The Seismic Refraction method depends on the principal that seismic waves possess varying compression and shear wave velocities within differing types of soil and rock material. Acoustic energy waves are refracted when they cross over between soil and/or rocks of differing (and increasing) seismic velocities. Analysis of refracted wavelet arrival times, velocities, and geophone geometries can be used to estimate general soil types and approximate depths to strata boundaries, water tables and/or the upper bedrock surface to be determined. The Seismic Refraction method is also used to estimate rock rippability characteristics for pre-construction planning using Caterpillar seismic velocity soil/rock rippability charts. Seismic refraction surveys commonly involve laying out a spread of geophones in a straight line, with seismic impact source points positioned with and off the ends of the geophone spread. Problem 1) Determine the depth to bedrock for a site. _meters 2) Determine the velocity of the overburden meter/second and 3) Determine the velocity of the bedrock_ _ meter/second. 4) Critical distance from the source point _meters Geophone 1 is 20 meters from the shot point and each geophone is 20meters from the next one. Geophone First Arrival time ( seconds) 10.015 2 0.031 3 0.046 4 0.062 5 0.077 6 0.089 7 0.094 8 0.099 9 0.105 10 0.110 11 0.115 12 0.121
The Seismic Refraction method depends on the principal that seismic waves possess varying compression and shear wave velocities within differing types of soil and rock material. Acoustic energy waves are refracted when they cross over between soil and/or rocks of differing (and increasing) seismic velocities. Analysis of refracted wavelet arrival times, velocities, and geophone geometries can be used to estimate general soil types and approximate depths to strata boundaries, water tables and/or the upper bedrock surface to be determined. The Seismic Refraction method is also used to estimate rock rippability characteristics for pre-construction planning using Caterpillar seismic velocity soil/rock rippability charts. Seismic refraction surveys commonly involve laying out a spread of geophones in a straight line, with seismic impact source points positioned with and off the ends of the geophone spread. Problem 1) Determine the depth to bedrock for a site. _meters 2) Determine the velocity of the overburden meter/second and 3) Determine the velocity of the bedrock_ _ meter/second. 4) Critical distance from the source point _meters Geophone 1 is 20 meters from the shot point and each geophone is 20meters from the next one. Geophone First Arrival time ( seconds) 10.015 2 0.031 3 0.046 4 0.062 5 0.077 6 0.089 7 0.094 8 0.099 9 0.105 10 0.110 11 0.115 12 0.121
Applications and Investigations in Earth Science (9th Edition)
9th Edition
ISBN:9780134746241
Author:Edward J. Tarbuck, Frederick K. Lutgens, Dennis G. Tasa
Publisher:Edward J. Tarbuck, Frederick K. Lutgens, Dennis G. Tasa
Chapter1: The Study Of Minerals
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1LR
Related questions
Question
provide A and B both answer with explanation
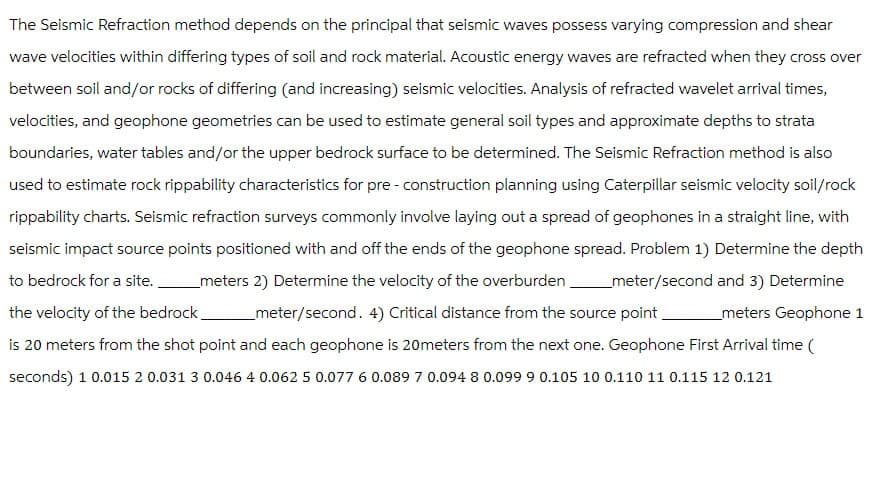
Transcribed Image Text:The Seismic Refraction method depends on the principal that seismic waves possess varying compression and shear
wave velocities within differing types of soil and rock material. Acoustic energy waves are refracted when they cross over
between soil and/or rocks of differing (and increasing) seismic velocities. Analysis of refracted wavelet arrival times,
velocities, and geophone geometries can be used to estimate general soil types and approximate depths to strata
boundaries, water tables and/or the upper bedrock surface to be determined. The Seismic Refraction method is also
used to estimate rock rippability characteristics for pre-construction planning using Caterpillar seismic velocity soil/rock
rippability charts. Seismic refraction surveys commonly involve laying out a spread of geophones in a straight line, with
seismic impact source points positioned with and off the ends of the geophone spread. Problem 1) Determine the depth
to bedrock for a site. _meters 2) Determine the velocity of the overburden meter/second and 3) Determine
the velocity of the bedrock_ _ meter/second. 4) Critical distance from the source point _meters Geophone 1
is 20 meters from the shot point and each geophone is 20meters from the next one. Geophone First Arrival time (
seconds) 10.015 2 0.031 3 0.046 4 0.062 5 0.077 6 0.089 7 0.094 8 0.099 9 0.105 10 0.110 11 0.115 12 0.121
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Recommended textbooks for you

Applications and Investigations in Earth Science …
Earth Science
ISBN:
9780134746241
Author:
Edward J. Tarbuck, Frederick K. Lutgens, Dennis G. Tasa
Publisher:
PEARSON

Exercises for Weather & Climate (9th Edition)
Earth Science
ISBN:
9780134041360
Author:
Greg Carbone
Publisher:
PEARSON

Environmental Science
Earth Science
ISBN:
9781260153125
Author:
William P Cunningham Prof., Mary Ann Cunningham Professor
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Applications and Investigations in Earth Science …
Earth Science
ISBN:
9780134746241
Author:
Edward J. Tarbuck, Frederick K. Lutgens, Dennis G. Tasa
Publisher:
PEARSON

Exercises for Weather & Climate (9th Edition)
Earth Science
ISBN:
9780134041360
Author:
Greg Carbone
Publisher:
PEARSON

Environmental Science
Earth Science
ISBN:
9781260153125
Author:
William P Cunningham Prof., Mary Ann Cunningham Professor
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Earth Science (15th Edition)
Earth Science
ISBN:
9780134543536
Author:
Edward J. Tarbuck, Frederick K. Lutgens, Dennis G. Tasa
Publisher:
PEARSON

Environmental Science (MindTap Course List)
Earth Science
ISBN:
9781337569613
Author:
G. Tyler Miller, Scott Spoolman
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physical Geology
Earth Science
ISBN:
9781259916823
Author:
Plummer, Charles C., CARLSON, Diane H., Hammersley, Lisa
Publisher:
Mcgraw-hill Education,