The inverse market demand for a certain good is: -2/ P = 100- where Q is the industry output. There are two symmetric firms producing the good, each with the following cost function: TC; = 10g, where q, is the output of the ith firm (i=1,2). (a) Suppose that the firms are competing in quantities. If someone produces more than their share of the cartel output, the other firm punishes them by re- verting to the Cournot output. What is the critical value of the discount factor 8? (b) Now assume that the detection lag (the time required to discover and re-
The inverse market demand for a certain good is: -2/ P = 100- where Q is the industry output. There are two symmetric firms producing the good, each with the following cost function: TC; = 10g, where q, is the output of the ith firm (i=1,2). (a) Suppose that the firms are competing in quantities. If someone produces more than their share of the cartel output, the other firm punishes them by re- verting to the Cournot output. What is the critical value of the discount factor 8? (b) Now assume that the detection lag (the time required to discover and re-
Managerial Economics: Applications, Strategies and Tactics (MindTap Course List)
14th Edition
ISBN:9781305506381
Author:James R. McGuigan, R. Charles Moyer, Frederick H.deB. Harris
Publisher:James R. McGuigan, R. Charles Moyer, Frederick H.deB. Harris
Chapter12: Price And Output Determination: Oligopoly
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 2E
Related questions
Question
please urgent
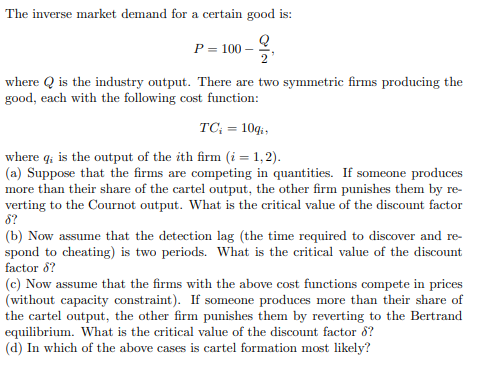
Transcribed Image Text:The inverse market demand for a certain good is:
Q
P = 100
2'
where is the industry output. There are two symmetric firms producing the
good, each with the following cost function:
TC; = 10qi,
where q; is the output of the ith firm (i = 1,2).
(a) Suppose that the firms are competing in quantities. If someone produces
more than their share of the cartel output, the other firm punishes them by re-
verting to the Cournot output. What is the critical value of the discount factor
8?
(b) Now assume that the detection lag (the time required to discover and re-
spond to cheating) is two periods. What is the critical value of the discount
factor 8?
(c) Now assume that the firms with the above cost functions compete in prices
(without capacity constraint). If someone produces more than their share of
the cartel output, the other firm punishes them by reverting to the Bertrand
equilibrium. What is the critical value of the discount factor 8?
(d) In which of the above cases is cartel formation most likely?
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Managerial Economics: Applications, Strategies an…
Economics
ISBN:
9781305506381
Author:
James R. McGuigan, R. Charles Moyer, Frederick H.deB. Harris
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Managerial Economics: Applications, Strategies an…
Economics
ISBN:
9781305506381
Author:
James R. McGuigan, R. Charles Moyer, Frederick H.deB. Harris
Publisher:
Cengage Learning
