To understand the behavior of the electric field at the surface of a conductor, and its relationship to surface charge on the conductor. because in that case, part of the Gaussian surface must lie outside the conducting object, where there is an electric field. A conductor is placed in an external electrostatic field. The external field is uniform before the conductor is placed within it. The conductor is completely isolated from any source of current or charge. Part C Assume that at some point just outside the surface of the conductor, the electric field has magnitude E and is directed toward the surface of the conductor. What is the charge density o on the surface of the conductor at that point? Express your answer in terms of E and En- • View Available Hint(s) Hνα ΑΣφ
To understand the behavior of the electric field at the surface of a conductor, and its relationship to surface charge on the conductor. because in that case, part of the Gaussian surface must lie outside the conducting object, where there is an electric field. A conductor is placed in an external electrostatic field. The external field is uniform before the conductor is placed within it. The conductor is completely isolated from any source of current or charge. Part C Assume that at some point just outside the surface of the conductor, the electric field has magnitude E and is directed toward the surface of the conductor. What is the charge density o on the surface of the conductor at that point? Express your answer in terms of E and En- • View Available Hint(s) Hνα ΑΣφ
Chapter6: Gauss's Law
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 86AP: Two non-conducting spheres of radii R1 and R2 are uniformly charged with charge densities p1 and p2...
Related questions
Question
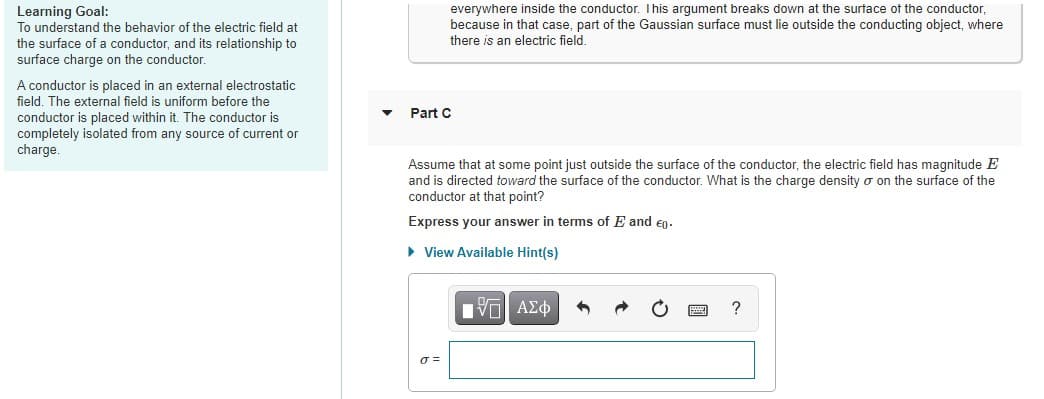
Transcribed Image Text:Learning Goal:
To understand the behavior of the electric field at
the surface of a conductor, and its relationship to
surface charge on the conductor.
everywhere inside the conductor. This argument breaks down at the surtace of the conductor,
because in that case, part of the Gaussian surface must lie outside the conducting object, where
there is an electric field.
A conductor is placed in an external electrostatic
field. The external field is uniform before the
Part C
conductor is placed within it. The conductor is
completely isolated from any source of current or
charge.
Assume that at some point just outside the surface of the conductor, the electric field has magnitude E
and is directed toward the surface of the conductor. What is the charge density o on the surface of the
conductor at that point?
Express your answer in terms of E and en.
• View Available Hint(s)
ΠV ΑΣφ
?
O =
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 1 images

Recommended textbooks for you

