Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897, 0079039898, 2018
18th Edition
ISBN:9780079039897
Author:Carter
Publisher:Carter
Chapter5: Linear Inequalities
Section5.4: Solving Compound Inqualities
Problem 36PPS
Related questions
Question
4.) The sum of the lengths of any two sides of a
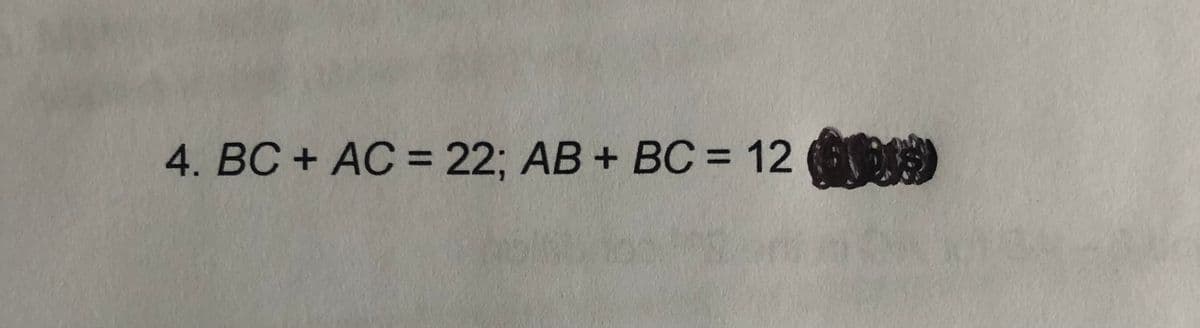
Transcribed Image Text:4. BC + AC = 22; AB + BC = 12
%3D
%3D

Transcribed Image Text:Geometry The sum of the lengths of any two sides of a triangle is greater than the length of the third
side. In AABC, BC = 4 and AC = 8- AB. What can you conclude about AB? AABC has three sides,
so you can use the Triangle Inequality Theorem and write 3 conditions of the sides.
%3D
AC + BC > AB
1st Triangle Inequality condition
AB + BC > AC
2nd Triangle Inequality condition
AB + AC > BC
3rd Triangle Inequality condition
BC = 4 and AC = 8- AB
Given
(8- AB) + 4 > AB
Substitute 4 for BC and 8- AB for AC in the 1st condition.
12 > 2AB
Solve and simplify.
AB < 6
AB + 4 > 8 – AB
Substitute 4 for BC and 8- AB for AC in the 2nd condition.
2AB > 4
Solve and simplify.
AB > 2
AB + (8 - AB) > 4
Substitute 4 for BC and 8- AB for AC in the 3rd condition.
8 > 4
Simplify. True Statement.
2 < AB < 6
Conclusion about AB.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, algebra and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897…
Algebra
ISBN:
9780079039897
Author:
Carter
Publisher:
McGraw Hill

Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition…
Algebra
ISBN:
9780547587776
Author:
HOLT MCDOUGAL
Publisher:
HOLT MCDOUGAL

Big Ideas Math A Bridge To Success Algebra 1: Stu…
Algebra
ISBN:
9781680331141
Author:
HOUGHTON MIFFLIN HARCOURT
Publisher:
Houghton Mifflin Harcourt

Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897…
Algebra
ISBN:
9780079039897
Author:
Carter
Publisher:
McGraw Hill

Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition…
Algebra
ISBN:
9780547587776
Author:
HOLT MCDOUGAL
Publisher:
HOLT MCDOUGAL

Big Ideas Math A Bridge To Success Algebra 1: Stu…
Algebra
ISBN:
9781680331141
Author:
HOUGHTON MIFFLIN HARCOURT
Publisher:
Houghton Mifflin Harcourt

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage

College Algebra (MindTap Course List)
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305652231
Author:
R. David Gustafson, Jeff Hughes
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

College Algebra
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305115545
Author:
James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem Watson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning