mass of the particles. (Express your answer to two significant figures.)
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images









