The Implicit Function Theorem and the Marginal Rate of Substitution. An important result from multi-variable calculus is the implicit function theorem, which states that given a function f (x, y), the derivative of y with respect to x is given by dy ôf l ôx ôf l ây' dx where ôf / ôx denotes the partial derivative of f with respect to x and ôf /ôy denotes the partial derivative of f with respect to y . Simply stated, a partial derivative of a multivariable function is the derivative of that function with respect to one particular variable, treating all other variables as constant. For example, suppose f(x, y) = xy². To compute the partial derivative of f with respect to x , we treat y as a constant, in which case we obtain ôf / ôx = y² , and to compute the partial derivative of f with respect to y , we treat x as a constant, in which case we obtain ôf l ôy = 2.xy. We have described the slope of an indifference curve as the marginal rate of substitution between the two goods. Supposing that c, is plotted on the vertical axis and c, plotted on the horizontal axis, use the implicit function theorem to compute the marginal rate of substitution for the following utility functions. a. u(c,,c,) = In(c,)+B·In(c,), in which ße (0,1) is an exogenous constant parameter b. u(c,,c,) = (G - 7) – 1 , (c, -y)-0: –1 in which y>0, o, >0, and o, >0 are 1-0 1-0,
The Implicit Function Theorem and the Marginal Rate of Substitution. An important result from multi-variable calculus is the implicit function theorem, which states that given a function f (x, y), the derivative of y with respect to x is given by dy ôf l ôx ôf l ây' dx where ôf / ôx denotes the partial derivative of f with respect to x and ôf /ôy denotes the partial derivative of f with respect to y . Simply stated, a partial derivative of a multivariable function is the derivative of that function with respect to one particular variable, treating all other variables as constant. For example, suppose f(x, y) = xy². To compute the partial derivative of f with respect to x , we treat y as a constant, in which case we obtain ôf / ôx = y² , and to compute the partial derivative of f with respect to y , we treat x as a constant, in which case we obtain ôf l ôy = 2.xy. We have described the slope of an indifference curve as the marginal rate of substitution between the two goods. Supposing that c, is plotted on the vertical axis and c, plotted on the horizontal axis, use the implicit function theorem to compute the marginal rate of substitution for the following utility functions. a. u(c,,c,) = In(c,)+B·In(c,), in which ße (0,1) is an exogenous constant parameter b. u(c,,c,) = (G - 7) – 1 , (c, -y)-0: –1 in which y>0, o, >0, and o, >0 are 1-0 1-0,
Chapter11: Profit Maximization
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 11.14P
Related questions
Question
100%
Solve the following questions.
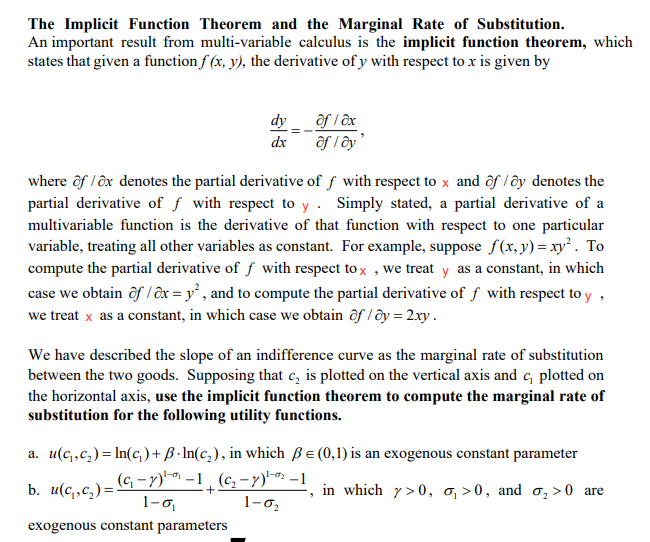
Transcribed Image Text:The Implicit Function Theorem and the Marginal Rate of Substitution.
An important result from multi-variable calculus is the implicit function theorem, which
states that given a function f (x, y), the derivative of y with respect to x is given by
dy ôf l ôx
ôf l ây'
dx
where ôf / ôx denotes the partial derivative of f with respect to x and ôf /ôy denotes the
partial derivative of f with respect to y . Simply stated, a partial derivative of a
multivariable function is the derivative of that function with respect to one particular
variable, treating all other variables as constant. For example, suppose f(x, y) = xy². To
compute the partial derivative of f with respect to x , we treat y as a constant, in which
case we obtain ôf / ôx = y² , and to compute the partial derivative of f with respect to y ,
we treat x as a constant, in which case we obtain ôf l ôy = 2.xy.
We have described the slope of an indifference curve as the marginal rate of substitution
between the two goods. Supposing that c, is plotted on the vertical axis and c, plotted on
the horizontal axis, use the implicit function theorem to compute the marginal rate of
substitution for the following utility functions.
a. u(c,,c,)= In(c,)+ B · In(c,), in which Be (0,1) is an exogenous constant parameter
b. u(c,,c,)= G -Y)" -1¸ (c, -7)-o: -1
1-の
in which y>0, o, >0, and o,>0 are
1-02
exogenous constant parameters
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 1 images

Recommended textbooks for you

