The table below shows the results of using X-ray imaging as a diagnostic test for tuberculosis in patients with known TB status. Use it to answer the questions below. Test for TB TB absent TB present Negative 1739 8 Positive 51 22
The table below shows the results of using X-ray imaging as a diagnostic test for tuberculosis in patients with known TB status. Use it to answer the questions below. Test for TB TB absent TB present Negative 1739 8 Positive 51 22
Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897, 0079039898, 2018
18th Edition
ISBN:9780079039897
Author:Carter
Publisher:Carter
Chapter10: Statistics
Section10.1: Measures Of Center
Problem 9PPS
Related questions
Question
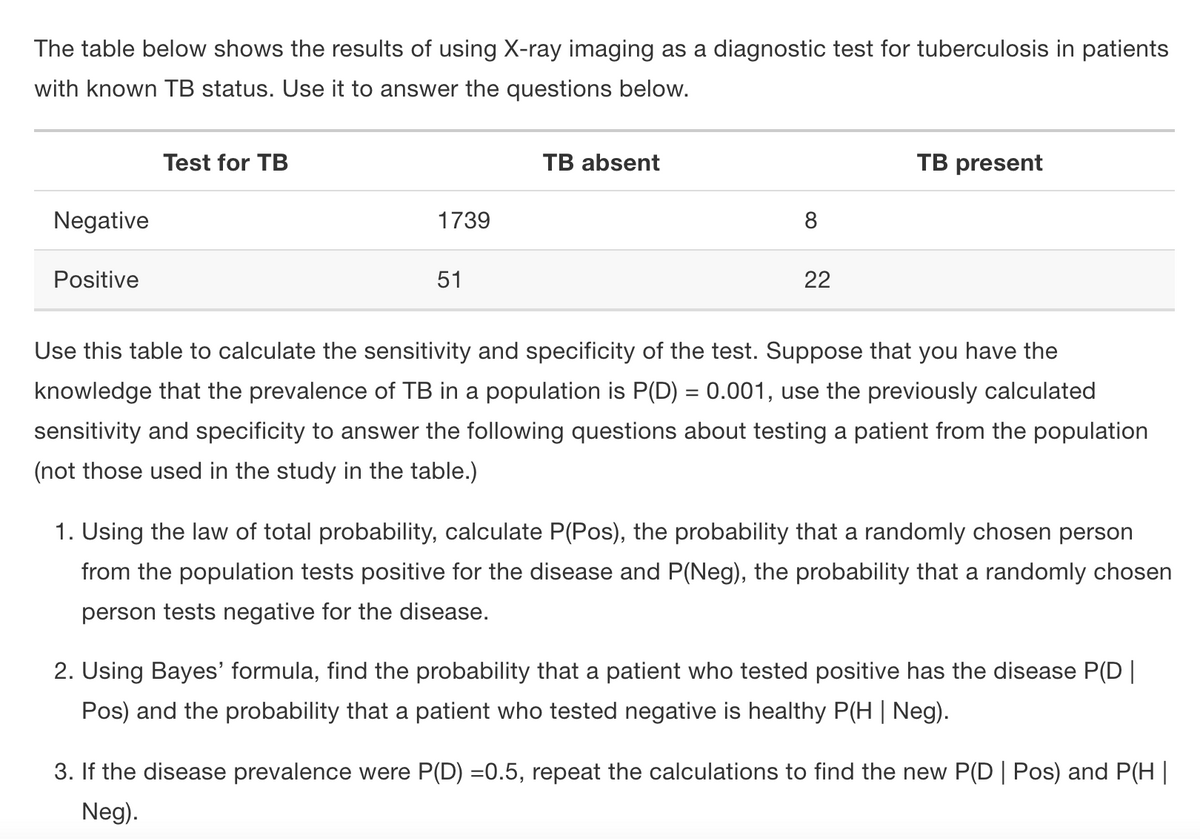
Transcribed Image Text:The table below shows the results of using X-ray imaging as a diagnostic test for tuberculosis in patients
with known TB status. Use it to answer the questions below.
Test for TB
TB absent
TB present
Negative
1739
8
Positive
51
22
Use this table to calculate the sensitivity and specificity of the test. Suppose that you have the
knowledge that the prevalence of TB in a population is P(D) = 0.001, use the previously calculated
sensitivity and specificity to answer the following questions about testing a patient from the population
(not those used in the study in the table.)
1. Using the law of total probability, calculate P(Pos), the probability that a randomly chosen person
from the population tests positive for the disease and P(Neg), the probability that a randomly chosen
person tests negative for the disease.
2. Using Bayes' formula, find the probability that a patient who tested positive has the disease P(D||
Pos) and the probability that a patient who tested negative is healthy P(H| Neg).
3. If the disease prevalence were P(D) =0.5, repeat the calculations to find the new P(D | Pos) and P(H|
Neg).
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 5 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, probability and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897…
Algebra
ISBN:
9780079039897
Author:
Carter
Publisher:
McGraw Hill

Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897…
Algebra
ISBN:
9780079039897
Author:
Carter
Publisher:
McGraw Hill