Theorem: If a and b are consecutive integers, then the Choose a match sum a + b is odd. Proof: Assume that a and b are consecutive integers. Because Proof by Contradiction a and b are consecutive we know that b = a + 1. Thus, the sum a +b may be re-written as 2a + 1. Thus, there exists a number k such that a + b = 2k + 1 so the sum a + Proof by Contrapositive b is odd. Direct Proof Theorem: If a and b are consecutive integers, then the sum a + b is odd. Proof: Assume that a and b are consecutive integers. Assume also that the sum a + b is not odd. Because the sum a + b is not odd, there exists no number k such that a + b = 2k + 1. However, the integers a and b are consecutive, so we may write the sum a +b as 2a + 1. Thus, we have derived that a+ b k+1 for any integer k and also that a + b = 20 + 1. If we hold that a and b are consecutive then we know that the sum a +b must be odd.
Theorem: If a and b are consecutive integers, then the Choose a match sum a + b is odd. Proof: Assume that a and b are consecutive integers. Because Proof by Contradiction a and b are consecutive we know that b = a + 1. Thus, the sum a +b may be re-written as 2a + 1. Thus, there exists a number k such that a + b = 2k + 1 so the sum a + Proof by Contrapositive b is odd. Direct Proof Theorem: If a and b are consecutive integers, then the sum a + b is odd. Proof: Assume that a and b are consecutive integers. Assume also that the sum a + b is not odd. Because the sum a + b is not odd, there exists no number k such that a + b = 2k + 1. However, the integers a and b are consecutive, so we may write the sum a +b as 2a + 1. Thus, we have derived that a+ b k+1 for any integer k and also that a + b = 20 + 1. If we hold that a and b are consecutive then we know that the sum a +b must be odd.
Elements Of Modern Algebra
8th Edition
ISBN:9781285463230
Author:Gilbert, Linda, Jimmie
Publisher:Gilbert, Linda, Jimmie
Chapter2: The Integers
Section2.2: Mathematical Induction
Problem 50E: Show that if the statement 1+2+3+...+n=n(n+1)2+2 is assumed to be true for n=k, the same equation...
Related questions
Question
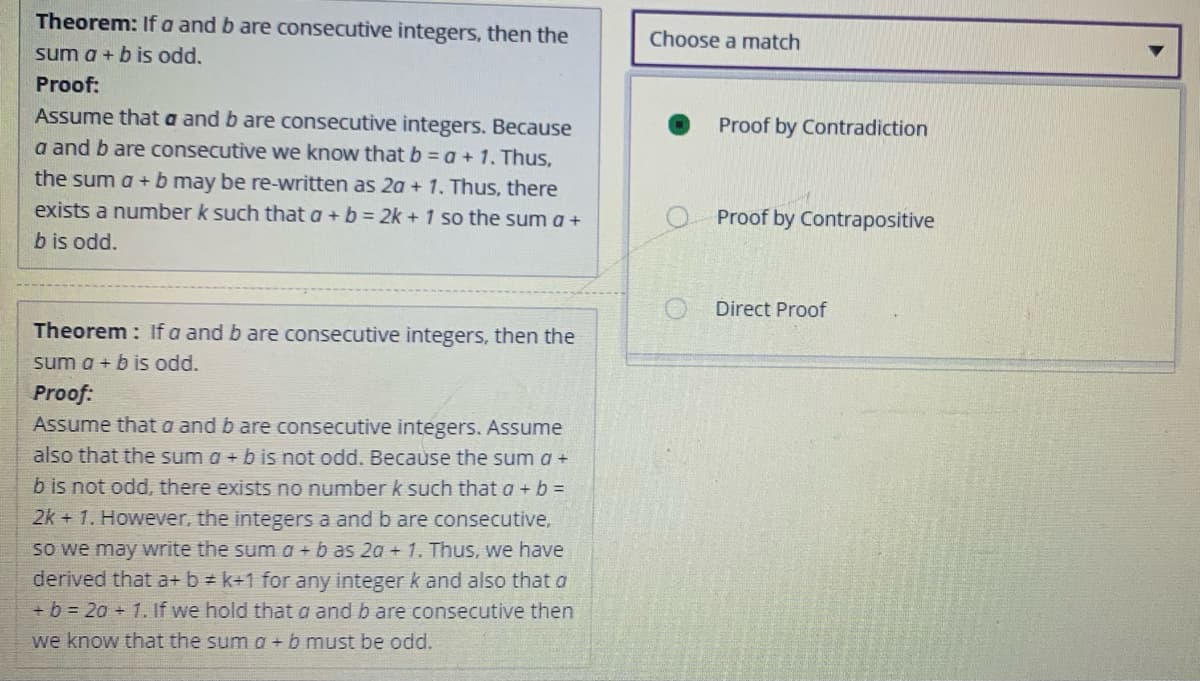
Transcribed Image Text:Theorem: If a and b are consecutive integers, then the
Choose a match
sum a + b is odd.
Proof:
Assume that a and b are consecutive integers. Because
Proof by Contradiction
a and b are consecutive we know that b = a + 1. Thus,
the sum a +b may be re-written as 2a + 1. Thus, there
exists a number k such that a + b = 2k + 1 so the sum a +
Proof by Contrapositive
b is odd.
O Direct Proof
Theorem: If a and b are consecutive integers, then the
sum a + b is odd.
Proof:
Assume that a and b are consecutive integers. Assume
also that the sum a + b is not odd. Because the sum a +
b is not odd, there exists no number k such that a + b =
2k + 1. However, the integers a and b are consecutive,
so we may write the sum a + b as 2a + 1. Thus, we have
derived that a+ b k+1 for any integer k and also that a
+ b = 20 + 1. If we hold that a and b are consecutive then
we know that the sum a + b must be odd.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 1 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Elements Of Modern Algebra
Algebra
ISBN:
9781285463230
Author:
Gilbert, Linda, Jimmie
Publisher:
Cengage Learning,

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage

College Algebra (MindTap Course List)
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305652231
Author:
R. David Gustafson, Jeff Hughes
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Elements Of Modern Algebra
Algebra
ISBN:
9781285463230
Author:
Gilbert, Linda, Jimmie
Publisher:
Cengage Learning,

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage

College Algebra (MindTap Course List)
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305652231
Author:
R. David Gustafson, Jeff Hughes
Publisher:
Cengage Learning