Using all 1991 birth records in the computerized national birth certificate registry compiled by the National Center for Health Statistics (NCHS), statisticians Traci Clemons and Marcello Pagano found that the birth weights of babies in the United States are not symmetric ("Are babies normal?" The American Statistician, Nov 1999, 53:4). However, they also found that when infants born outside of the "typical" 37-43 weeks and infants born to mothers with a history of diabetes are excluded, the birth weights of the remaining infants do follow a Normal model with mean p = 3432 g and standard deviation o = 482 g. The following questions refer to infants born from 37 to 43 weeks whose mothers did not have a history of diabetes. Compute the z-score of an infant who weighs 2632 g. (Round your answer to two decimal places.) Approximately what fraction of infants would you expect to have birth weights between 2910 g and 3820 g? (Express your answer as a decimal, not a percent, and round to three decimal places.) Approximately what fraction of infants would you expect to have birth weights above 3820 g? (Express your answer as a decimal, not a percent, and round to three decimal places.) A medical researcher wishes to study infants with high birth weights and seeks infants with birth weights among the heaviest 18%. Above what weight must an infant's birth weight be in order for the infant be included in the study? (Round your answer to the nearest gram.)
Using all 1991 birth records in the computerized national birth certificate registry compiled by the National Center for Health Statistics (NCHS), statisticians Traci Clemons and Marcello Pagano found that the birth weights of babies in the United States are not symmetric ("Are babies normal?" The American Statistician, Nov 1999, 53:4). However, they also found that when infants born outside of the "typical" 37-43 weeks and infants born to mothers with a history of diabetes are excluded, the birth weights of the remaining infants do follow a Normal model with mean p = 3432 g and standard deviation o = 482 g. The following questions refer to infants born from 37 to 43 weeks whose mothers did not have a history of diabetes. Compute the z-score of an infant who weighs 2632 g. (Round your answer to two decimal places.) Approximately what fraction of infants would you expect to have birth weights between 2910 g and 3820 g? (Express your answer as a decimal, not a percent, and round to three decimal places.) Approximately what fraction of infants would you expect to have birth weights above 3820 g? (Express your answer as a decimal, not a percent, and round to three decimal places.) A medical researcher wishes to study infants with high birth weights and seeks infants with birth weights among the heaviest 18%. Above what weight must an infant's birth weight be in order for the infant be included in the study? (Round your answer to the nearest gram.)
Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition 2012
1st Edition
ISBN:9780547587776
Author:HOLT MCDOUGAL
Publisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL
Chapter11: Data Analysis And Probability
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 8CR
Related questions
Question
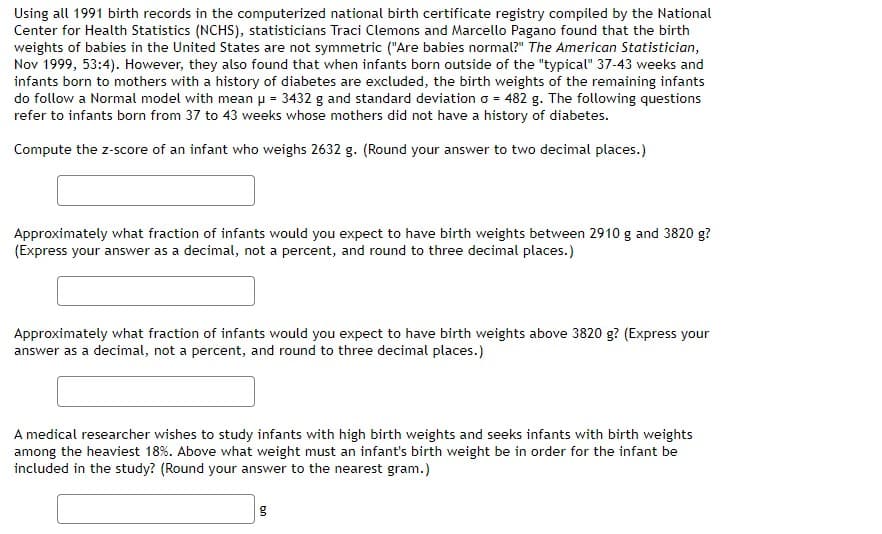
Transcribed Image Text:Using all 1991 birth records in the computerized national birth certificate registry compiled by the National
Center for Health Statistics (NCHS), statisticians Traci Clemons and Marcello Pagano found that the birth
weights of babies in the United States are not symmetric ("Are babies normal?" The American Statistician,
Nov 1999, 53:4). However, they also found that when infants born outside of the "typical" 37-43 weeks and
infants born to mothers with a history of diabetes are excluded, the birth weights of the remaining infants
do follow a Normal model with mean p = 3432 g and standard deviation o = 482 g. The following questions
refer to infants born from 37 to 43 weeks whose mothers did not have a history of diabetes.
Compute the z-score of an infant who weighs 2632 g. (Round your answer to two decimal places.)
Approximately what fraction of infants would you expect to have birth weights between 2910 g and 3820 g?
(Express your answer as a decimal, not a percent, and round to three decimal places.)
Approximately what fraction of infants would you expect to have birth weights above 3820 g? (Express your
answer as a decimal, not a percent, and round to three decimal places.)
A medical researcher wishes to study infants with high birth weights and seeks infants with birth weights
among the heaviest 18%. Above what weight must an infant's birth weight be in order for the infant be
included in the study? (Round your answer to the nearest gram.)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 3 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition…
Algebra
ISBN:
9780547587776
Author:
HOLT MCDOUGAL
Publisher:
HOLT MCDOUGAL

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage

Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition…
Algebra
ISBN:
9780547587776
Author:
HOLT MCDOUGAL
Publisher:
HOLT MCDOUGAL

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage