The figure shows a wire segment of length As = 3.5 cm, centered at the origin, carrying current i= 5.0 A in the positive y direction (as part of some complete circuit). To calculate the magnitude of the magnetic field B produced by the segment at a point several meters from the origin, we can use the Biot-Savart law as B = (H/4n)i As (sin 0)/r2. This is because r and 0 are essentially constant over the segment. Calculate B (in unit-vector notation) at the (x, y, z) coordinates (a) (0, 0, 6.2 m), (b) (0, 7.9 m, 0), (c) (9.6 m, 8.6 m, 0), and (d) (-5.1 m,-5.6 m,0). (a) (0,0, 6.2 m) = (Number i Units (b) |B| (0,7.9 m, 0) = Number i Units Units (c) B (9.6 m, 8.6 m, 0) = (Number i
The figure shows a wire segment of length As = 3.5 cm, centered at the origin, carrying current i= 5.0 A in the positive y direction (as part of some complete circuit). To calculate the magnitude of the magnetic field B produced by the segment at a point several meters from the origin, we can use the Biot-Savart law as B = (H/4n)i As (sin 0)/r2. This is because r and 0 are essentially constant over the segment. Calculate B (in unit-vector notation) at the (x, y, z) coordinates (a) (0, 0, 6.2 m), (b) (0, 7.9 m, 0), (c) (9.6 m, 8.6 m, 0), and (d) (-5.1 m,-5.6 m,0). (a) (0,0, 6.2 m) = (Number i Units (b) |B| (0,7.9 m, 0) = Number i Units Units (c) B (9.6 m, 8.6 m, 0) = (Number i
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations and Connections
1st Edition
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Katz, Debora M.
Chapter31: Gauss’s Law For Magnetism And Ampère’s Law
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 65PQ
Related questions
Question
Please type instead of hand writting
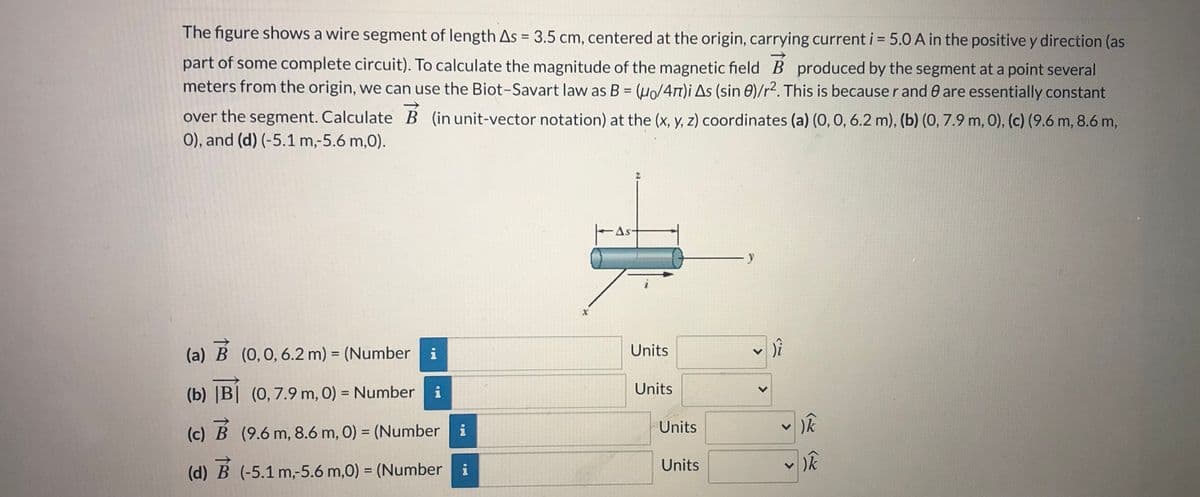
Transcribed Image Text:The figure shows a wire segment of length As = 3.5 cm, centered at the origin, carrying current i = 5.0 A in the positive y direction (as
%3D
part of some complete circuit). To calculate the magnitude of the magnetic field B produced by the segment at a point several
meters from the origin, we can use the Biot-Savart law as B = (µo/4rt)i As (sin 0)/r². This is because r and 0 are essentially constant
over the segment. Calculate B (in unit-vector notation) at the (x, y, z) coordinates (a) (0, 0, 6.2 m), (b) (0, 7.9 m, 0), (c) (9.6 m, 8.6 m,
0), and (d) (-5.1 m,-5.6 m,0).
As-
Units
(a) B (0,0, 6.2 m) = (Number i
%3D
IBI
Units
(b) |B| (0, 7.9 m, 0) = Number
i
%3D
Units
(c) B (9.6 m, 8.6 m, 0) = (Number i
%3D
(d) B (-5.1 m,-5.6 m,0) = (Number
i
Units
%3D
<>
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 5 steps with 4 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations…
Physics
ISBN:
9781133939146
Author:
Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:
9781133104261
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations…
Physics
ISBN:
9781133939146
Author:
Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:
9781133104261
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern …
Physics
ISBN:
9781337553292
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:
9781337553278
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning