The following concrete gravity wall of 7 m in height retains a sandy backfill. A sand sample from the backfill was brought to laboratory and tested in a direct shear device under a normal stress of 100 kPa and failure occurred at a shear stress level of 63.4 kl Using the Rankine theory, determine the total active earth pressure at the base of the wall when: a) the backfill is dry, b) the backfill is partially submerged in water for a water level at 3.5m from the base of the wall, c) the backfill is fully submerged in water, which means the water table is at the ground surface. Notes: - The saturated unit weight of the soil is 19 kN/m³ - The moist unit weight of the soil is 17 kN/m³ - The dry unit weight of the soil is 15 kN/m³ Summarize your results in this table: а) b) c) Total active earth pressure at the base of the wall (kPa)
The following concrete gravity wall of 7 m in height retains a sandy backfill. A sand sample from the backfill was brought to laboratory and tested in a direct shear device under a normal stress of 100 kPa and failure occurred at a shear stress level of 63.4 kl Using the Rankine theory, determine the total active earth pressure at the base of the wall when: a) the backfill is dry, b) the backfill is partially submerged in water for a water level at 3.5m from the base of the wall, c) the backfill is fully submerged in water, which means the water table is at the ground surface. Notes: - The saturated unit weight of the soil is 19 kN/m³ - The moist unit weight of the soil is 17 kN/m³ - The dry unit weight of the soil is 15 kN/m³ Summarize your results in this table: а) b) c) Total active earth pressure at the base of the wall (kPa)
Principles of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap Course List)
9th Edition
ISBN:9781305970939
Author:Braja M. Das, Khaled Sobhan
Publisher:Braja M. Das, Khaled Sobhan
Chapter13: Lateral Earth Pressure: At-rest, Rankine, And Coulomb
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 13.1CTP
Related questions
Question
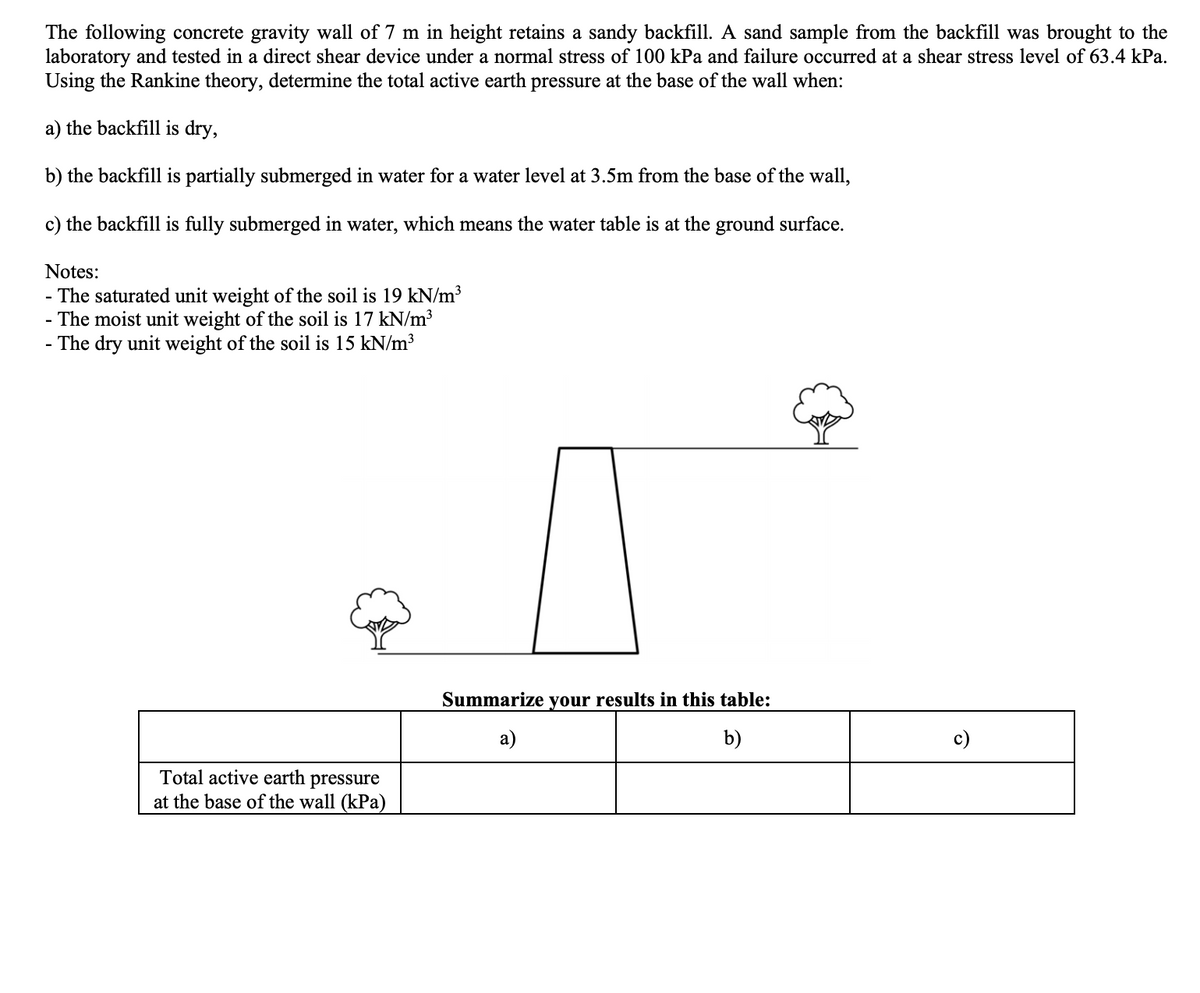
Transcribed Image Text:The following concrete gravity wall of 7 m in height retains a sandy backfill. A sand sample from the backfill was brought to the
laboratory and tested in a direct shear device under a normal stress of 100 kPa and failure occurred at a shear stress level of 63.4 kPa.
Using the Rankine theory, determine the total active earth pressure at the base of the wall when:
a) the backfill is dry,
b) the backfill is partially submerged in water for a water level at 3.5m from the base of the wall,
c) the backfill is fully submerged in water, which means the water table is at the ground surface.
Notes:
- The saturated unit weight of the soil is 19 kN/m³
-The moist unit weight of the soil is 17 kN/m³
- The dry unit weight of the soil is 15 kN/m³
Summarize your results in this table:
b)
Total active earth pressure
at the base of the wall (kPa)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 7 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, civil-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Principles of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap C…
Civil Engineering
ISBN:
9781305970939
Author:
Braja M. Das, Khaled Sobhan
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou…
Civil Engineering
ISBN:
9781337705028
Author:
Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou…
Civil Engineering
ISBN:
9781305081550
Author:
Braja M. Das
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap C…
Civil Engineering
ISBN:
9781305970939
Author:
Braja M. Das, Khaled Sobhan
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou…
Civil Engineering
ISBN:
9781337705028
Author:
Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou…
Civil Engineering
ISBN:
9781305081550
Author:
Braja M. Das
Publisher:
Cengage Learning