To identify how much heat is required to bring a kettle of water to its boiling point, you are required to calculate the specific heat of water at 61°C. The specific heat of water is given as a function of time in Table Q1(a). Q1 (a) Table Q1(a): Specific heat of water as a function of temperature Temperature, T (°C) J Specific heat, C, kg-°C 42 4179 52 4186 82 4199 100 4217 110 4300 (i) Determine the value of the specific heat at T = 61°C using a second order Lagrange polynomial. (ii) Determine the value of the specific heat at T = 61°C using a third order Lagrange polynomial. (iii) Find the absolute relative approximate error le obtained between the results from the second with third order polynomial.
To identify how much heat is required to bring a kettle of water to its boiling point, you are required to calculate the specific heat of water at 61°C. The specific heat of water is given as a function of time in Table Q1(a). Q1 (a) Table Q1(a): Specific heat of water as a function of temperature Temperature, T (°C) J Specific heat, C, kg-°C 42 4179 52 4186 82 4199 100 4217 110 4300 (i) Determine the value of the specific heat at T = 61°C using a second order Lagrange polynomial. (ii) Determine the value of the specific heat at T = 61°C using a third order Lagrange polynomial. (iii) Find the absolute relative approximate error le obtained between the results from the second with third order polynomial.
Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)
10th Edition
ISBN:9781337278461
Author:Ron Larson
Publisher:Ron Larson
ChapterP: Prerequisites
SectionP.7: A Library Of Parent Functions
Problem 47E
Related questions
Question
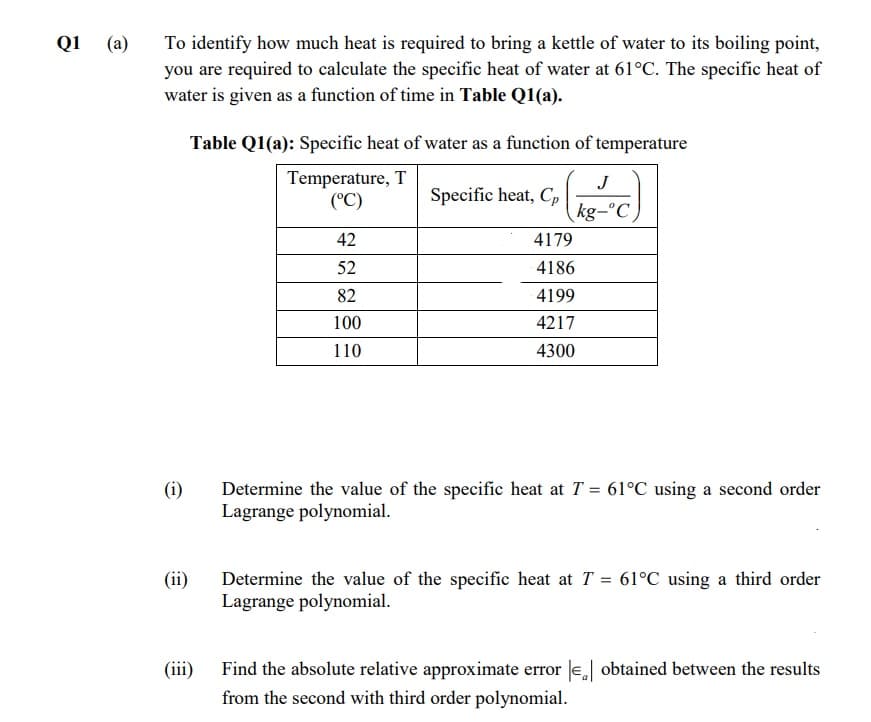
Transcribed Image Text:To identify how much heat is required to bring a kettle of water to its boiling point,
you are required to calculate the specific heat of water at 61°C. The specific heat of
water is given as a function of time in Table Q1(a).
Q1
(a)
Table Q1(a): Specific heat of water as a function of temperature
Temperature, T
(°C)
J
Specific heat, C,
kg-°C
42
4179
52
4186
82
4199
100
4217
110
4300
(i)
Determine the value of the specific heat at T = 61°C using a second order
Lagrange polynomial.
(ii)
Determine the value of the specific heat at T = 61°C using a third order
Lagrange polynomial.
(iii)
Find the absolute relative approximate error e obtained between the results
from the second with third order polynomial.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 5 steps with 1 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)
Trigonometry
ISBN:
9781337278461
Author:
Ron Larson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


College Algebra
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305115545
Author:
James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem Watson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)
Trigonometry
ISBN:
9781337278461
Author:
Ron Larson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


College Algebra
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305115545
Author:
James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem Watson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897…
Algebra
ISBN:
9780079039897
Author:
Carter
Publisher:
McGraw Hill

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage

Elementary Linear Algebra (MindTap Course List)
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305658004
Author:
Ron Larson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning