Use the green point (triangle symbol) to shade consumer surplus, and then use the purple point (diamond symbol) to shade producer surplus. 550 Domestic Demand Domestic Supply 525 Consumer Surplus 500 475 450 Producer Surplus 425 400 375 350 Pw 325 300 40 80 120 160 200 240 280 320 360 400 QUANTITY (Thousands of tons of soybeans) When Venezuela allows free trade of soybeans, the price of a ton of soybeans in Venezuela will be $350. At this price, tons of soybeans will be demanded in Venezuela, and tons will be supplied by domestic suppliers. Therefore, Venezuela will import tons of soybeans. Using the information from the previous tasks, complete the following table to analyze the welfare effect of allowing free trade. Without Free Trade With Free Trade (Millions of dollars) (Millions of dollars) Consumer Surplus Producer Surplus When Venezuela allows free trade, the country's consumer surplus by $ million, and producer surplus by million. So, the net effect of international trade on Venezuela's total surplus is a of million. PRICE (Dollars per tons)
Use the green point (triangle symbol) to shade consumer surplus, and then use the purple point (diamond symbol) to shade producer surplus. 550 Domestic Demand Domestic Supply 525 Consumer Surplus 500 475 450 Producer Surplus 425 400 375 350 Pw 325 300 40 80 120 160 200 240 280 320 360 400 QUANTITY (Thousands of tons of soybeans) When Venezuela allows free trade of soybeans, the price of a ton of soybeans in Venezuela will be $350. At this price, tons of soybeans will be demanded in Venezuela, and tons will be supplied by domestic suppliers. Therefore, Venezuela will import tons of soybeans. Using the information from the previous tasks, complete the following table to analyze the welfare effect of allowing free trade. Without Free Trade With Free Trade (Millions of dollars) (Millions of dollars) Consumer Surplus Producer Surplus When Venezuela allows free trade, the country's consumer surplus by $ million, and producer surplus by million. So, the net effect of international trade on Venezuela's total surplus is a of million. PRICE (Dollars per tons)
Principles of Economics, 7th Edition (MindTap Course List)
7th Edition
ISBN:9781285165875
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:N. Gregory Mankiw
Chapter14: Firms In Competitive Markets
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 11PA
Related questions
Question

Transcribed Image Text:Use the green point (triangle symbol) to shade consumer surplus, and then use the purple point (diamond symbol) to shade producer surplus.
550
Domestic Demand
Domestic Supply
A
525
Consumer Surplus
500
475
450
Producer Surplus
425
400
375
350
P.
325
300
40
80
120
160
200
240
280
320
360
400
QUANTITY (Thousands of tons of soybeans)
When Venezuela allows free trade of soybeans, the price of a ton of soybeans in Venezuela will be $350. At this price,
tons of soybeans
will be demanded in Venezuela, and
tons will be supplied by domestic suppliers. Therefore, Venezuela will import
tons of
soybeans.
Using the information from the previous tasks, complete the following table to analyze the welfare effect of allowing free trade.
Without Free Trade
With Free Trade
(Millions of dollars)
(Millions of dollars)
Consumer Surplus
Producer Surplus
When Venezuela allows free trade, the country's consumer surplus
by $
million, and producer surplus
by
million. So, the net effect of international trade on Venezuela's total surplus is a
million.
PRICE (Dollars per tons)
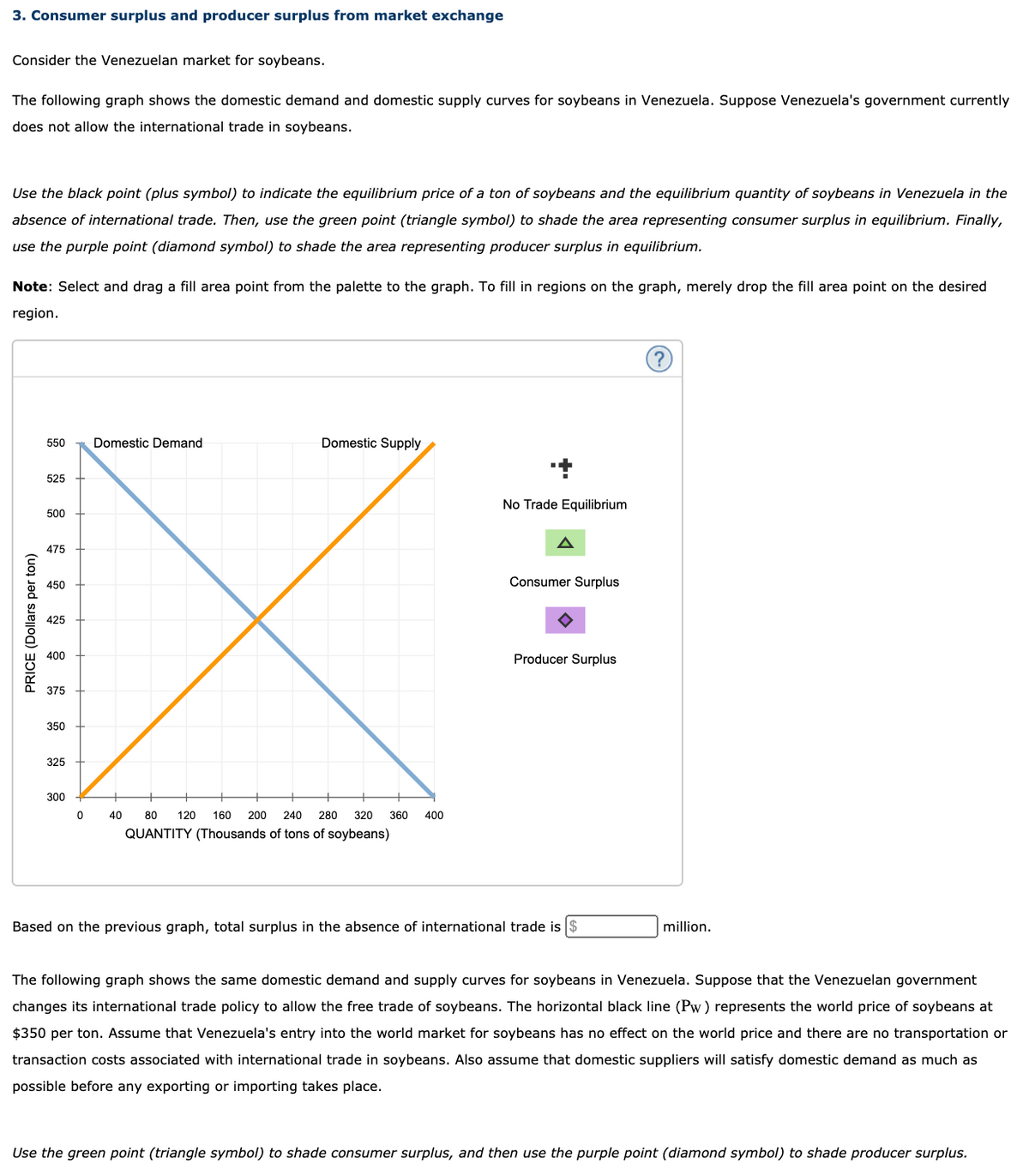
Transcribed Image Text:3. Consumer surplus and producer surplus from market exchange
Consider the Venezuelan market for soybeans.
The following graph shows the domestic demand and domestic supply curves for soybeans in Venezuela. Suppose Venezuela's government currently
does not allow the international trade in soybeans.
Use the black point (plus symbol) to indicate the equilibrium price of a ton of soybeans and the equilibrium quantity of soybeans in Venezuela in the
absence of international trade. Then, use the green point (triangle symbol) to shade the area representing consumer surplus in equilibrium. Finally,
use the purple point (diamond symbol) to shade the area representing producer surplus in equilibrium.
Note: Select and drag a fill area point from the palette to the graph. To fill in regions on the graph, merely drop the fill area point on the desired
region.
550
Domestic Demand
Domestic Supply
525
No Trade Equilibrium
500
A
475
450
Consumer Surplus
425
400
Producer Surplus
375
350
325
300
40
80
120
160
200
240
280
320
360
400
QUANTITY (Thousands of tons of soybeans)
Based on the previous graph, total surplus in the absence of international trade is $
million.
The following graph shows the same domestic demand and supply curves for soybeans in Venezuela. Suppose that the Venezuelan government
changes its international trade policy to allow the free trade of soybeans. The horizontal black line (Pw) represents the world price of soybeans at
$350 per ton. Assume that Venezuela's entry into the world market for soybeans has no effect on the world price and there are no transportation or
transaction costs associated with international trade in soybeans. Also assume that domestic suppliers will satisfy domestic demand as much as
possible before any exporting or importing takes place.
Use the green point (triangle symbol) to shade consumer surplus, and then use the purple point (diamond symbol) to shade producer surplus.
PRICE (Dollars per ton)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Principles of Economics, 7th Edition (MindTap Cou…
Economics
ISBN:
9781285165875
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Essentials of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:
9781337091992
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Macroeconomics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:
9781305971509
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Economics, 7th Edition (MindTap Cou…
Economics
ISBN:
9781285165875
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Essentials of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:
9781337091992
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Macroeconomics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:
9781305971509
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:
9781305585126
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Macroeconomics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:
9781285165912
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Microeconomics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:
9781305971493
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning