Using the table provided, calculate the thermodynamic property of interest for each given reaction. Thermodynamic Data at 25 °C Species AHe in kJ/mol AGº in kJ/mol So in J/(mol·K) Cu (s) 33.2 Cu (g) 337.4 297.7 166.4 CuO (s) -157.3 -129.7 42.6 H2 (g) 131.0 H2O (g) -241.8 -228.6 188.7 H2O (€) -285.8 -237.2 69.9 NO (g) 91.3 87.6 210.8 NO2 (g) 33.2 51.3 240.1 N¿O4 (E) -19.5 97.5 209.2 N2O4 (g) 9.16 99.8 304.4 O2 (g) 205.0 O Determine AS° for H2 (g) + ½ O2 (g) → H2O (g) at 25 °C. (11) Determine AG° for 2 Cu (s) + O2 (g) → 2 CuO (s) at 25 °C. (1i1) Determine AH° for H2O (€) → H2O (g) at 100 °C.
Using the table provided, calculate the thermodynamic property of interest for each given reaction. Thermodynamic Data at 25 °C Species AHe in kJ/mol AGº in kJ/mol So in J/(mol·K) Cu (s) 33.2 Cu (g) 337.4 297.7 166.4 CuO (s) -157.3 -129.7 42.6 H2 (g) 131.0 H2O (g) -241.8 -228.6 188.7 H2O (€) -285.8 -237.2 69.9 NO (g) 91.3 87.6 210.8 NO2 (g) 33.2 51.3 240.1 N¿O4 (E) -19.5 97.5 209.2 N2O4 (g) 9.16 99.8 304.4 O2 (g) 205.0 O Determine AS° for H2 (g) + ½ O2 (g) → H2O (g) at 25 °C. (11) Determine AG° for 2 Cu (s) + O2 (g) → 2 CuO (s) at 25 °C. (1i1) Determine AH° for H2O (€) → H2O (g) at 100 °C.
Chemistry for Engineering Students
4th Edition
ISBN:9781337398909
Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom Holme
Publisher:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom Holme
Chapter10: Entropy And The Second Law Of Thermodynamics
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 10.50PAE: For the reaction NO(g)+NO2(g)N2O3(g) , use tabulated thermodynamic data to calculate H and S. Then...
Related questions
Question
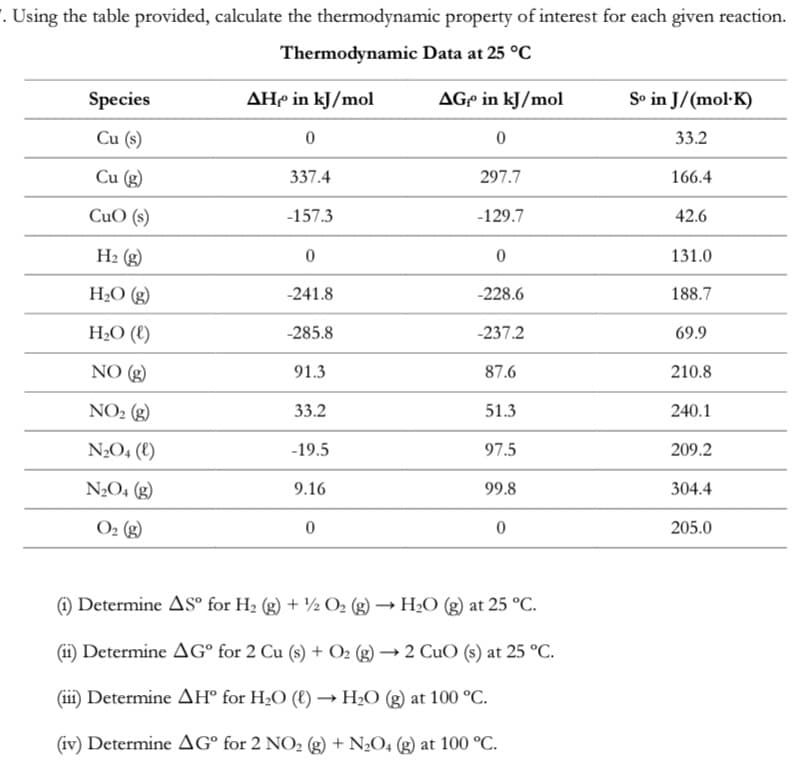
Transcribed Image Text:. Using the table provided, calculate the thermodynamic property of interest for each given reaction.
Thermodynamic Data at 25 °C
Species
AH in kJ/mol
AGº in kJ/mol
So in J/(mol·K)
Cu (s)
33.2
Cu (g)
337.4
297.7
166.4
CuO (s)
-157.3
-129.7
42.6
H2 (g)
131.0
H2O (g)
-241.8
-228.6
188.7
H2O (€)
-285.8
-237.2
69.9
NO (g)
91.3
87.6
210.8
NO2 (g)
33.2
51.3
240.1
N2O4 (E)
-19.5
97.5
209.2
N2O4 (g)
9.16
99.8
304.4
O2 (g)
205.0
) Determine AS° for H2 (g) + ½ O2 (g) → H2O (g) at 25 °C.
(ii) Determine AG° for 2 Cu (s) + O2 (g) → 2 CuO (s) at 25 °C.
(iii) Determine AH° for H2O (8) → H2O (g) at 100 °C.
(iv) Determine AG° for 2 NO2 (g) + N2O4 (g) at 100 °C.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 4 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Chemistry for Engineering Students
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337398909
Author:
Lawrence S. Brown, Tom Holme
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285199047
Author:
John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079373
Author:
William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry for Engineering Students
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337398909
Author:
Lawrence S. Brown, Tom Holme
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285199047
Author:
John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079373
Author:
William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour…
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305580343
Author:
Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; Darrell
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781133949640
Author:
John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning
