В 3 0. -2 12 15 10 -7 2 -3 0 15 0. 12 0 10 anglusis (on ugur own pgper), and determine the
В 3 0. -2 12 15 10 -7 2 -3 0 15 0. 12 0 10 anglusis (on ugur own pgper), and determine the
Linear Algebra: A Modern Introduction
4th Edition
ISBN:9781285463247
Author:David Poole
Publisher:David Poole
Chapter2: Systems Of Linear Equations
Section2.2: Direct Methods For Solving Linear Systems
Problem 21EQ: Students frequently perform the following type of calculation to introduce a zero into a matrix:...
Related questions
Question
Transcribed Image Text:+ Algoma University
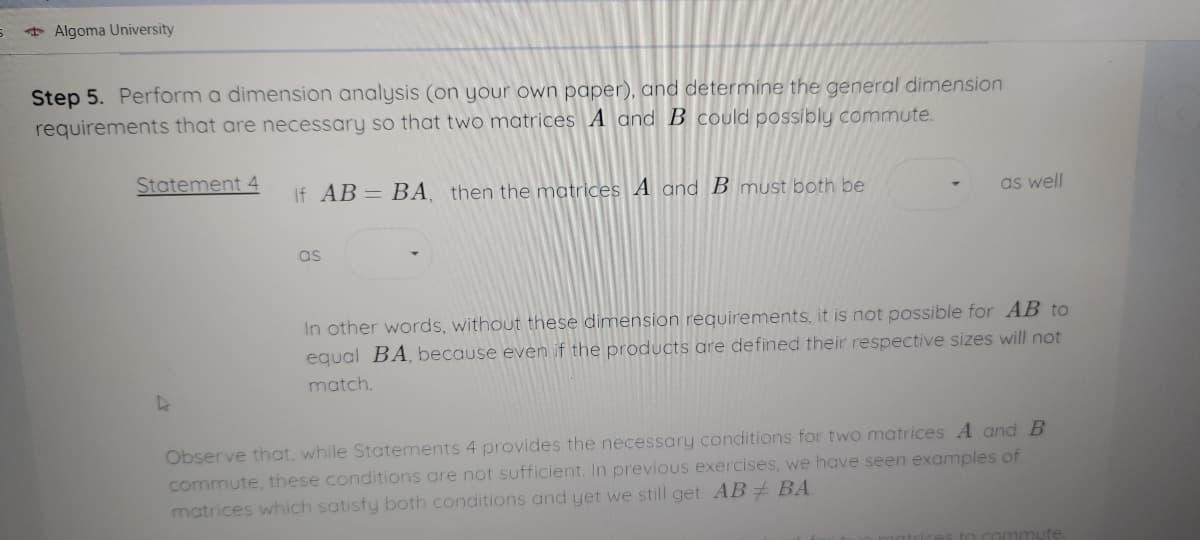
Step 5. Perform a dimension analysis (on your own paper), and determine the general dimension
requirements that are necessary so that two matrices A and B could possibly commute.
Statement 4
If AB= BA, then the matrices A and B must both be
as well
as
In other words, without these dimension requirements, it is not possible for AB to
equal BA, because even if the products are defined their respective sizes will not
match.
Observe that, while Statements 4 provides the necessary conditions for two matrices A and B
commute, these conditions are not sufficient. In previous exercises, we have seen examples of
matrices which satisfy both conditions and yet we still get AB BA
commute

Transcribed Image Text:Step 4. Here is an easy example illustrating the veracity of Statement 3. In the the following problem, A
and B are each diagonal matrices: the only nonzero entries are on the main diagonal. Calculate the matrix
products AB and BA and enter your results into the tables below. Verify that the matrices A and B do
commute. So, for this special example, it is true that: AB= BA
%3D
В
АВ
3
0.
-2
12
0.
15
0.
10
-7
B
A
BA
-2
3
15
0.
12
-7
10
Step 5
anal
(on your own paper), and determine the general dimension
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 1 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Linear Algebra: A Modern Introduction
Algebra
ISBN:
9781285463247
Author:
David Poole
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Algebra for College Students
Algebra
ISBN:
9781285195780
Author:
Jerome E. Kaufmann, Karen L. Schwitters
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Linear Algebra: A Modern Introduction
Algebra
ISBN:
9781285463247
Author:
David Poole
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Algebra for College Students
Algebra
ISBN:
9781285195780
Author:
Jerome E. Kaufmann, Karen L. Schwitters
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

College Algebra (MindTap Course List)
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305652231
Author:
R. David Gustafson, Jeff Hughes
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

College Algebra
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305115545
Author:
James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem Watson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Algebra and Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305071742
Author:
James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem Watson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning