Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology Update (No access codes included)
9th Edition
ISBN:9781305116399
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Chapter29: Magnetic Fields
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 29.12OQ
Related questions
Question

Transcribed Image Text:Questions
Magnetic Force
1.
Use Fleming's Left Hand Rule to predict the direction of movement of the current-carrying wire in the magnetic field
below:
2.
Consider the situation below:
| = 0.15A
%3D
L = 0.50m
63°
B = 40mT
a)
Calculate the magnitude of magnetic force experienced by the wire.
b)
The wire is placed at an angle of 0° to the magnetic field. Calculate the magnitude of magnetic force
experienced by the wire at this angle.
c)
State the angle between the magnetic field and the wire that will generate the largest magnetic force.
Transcribed Image Text:Questions Continued
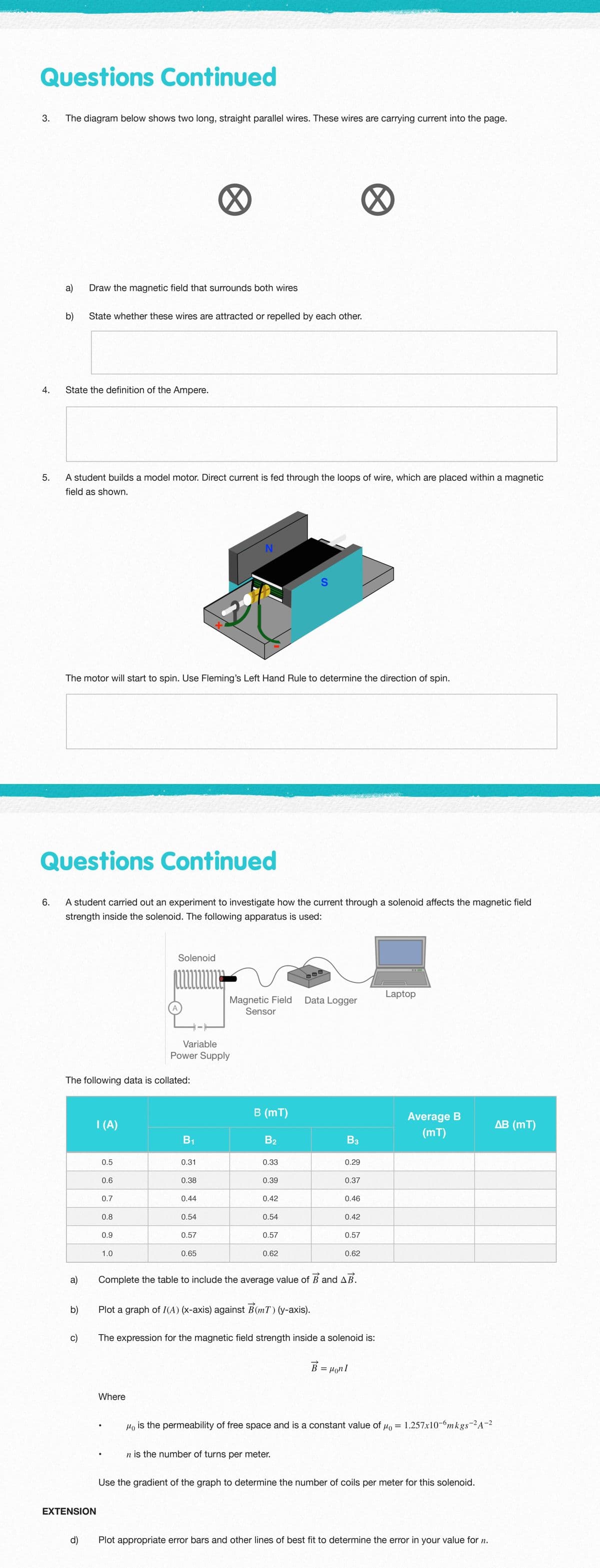
3.
The diagram below shows two long, straight parallel wires. These wires are carrying current into the page.
a)
Draw the magnetic field that surrounds both wires
b)
State whether these wires are attracted or repelled by each other.
4.
State the definition of the Ampere.
A student builds a model motor. Direct current is fed through the loops of wire, which are placed within a magnetic
field as shown.
N
The motor will start to spin. Use Fleming's Left Hand Rule to determine the direction of spin.
Questions Continued
6.
A student carried out an experiment to investigate how the current through a solenoid affects the magnetic field
strength inside the solenoid. The following apparatus is used:
Solenoid
Laptop
Magnetic Field
Sensor
Data Logger
A
Variable
Power Supply
The following data is collated:
В (mT)
Average B
I (A)
ДВ (mT)
(mT)
B1
B2
Вз
0.5
0.31
0.33
0.29
0.6
0.38
0.39
0.37
0.7
0.44
0.42
0.46
0.8
0.54
0.54
0.42
0.9
0.57
0.57
0.57
1.0
0.65
0.62
0.62
a)
Complete the table to include the average value of B and AB.
b)
Plot a graph of I(A) (x-axis) against B(mT) (y-axis).
c)
The expression for the magnetic field strength inside a solenoid is:
B =
HonI
Where
Ho
is the permeability of free space and is a constant value of
Ho
= 1.257x10-6mkgs-2A-2
n is the number of turns per meter.
Use the gradient of the graph to determine the number of coils per meter for this solenoid.
EXTENSION
d)
Plot appropriate error bars and other lines of best fit to determine the error in your value for n.
SI
5.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology …
Physics
ISBN:
9781305116399
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student…
Physics
ISBN:
9780078807213
Author:
Paul W. Zitzewitz
Publisher:
Glencoe/McGraw-Hill


Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology …
Physics
ISBN:
9781305116399
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student…
Physics
ISBN:
9780078807213
Author:
Paul W. Zitzewitz
Publisher:
Glencoe/McGraw-Hill



Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:
9781133104261
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:
9781938168000
Author:
Paul Peter Urone, Roger Hinrichs
Publisher:
OpenStax College