The June Bootids meteor shower produces about 6 observable meteors per hour. Suppose that X, the number of observable meteors we see in a one- hour per Poisson distribution with parameter 2 = 6. The Poisson distribution is very useful in analyzing phenomena which occur randomly in space or time. Let Y be the observable meteors we see in a two-hour period. Y can also be modeled as a Poisson random variable. a. For our model, what is expected value of X? 6 b. What is the probability that X = 7? 0.1331 c. What is the probability that X < 7? 0.6063 d. What is the probability that X > 7 0.2561 e. What is the probability that X > 9 0.2561 f. Y also has a Poisson distribution. What is the parameter åy for Y? g. What is variance of X? h. What is the standard deviation of X? i. What is the probability that Y = 9 j. What is the probability that X>9 given that X>7?
The June Bootids meteor shower produces about 6 observable meteors per hour. Suppose that X, the number of observable meteors we see in a one- hour per Poisson distribution with parameter 2 = 6. The Poisson distribution is very useful in analyzing phenomena which occur randomly in space or time. Let Y be the observable meteors we see in a two-hour period. Y can also be modeled as a Poisson random variable. a. For our model, what is expected value of X? 6 b. What is the probability that X = 7? 0.1331 c. What is the probability that X < 7? 0.6063 d. What is the probability that X > 7 0.2561 e. What is the probability that X > 9 0.2561 f. Y also has a Poisson distribution. What is the parameter åy for Y? g. What is variance of X? h. What is the standard deviation of X? i. What is the probability that Y = 9 j. What is the probability that X>9 given that X>7?
A First Course in Probability (10th Edition)
10th Edition
ISBN:9780134753119
Author:Sheldon Ross
Publisher:Sheldon Ross
Chapter1: Combinatorial Analysis
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1.1P: a. How many different 7-place license plates are possible if the first 2 places are for letters and...
Related questions
Question
I need some help with this question. I have answered the half but need help as I am using the r program. I need help from sections e.
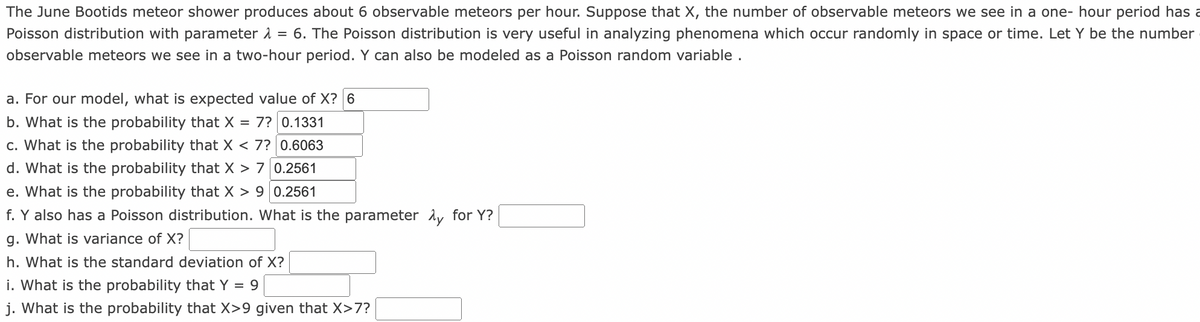
Transcribed Image Text:The June Bootids meteor shower produces about 6 observable meteors per hour. Suppose that X, the number of observable meteors we see in a one- hour period has a
Poisson distribution with parameter 1 = 6. The Poisson distribution is very useful in analyzing phenomena which occur randomly in space or time. Let Y be the number
observable meteors we see in a two-hour period. Y can also be modeled as a Poisson random variable .
a. For our model, what is expected value of X? 6
b. What is the probability that X = 7? 0.1331
c. What is the probability that X < 7? 0.6063
d. What is the probability that X > 7 0.2561
e. What is the probability that X > 9 0.2561
f. Y also has a Poisson distribution. What is the parameter Ay for Y?
g. What is variance of X?
h. What is the standard deviation of X?
i. What is the probability that Y = 9
j. What is the probability that X>9 given that X>7?
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Recommended textbooks for you

A First Course in Probability (10th Edition)
Probability
ISBN:
9780134753119
Author:
Sheldon Ross
Publisher:
PEARSON


A First Course in Probability (10th Edition)
Probability
ISBN:
9780134753119
Author:
Sheldon Ross
Publisher:
PEARSON
