The value of an asset is the present value of the expected returns from the asset during the holding period. An investment will provide a stream of returns during this period, and it is necessary to discount this stream of returns at an appropriate rate to determine the asset’s present value. A dividend valuation model such as the following is frequent. where: Pi = the current price of Common Stock i D1 = the expected dividend in Period 1 ki = the required rate of return on Stock i gi = the expected constant-growth rate of dividends for Stock i A. Identify the three factors that must be estimated for any valuation model, and explain why these estimates are more difficult to derive for common stocks than for bonds. B. Explain the principal problem involved in using a dividend valuation model to value : (1) companies whose operations are closely correlated with economic cycles. (2) companies that are of very large and mature. (3) companies that are quite small and are growing rapidly
The value of an asset is the present value of the expected
holding period. An investment will provide a stream of returns during this period, and it is
necessary to discount this stream of returns at an appropriate rate to determine the asset’s
present value. A dividend valuation model such as the following is frequent.
where:
Pi = the current price of Common Stock i
D1 = the expected dividend in Period 1
ki = the required
gi = the expected constant-growth rate of dividends for Stock i
A. Identify the three factors that must be estimated for any valuation model, and explain why
these estimates are more difficult to derive for common stocks than for bonds.
B. Explain the principal problem involved in using a dividend valuation model to value :
(1) companies whose operations are closely correlated with economic cycles.
(2) companies that are of very large and mature.
(3) companies that are quite small and are growing rapidly.
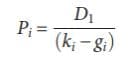
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps









