The main chemicals present in a cup of coffee are water, caffeine, and tannins (acidic polyphenols which give coffee its brown color and bitter taste). You decide to extract caffeine from a cup of coffee using sodium bicarbonate and chlorofom, which has a density of 1.49 g/mL. In which layer would you expect to find caffeine? OH он HO. но. HO OH COOH HO COOH COOH Caffeine Tannins O The top organic layer O The bottom aqueous layer The top aqueous layer The bottom organic layer
The main chemicals present in a cup of coffee are water, caffeine, and tannins (acidic polyphenols which give coffee its brown color and bitter taste). You decide to extract caffeine from a cup of coffee using sodium bicarbonate and chlorofom, which has a density of 1.49 g/mL. In which layer would you expect to find caffeine? OH он HO. но. HO OH COOH HO COOH COOH Caffeine Tannins O The top organic layer O The bottom aqueous layer The top aqueous layer The bottom organic layer
General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Course List)
11th Edition
ISBN:9781305580343
Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; Darrell
Publisher:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; Darrell
Chapter1: Chemistry And Measurement
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1.127QP: Some bottles of colorless liquids were being labeled when the technicians accidentally mixed them up...
Related questions
Question
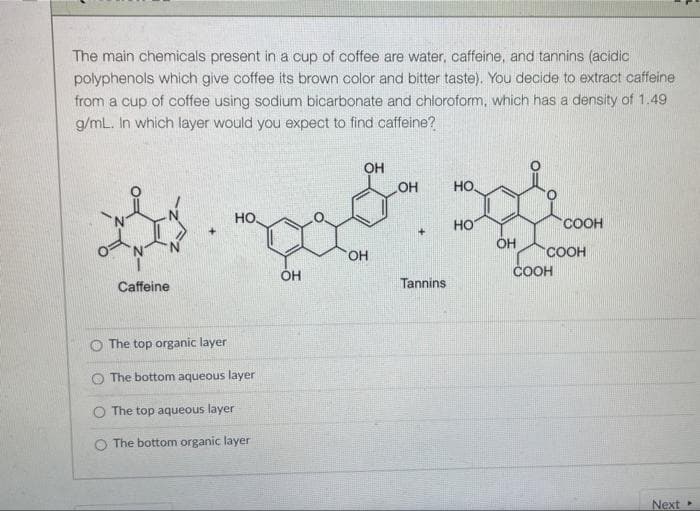
Transcribed Image Text:The main chemicals present in a cup of coffee are water, caffeine, and tannins (acidic
polyphenols which give coffee its brown color and bitter taste). You decide to extract caffeine
from a cup of coffee using sodium bicarbonate and chloroform, which has a density of 1.49
g/mL. In which layer would you expect to find caffeine?
OH
OH
HO,
но.
HO
COOH
OH
OH
COOH
ÓH
COOH
Caffeine
Tannins
The top organic layer
O The bottom aqueous layer
O The top aqueous layer
The bottom organic layer
Next
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour…
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305580343
Author:
Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; Darrell
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285199047
Author:
John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337399074
Author:
John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour…
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305580343
Author:
Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; Darrell
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285199047
Author:
John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337399074
Author:
John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781133949640
Author:
John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079373
Author:
William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry for Engineering Students
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337398909
Author:
Lawrence S. Brown, Tom Holme
Publisher:
Cengage Learning