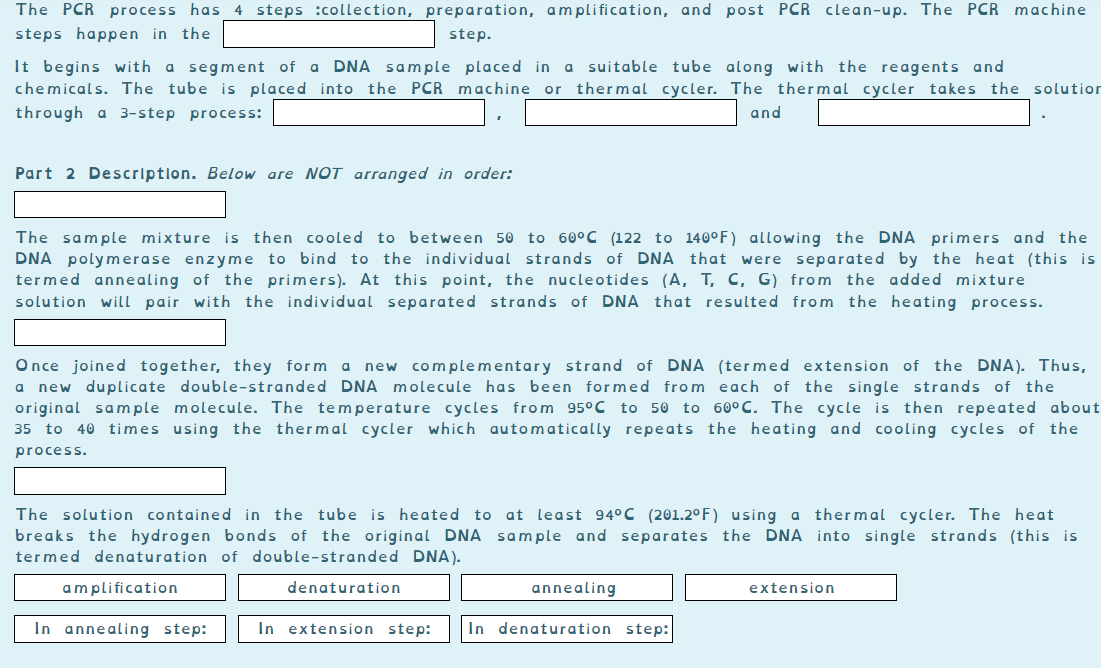
The PCR process has 4 steps :collection, preparation, amplification, and post PCR clean-up. The PCR machine steps happen in the step. It begins with chemicals. The tube is placed into the PCR machine or thermal cycler. The thermal cycler takes the solutior a segment of a DNA sample placed in a suitable tube along with the reagents and through a 3-step process: and Part 2 Descriptlon. Below are NOT arranged in order: The sample mixture DNA polymerase enzyme to bind to the individual strands of DNA that were separated by the heat (this is termed annealing of the primers). At this point, the nucleotides (A, T, C, G) from the added mixture solution will pair with the individual separated strands of is then cooled to between 50 to 60°C (122 to 140°F) allowing the DNA primers and the DNA that resulted from the heating process. Once joined together, they form a new duplicate double-stranded DNA molecule has been formed from each of the single strands of the original sam ple molecule. The temperature cycles from 95°C to 50 to 60°C. The cycle is then repeated about 35 to 40 times using the thermal cycler which automatically repeats the heating and cooling cycles of the new complementary strand of DNA (termed extension of the DNA). Thus, process. The solution contained in the tube is heated to at least 94°C (201.2°F) using a thermal cycler. The heat breaks the hydrogen bonds of the original DNA sample and separates the DNA into single strands (this is termed denaturation of double-stranded DNA). amplification denaturation annealing extension In annealing step: In extension step: In denaturation step:
The PCR process has 4 steps :collection, preparation, amplification, and post PCR clean-up. The PCR machine steps happen in the step. It begins with chemicals. The tube is placed into the PCR machine or thermal cycler. The thermal cycler takes the solutior a segment of a DNA sample placed in a suitable tube along with the reagents and through a 3-step process: and Part 2 Descriptlon. Below are NOT arranged in order: The sample mixture DNA polymerase enzyme to bind to the individual strands of DNA that were separated by the heat (this is termed annealing of the primers). At this point, the nucleotides (A, T, C, G) from the added mixture solution will pair with the individual separated strands of is then cooled to between 50 to 60°C (122 to 140°F) allowing the DNA primers and the DNA that resulted from the heating process. Once joined together, they form a new duplicate double-stranded DNA molecule has been formed from each of the single strands of the original sam ple molecule. The temperature cycles from 95°C to 50 to 60°C. The cycle is then repeated about 35 to 40 times using the thermal cycler which automatically repeats the heating and cooling cycles of the new complementary strand of DNA (termed extension of the DNA). Thus, process. The solution contained in the tube is heated to at least 94°C (201.2°F) using a thermal cycler. The heat breaks the hydrogen bonds of the original DNA sample and separates the DNA into single strands (this is termed denaturation of double-stranded DNA). amplification denaturation annealing extension In annealing step: In extension step: In denaturation step:
Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (MindTap Course List)
5th Edition
ISBN:9781305117396
Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa Starr
Publisher:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa Starr
Chapter10: Biotechnology
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 10SQ
Related questions
Question
help...
Transcribed Image Text:The PCR process has 4 steps :collection, preparation, amplification, and post PCR clean-up. The PCR machine
steps happen in the
step.
It begins with
chemicals. The tube is placed into the PCR machine or thermal cycler. The thermal cycler takes the solutior
a segment of a
DNA sample placed in
a suitable tube along with the reagents and
through a 3-step process:
and
Part 2 Descriptlon. Below are NOT arranged in order:
The sample mixture
DNA polymerase enzyme to bind to the individual strands of DNA that were separated by the heat (this is
termed annealing of the primers). At this point, the nucleotides (A, T, C, G) from the added mixture
solution will pair with the individual separated strands of
is
then cooled to between 50 to 60°C (122 to 140°F) allowing the DNA primers and the
DNA that resulted from the heating process.
Once joined together, they form a
new duplicate double-stranded DNA molecule has been formed from each of the single strands of the
original sam ple molecule. The temperature cycles from 95°C to 50 to 60°C. The cycle is then repeated about
35 to 40 times using the thermal cycler which automatically repeats the heating and cooling cycles of the
new complementary strand of DNA (termed extension of the DNA). Thus,
process.
The solution contained in the tube is heated to at least 94°C (201.2°F) using a thermal cycler. The heat
breaks the hydrogen bonds of the original DNA sample and separates the DNA into single strands (this is
termed denaturation of double-stranded DNA).
amplification
denaturation
annealing
extension
In annealing step:
In extension step:
In denaturation step:
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi…
Biology
ISBN:
9781305117396
Author:
Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa Starr
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi…
Biology
ISBN:
9781305117396
Author:
Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa Starr
Publisher:
Cengage Learning