The figure below shows the equipotential surfaces of a parallel plate capacitor. If a positive charge, q = +2 C, is moved between two equipotential surfaces (green surfaces: A and B) of a parallel plate capacitor as shown in the figure below, what is the work done by electric force when the charge q is moved from surface A to B? [Hint: Use the relation between work and potential difference.] 2 cm A. + 6J В. + 1.5J C. OJ D. - 6J Е. - 1.5 J B OV | 6V 3V
The figure below shows the equipotential surfaces of a parallel plate capacitor. If a positive charge, q = +2 C, is moved between two equipotential surfaces (green surfaces: A and B) of a parallel plate capacitor as shown in the figure below, what is the work done by electric force when the charge q is moved from surface A to B? [Hint: Use the relation between work and potential difference.] 2 cm A. + 6J В. + 1.5J C. OJ D. - 6J Е. - 1.5 J B OV | 6V 3V
Chapter8: Capacitance
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 61P: The dielectric to be used in a parallel-plate capacitor has a dielectric constant of 3.60 and a...
Related questions
Concept explainers
Dielectric Constant Of Water
Water constitutes about 70% of earth. Some important distinguishing properties of water are high molar concentration, small dissociation constant and high dielectric constant.
Electrostatic Potential and Capacitance
An electrostatic force is a force caused by stationary electric charges /fields. The electrostatic force is caused by the transfer of electrons in conducting materials. Coulomb’s law determines the amount of force between two stationary, charged particles. The electric force is the force which acts between two stationary charges. It is also called Coulomb force.
Question
![The figure below shows the equipotential surfaces of a parallel
plate capacitor. If a positive charge, q = +2 C, is moved between
two equipotential surfaces (green surfaces: A and B) of a parallel
plate capacitor as shown in the figure below, what is the work
done by electric force when the charge q is moved from surface
A to B? [Hint: Use the relation between work and potential
difference.]
2 cm
A. + 6J
B. + 1.5 J
A
B
C. OJ
D. - 6J
OV
Е.
- 1.5 J](/v2/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fcontent.bartleby.com%2Fqna-images%2Fquestion%2F0354e96c-19e1-48ec-9f97-15735d424a19%2Fef88e3b6-d0e0-4e2b-b447-392aed5817b5%2Fvkty2la_processed.png&w=3840&q=75)
Transcribed Image Text:The figure below shows the equipotential surfaces of a parallel
plate capacitor. If a positive charge, q = +2 C, is moved between
two equipotential surfaces (green surfaces: A and B) of a parallel
plate capacitor as shown in the figure below, what is the work
done by electric force when the charge q is moved from surface
A to B? [Hint: Use the relation between work and potential
difference.]
2 cm
A. + 6J
B. + 1.5 J
A
B
C. OJ
D. - 6J
OV
Е.
- 1.5 J
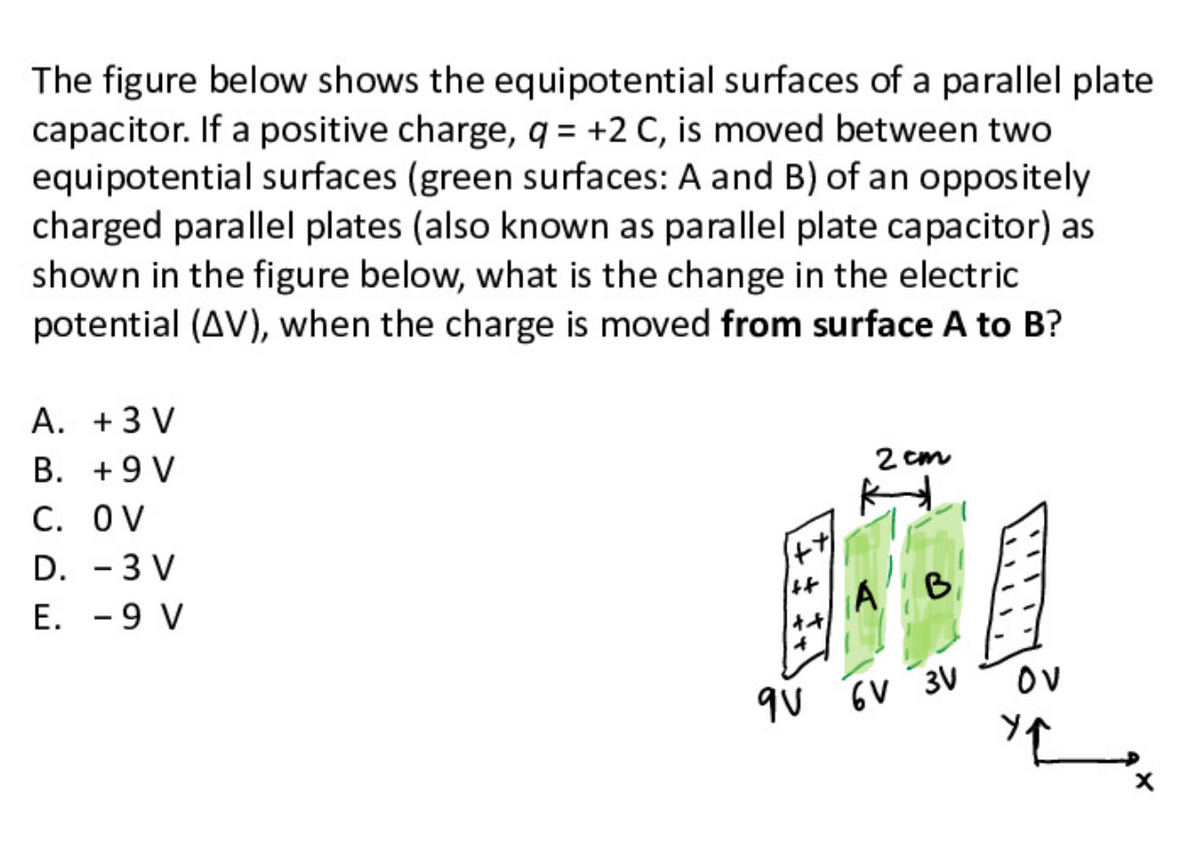
Transcribed Image Text:The figure below shows the equipotential surfaces of a parallel plate
capacitor. If a positive charge, q = +2 C, is moved between two
equipotential surfaces (green surfaces: A and B) of an oppositely
charged parallel plates (also known as parallel plate capacitor) as
shown in the figure below, what is the change in the electric
potential (AV), when the charge is moved from surface A to B?
A. +3 V
B. +9 V
2 cm
С. OV
D. - 3 V
E. -9 V
OV
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you


Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:
9781133104261
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student…
Physics
ISBN:
9780078807213
Author:
Paul W. Zitzewitz
Publisher:
Glencoe/McGraw-Hill


Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:
9781133104261
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student…
Physics
ISBN:
9780078807213
Author:
Paul W. Zitzewitz
Publisher:
Glencoe/McGraw-Hill

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:
9781285737027
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations…
Physics
ISBN:
9781133939146
Author:
Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology …
Physics
ISBN:
9781305116399
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning