Two particles having charges of 0.550 nCnC and 13.8 nCnC are separated by a distance of 1.30 mm. PART A At what point along the line connecting the two charges is the net electric field due to the two charges equal to zero? Express your answer in meters. CORRECT ANSER IN BOX The electric field is zero at a point = 0.217 mm from 0.550 nCnC . PART B Where would the net electric field be zero if one of the charges were negative? Enter your answer as a distance in meters from the charge initially equal to 0.550 nCnC.
I cant seem to figure this question out. No matter what formula I use I keep getting it wrong. Really need help finding the correct answer. Thanks Below is a transcript of the question incase its hard to see the picture
Two particles having charges of 0.550 nCnC and 13.8 nCnC are separated by a distance of 1.30 mm.
PART A
|
The electric field is zero at a point =
|
0.217
|
mm from 0.550 nCnC .
|
PART B
Part-(a):
Electric field is a vector field which can be defined as the electric force exerted per unit charge, if a test charge is placed in the region of space around a source charge.
Let's assume two charges, and are placed along - axis. Now at a distance of from the first charge in between the given two charges (as both the charges are positive so the net zero point must be in between the charges), be the point where the net electric field due to these two charges be zero. is placed at the origin and is placed at a distance of . The left side is negative direction and right side is the positive direction.
Now let's draw a diagrammatic representation for the given case
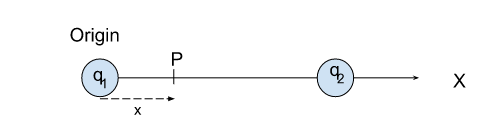
The formula to calculate the magnitude electric field at due to charge is given by
where is the coulomb constant and is the distance from and point .
Again the formula to calculate the magnitude of electric field at point due to charge is given by
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 7 steps with 2 images









